
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
The product life cycle (plc)
|
|
|
|
Task 1. Read the article and answer the following question by naming the stages according to the passage.
READING 2
E. Read the following passage and fill the gaps with the appropriate form of words from the box.
| attract consumers fad persuaded compared convince inspire product competes current market satisfied |
Yassir is getting ready to realize his dream: opening a business that sells plants on the Internet. After completing a business plan that helped him to determine that there was demand for his (1) ____________ in the (2) _______________, Yassir is ready to start promoting his business. Having (3) _________________ the bank that there was a market, that there were consumers willing to buy flowers on the Internet, he needed to find these (4) _________________.
Once he has an established base, Yassir, like other business owners will have to continually (5) ______________ new customers. At the same time, he must make sure current customers are (6) _____________. In order to be satisfied, (7) ____________ customers must be happy with the product they receive. Yassir’s job is to (8) ________________ these customers to gain their repeat business. To do this, he will have to (9) ________________ consumers that he offers a good product at a good price, especially when (10) __________________ to the businesses with which he (11) ______________. And, of course, he will have to compete with other businesses on the price he charges and service he offers. He hopes that Internet businesses are here to stay and not a (12) ____________.
1 What are the first and last stages of the lifecycle of a product?
2 During which stage will sales increase?
3 Which stage usually generates the highest revenue?
4 At which stage are there no sales?
The product life cycle is a marketing concept that describes the way the revenue s from the sale of a product behave over time. Typically the product life cycle is drawn as a bell curve, shown below, with the life cycle being divided into four stages:
introduction
growth
maturity
decline
The life cycle concept can apply to a brand or a category of products, services, and the market as a whole. Its duration may be as short as a few months for a fad item or a century or more for such categories as the gasoline-powered automobile.
Product development is the incubation stage of the product life cycle. There are no sales and the firm prepares to introduce the product.
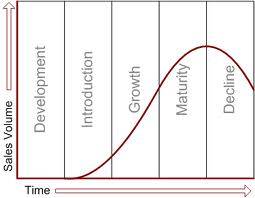
Introduction
For the product life cycle to begin, the product must be launched in the market. This is done after target market is identified and ensured that the need for your product or service exists.
When the product is introduced, sales will be low until customers become aware of the product and its benefits. Some firms may announce their product before it is introduced, but such announcements also alert competitors and remove the element of surprise. Advertising costs typically are high during this stage in order to rapidly increase customer awareness of the product and to target the early adopters. During the introductory stage the firm is likely to incur additional costs associated with the initial distribution of the product. These higher costs coupled with a low sales volume usually make the introduction stage a period of negative profits.
|
|
|
During the introduction stage, the primary goal is to establish a market and build primary demand for the product class.
Growth
The growth stage is characterized by rapid revenue growth. Sales increase as more customers become aware of the product and its benefits and additional market segments are targeted. Once the product has been proven a success and customers begin asking for it, sales will increase further as more retailers become interested in selling it. The marketing team may expand the distribution at this point. When competitors enter the market, often during the later part of the growth stage, there may be price competition and/or increased promotional costs in order to convince consumers that the firm's product is better than that of the competition.
During the growth stage, the goal is to gain consumer preference and increase sales.
Maturity
The maturity stage is the most profitable. While sales continue to increase into this stage, they do so at a slower pace. Because brand awareness is strong, advertising expenditures will be reduced. Competition may result in decreased market share and/or prices. The competing products may be very similar at this point, increasing the difficulty of differentiating the product. The firm makes an effort to encourage competitors' customers to switch, increasing usage per customer, and convert non-users into customers. Sales promotions may be offered to encourage retailers to give the product more shelf space over competing products.
During the maturity stage, the primary goal is to maintain market share and extend the product life cycle.
Decline
Eventually sales begin to decline as the market becomes saturated, the product becomes technologically obsolete, or customer tastes change. If the product has developed brand loyalty, the profitability may be maintained longer. Unit costs may increase with the declining production volumes and eventually no more profit can be made.
During the decline phase, the firm generally has three options:
· Maintain the product in hopes that competitors will exit. Reduce costs and find new uses for the product.
· Harvest it, reducing marketing support and coasting along until no more profit can be made.
· Discontinue the product when no more profit can be made or there is a successor product.
Limitations of the Product Life Cycle Concept
The term "life cycle" implies a well-defined life cycle as observed in living organisms, but products do not have such a predictable life and the specific life cycle curves followed by different products vary substantially. Consequently, the life cycle concept is not well-suited for the forecasting of product sales. Furthermore, critics have argued that the product life cycle may become self-fulfilling. For example, if sales peak and then decline, managers may conclude that the product is in the decline phase and therefore cut the advertising budget, thus precipitating a further decline.
Nonetheless, the product life cycle concept helps marketing managers to plan alternate marketing strategies to address the challenges that their products are likely to face.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-07; Просмотров: 522; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!