
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Heterochromatin
|
|
|
|
Euchromatin
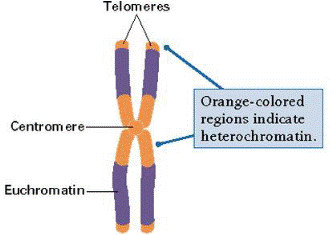
The euchromatin is the extended form of chromatin and it forms the major, portion of chromosomes. The euchromatin has special affinity for basic stains and is genetically active because its component DNA molecule synthesizes RNA molecules only in the extended form of chromatin.
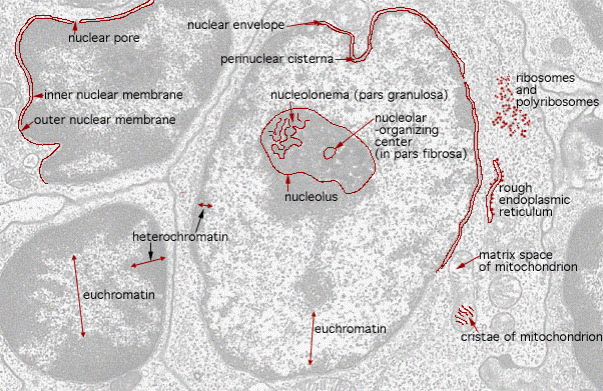
The heterochromatin is a condensed intercoiled state of chromatin, containing two to three times more DNA than euchromatin. However, it is genetically inert as it does not direct synthesize RNA (i.e., transcription) and protein and is often replicated at a different time from the rest of the DNA.
Recent molecular biological studies have identified three kinds of heterochromatins, namely constitutive, facultative and condensed heterochromatin. The constitutive heterochromatin is present at all times and in the nuclei of virtually all the cells of an organism. In a interphase nucleus, it tends to clump together to form chromocentre or false nucleoli. In Drosophila, for example, most pupal, larval and adult cells contain large blocks of constitutive heterochromatin that lie adjacent to centromeres. Constitutive heterochromatin contain highly repititive satellite DNA which is late replicating, it fails to replicate until late in the 5-phase and is then replicated during a brief period just before the G2. The facultative heterochromatin reflect the existence of a regulatory device designed to adjust the "dosages" of certain genes in the nucleus.
It is originated during the process called facultative heterochromatization: a process in which a chromosome or a set of chromosome becomes heterochromatic (turned off) in the cells of one sex, while remaining become heterochromatic (turned on) in the cells of opposite sex. In other words, it remains indirectly related to, sexual differentiation. The condensed heterochromatin is deeply staining tightly coiled chromatin which does not resemble with two other kinds of chromatin, has some specific role in gene regulation and is found in many interphase nuclei.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-16; Просмотров: 382; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!