
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Key principals
|
|
|
|
LABORATORY WORK № 5
REQUIREMENTS TO CONTENT OF THE PROTOCOL
4.6.1 The name of laboratory work.
4.6.2 Purpose of the work.
4.6.3 Results of home assignments.
4.6.4 Short description of the work done.
4.6.5 Conclusions about the work done.
4.6.6 Date, the signature of a student, the remark of a teacher.
THEME: STUDYING AND SETTING OF PORTS OF TCP/IP STACK
5.1 PURPOSE OF THE WORK:
5.1.1 Research of the basic principles of work of a stack of the TCP/IP protocols.
5.1.2 Getting of practical skills on setting of the main ports of the TCP/IP stack protocol by organization of the IP – firewall using built-in means of Windows 2000 and XP.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is an industrial standard of a stack of the protocols, developed for global networks. The protocol is rules of work of the software.
Are distinguished:
- connection oriented protocols - establish connection between applications before the beginning of data transmission;
- connection non-oriented protocols - don't establish direct network connection;
- secure protocols - guarantee delivery of data;
- unsecure protocols - don't guarantee delivery of data;
- stream protocols - consider data as a consecutive continuous stream;
- datagram protocols - consider data as independent single blocks.
As the term «TCP/IP» usually is understood everything that is connected with the TCP and IP protocols. These are not only protocols of TCP and IP, but also the protocols constructed on their basis, and applications.
The main task of a stack of TCP/IP is uniting in a network of packet subnets through gateways. Each network works under its own laws, however it is supposed that the gateway can receive a packet from other network and to deliver it to the specified address. Really, the packet from one network is transferred in other subnet through sequence of gateways which provides through routing of packets on whole network. In this case, the gateway is understood as a point of connection of networks. Thus it can connect both local networks, and global networks. As a gateway can act as special devices, routers, for example, and computers which have the software which is carrying out routing of packets. Routing is a procedure of finding the transit of a packet from one network to another.
The TCP/IP standards are published in a series of the documents called Request for Comment (RFC). The RFC documents describe internal work of the Internet network. Some RFC describe network services or protocols and their realization while others-generalize application conditions. The TCP/IP standards are always published in a type of the RFC documents, but not all RFC define standards.
5.2.1 Structure of a stack of TCP/IP. Short characteristic of protocols
By consideration of procedures of internetwork interaction always lean on the standards developed by International Standard Organization (ISO). These standards received the name “Seven-layers model of a network exchange”. In this model exchange of information can be presented in the form of a stack shown in Figure 5.2.1.
|
|
|
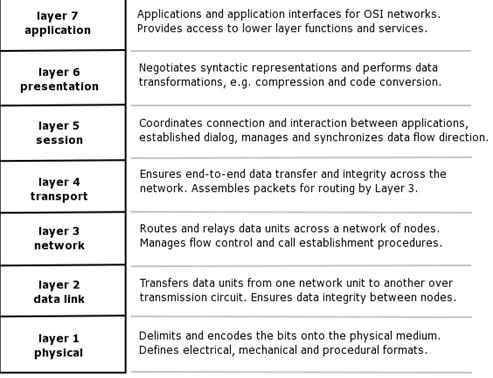
Figure 5.2.1 - OSI model
The stack of the TCP/IP protocols differs from an OSI model stack. Usually it is possible to present it in the form of the model presented in Figure 5.2.2.
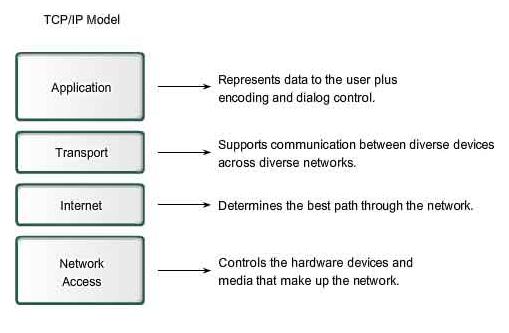
Figure 5.2.2 - Structure of TCP/IP stack protocols
Structure of stack of protocols TCP/IP and its correspondence to OSI model is represented in Figure 5.2.3.
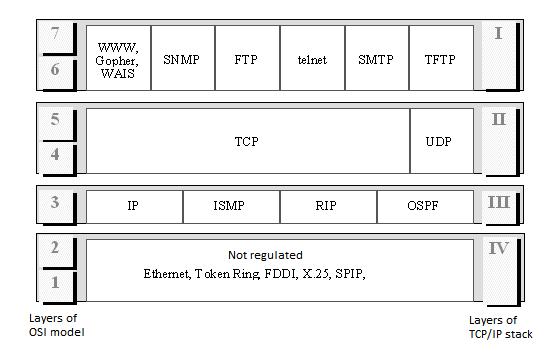
Figure 5.2.3 - Structure of stack of protocols TCP/IP and its correspondence to OSI model
The lowest (layer IV) corresponds to physical and channel levels of the OSI model. This layer in the TCP/IP protocols isn't regulated, but supports all popular standards of physical and channel level: for local networks it is Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, Fast Ethernet, for global networks - protocols of connections SLIP and PPP «point-to-point", protocols of territorial networks with switching of packets X.25, frame relay, ATM.
The following layer (layer III) is layer of inter-network interaction which transfers packets with using of various transport technologies of local networks, territorial networks, lines of special communication, etc.
The main protocol of network layer (in terms of OSI model) in a stack is IP protocol which was initially projected as the protocol of transfer of packets in the compound networks consisting of a large number of local networks, united using both local, and global links. Therefore the IP protocol works well in networks with difficult topology, rationally using existence in them of subsystems and economically spending capacity of low-speed communication lines. The IP protocol is the datagram protocol, it means that it doesn't guarantee delivery of packets to destination node, but it tries to make it.
All protocols connected with forming and updating of tables of routing belong to level of inter-network interaction, such as protocols of collecting of route information RIP (Routing Internet Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), and also the protocol of inter-network managing messages ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol). The last protocol is intended for exchange of information about mistakes between routers of a network and node- a source of a packet (ping). By means of special ICMP packets it is reported about impossibility of delivery of a packet, about excess of time of life or duration of assembly of a packet from fragments, about abnormal values of parameters, about change of a route of transfer and service type, about a system state, etc
The following layer (layer II) is called the basic. At this layer the protocol of management of transmitting TCP (Transfer Control Protocol) and the protocol of user’s datagrams UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are work. The TCP protocol provides secure transmission of messages between remote applications with the help in formation of virtual connections. The UDP protocol provides transfer of application’s packets by datagram way, as well as IP, and carries out only link functions between the network protocol and numerous applications.
The top layer (layer I) is called application layer. At this layer the following protocols - the protocol of a file transfer of FTP, the protocol of emulation of the terminal-telnet, the post SMTP protocol and others are work.
|
|
|
At work with such programs at the application layer as FTP or telnet, is formed a stack of protocols with the TCP module use, presented in Figure 5.2.4.
| FTP application |
| TCP module |
| IP module |
| ENET driver |
Figure 5.2.4 - Stack of protocols when using TCP module
At work with the applications using the transport UDP protocol, for example, software of Network File System (NFS), another stack is used where instead of the TCP module the UDP module is used (Fig. 5.2.5)
| NFS application |
| UDP module |
| IP module |
| ENET driver |
Figure 5.2.5 - Stack of protocols when using transport protocol UDP
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 487; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!