
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Open Wounds
|
|
|
|
WOUNDS
Do not--
- Give the victim alcoholic beverages or tobacco products.
- Give morphine or other central nervous system (CNS) depressors.
- Make any deep cuts at the bite site. Cutting opens capillaries that in turn open a direct route into the blood stream for venom and infection.
Note: If medical treatment is over one hour away, make an incision (no longer than 6 millimeters and no deeper than 3 millimeter) over each puncture, cutting just deep enough to enlarge the fang opening, but only through the first or second layer of skin. Place a suction cup over the bite so that you have a good vacuum seal. Suction the bite site 3 to 4 times. Use mouth suction only as a last resort and only if you do not have open sores in your mouth. Spit the envenomed blood out and rinse your mouth with water. This method will draw out 25 to 30 percent of the venom.
- Put your hands on your face or rub your eyes, as venom may be on your hands. Venom may cause blindness.
- Break open the large blisters that form around the bite site.
After caring for the victim as described above, take the following actions to minimize local effects:
- If infection appears, keep the wound open and clean.
- Use heat after 24 to 48 hours to help prevent the spread of local infection. Heat also helps to draw out an infection.
- Keep the wound covered with a dry, sterile dressing.
- Have the victim drink large amounts of fluids until the infection is gone.
An interruption of the skin's integrity characterizes wounds. These wounds could be open wounds, skin diseases, frostbite, trench foot, and burns.
Open wounds are serious in a survival situation, not only because of tissue damage and blood loss, but also because they may become infected. Bacteria on the object that made the wound, on the individual's skin and clothing, or on other foreign material or dirt that touches the wound may cause infection.
By taking proper care of the wound you can reduce further contamination and promote healing. Clean the wound as soon as possible after it occurs by--
- Removing or cutting clothing away from the wound.
- Always looking for an exit wound if a sharp object, gun shot, or projectile caused a wound.
- Thoroughly cleaning the skin around the wound.
- Rinsing (not scrubbing) the wound with large amounts of water under pressure. You can use fresh urine if water is not available.
The "open treatment" method is the safest way to manage wounds in survival situations. Do not try to close any wound by suturing or similar procedures. Leave the wound open to allow the drainage of any pus resulting from infection. As long as the wound can drain, it generally will not become life-threatening, regardless of how unpleasant it looks or smells.
Cover the wound with a clean dressing. Place a bandage on the dressing to hold it in place. Change the dressing daily to check for infection.
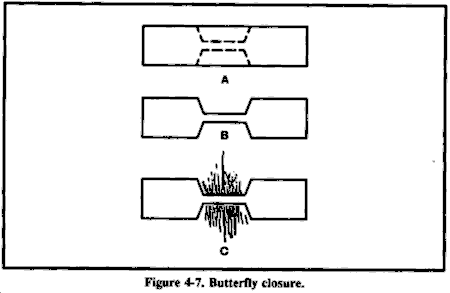
If a wound is gaping, you can bring the edges together with adhesive tape cut in the form of a "butterfly" or "dumbbell" (Figure 4-7).
|
|
|
In a survival situation, some degree of wound infection is almost inevitable. Pain, swelling, and redness around the wound, increased temperature, and pus in the wound or on the dressing indicate infection is present.
To treat an infected wound--
- Place a warm, moist compress directly on the infected wound. Change the compress when it cools, keeping a warm compress on the wound for a total of 30 minutes. Apply the compresses three or four times daily.
- Drain the wound. Open and gently probe the infected wound with a sterile instrument.
- Dress and bandage the wound.
- Drink a lot of water.
Continue this treatment daily until all signs of infection have disappeared.
If you do not have antibiotics and the wound has become severely infected, does not heal, and ordinary debridement is impossible, consider maggot therapy, despite its hazards:
- Expose the wound to flies for one day and then cover it.
- Check daily for maggots.
- Once maggots develop, keep wound covered but check daily.
- Remove all maggots when they have cleaned out all dead tissue and before they start on healthy tissue. Increased pain and bright red blood in the wound indicate that the maggots have reached healthy tissue.
- Flush the wound repeatedly with sterile water or fresh urine to remove the maggots.
- Check the wound every four hours for several days to ensure all maggots have been removed.
- Bandage the wound and treat it as any other wound. It should heal normally.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 388; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!