
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
ANP binding causes a twisting motion of the two ECD monomers from the apo position (blue) to the complex position (orange)
|
|
|
|
The ECD contains five N-linked oligosaccharides (boxes) and three disulfide-bonds (orange lines). The glycosylated Asn and disulfide-bonded Cys residues are indicated. No free Cys residue is present in the ECD.

(a,b)Crystal structures of apo ECD dimer (PDB: 1DP4) and ANP-ECD complex. ANP is shown in green. Protein-bound chloride atoms are shown by magenta balls.
(c)ANP binding interactions. Major interactions are shown circled.
(d)Chloride binding site in the apo ECD. Chloride is hydrogen bonded to the hydroxyl-group of Ser53, and the backbone NH moieties of Gly85 and Cys86. The binding site also contains the Cys60-Cys-86 disulfide bond. The van der Waals radius of the chloride atom is represented by a green dotted ball.
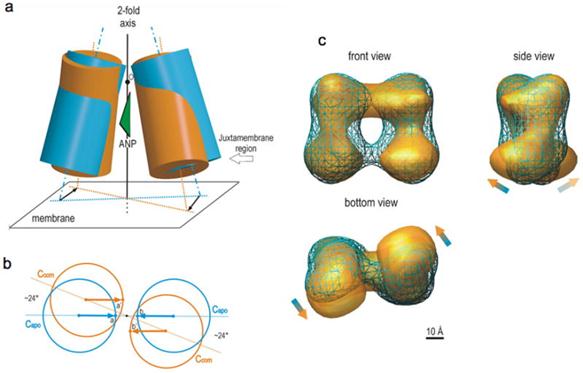
(a)ANP-induced change in the ECD dimer structure.
(b)Viewed toward the membrane, the juxtamembrane domains in the apo form (blue circles) translate to the complex position (orange circles) with essentially no change in the inter-domain distance. The arrows depict parallel translocation. This motion causes a change in the angular relationship between the two domains equivalent to rotating each domain by 24° counter-clockwise. Because the dimerized receptor is free to spin or move about in the cell membrane, this rotation motion occurring in the juxtamembrane domains would be the only structural change that is “recognized” by the receptor upon ANP binding.
(c)ANP-induced conformational change observed by single-particle electron microscopy. Reconstruction of the apo ECD dimer (blue mesh) is superimposed onto that of the ANP-ECD complex (gold surface).
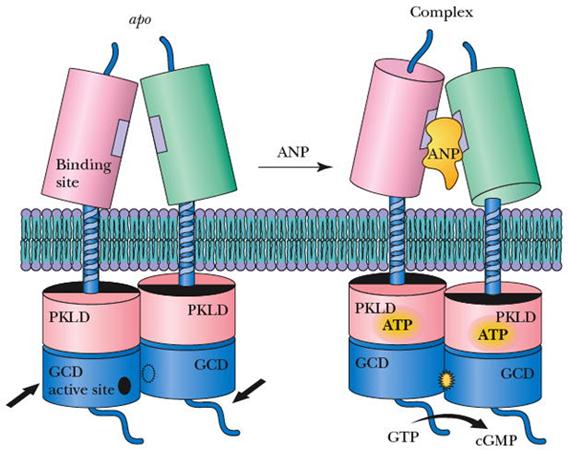
Rotation mechanism proposed for transmembrane signaling by the NPRA.
These structures closely resemble that of the adenylyl cyclase catalytic domain, consisting of a C1 and C2 subdomain heterodimer. Adenylyl cyclase is activated by binding of G(s)α to C2 and the ensuing 7° rotation of C1 around an axis parallel to the central cleft, thereby inducing the heterodimer to adopt a catalytically active conformation.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-14; Просмотров: 598; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!