
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Key information Section 2. Many different forms of storagehave been invented
|
|
|
|

| 
| 
|
Many different forms of storage have been invented. So far, no practical universal storage medium exists, and all forms of storage have some drawbacks. Therefore a computer system usually contains several kinds of storage, each with an individual purpose. The most commonly used storage technologies are semiconductor, magnetic, and optical.
The most important performance characteristics of a storage unit are:
- Speed, measured in cycle time.
- Capacity, measured by the number of machine words or binary digits.
- Reliability, measured by the number of failures per unit of time.
Semiconductor memory uses semiconductor-based integrated circuits to store information. A semiconductor memory chip may contain millions of tiny transistors or capacitors. Both volatile and non-volatile forms of semiconductor memory exist. In modern computers, primary storage almost exclusively consists of dynamic volatile semiconductor memory or dynamic random access memory. Since the turn of the century, a type of non-volatile semiconductor memory known as flash memory has steadily gained share as off-line storage for home computers. Removable flash memory is solid-state, rewritable memory; it is non-volatile, so it retains data when the power is turned off. This explains its popularity in small devices.
Flash memory cards are found in cameras, PDAs and music players.
Flash drives, also known as thumb or pen drives, are connected to a USB port of the computer. They let you save and transfer data easily.
Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetization on a magnetically coated surface to store information. It is non-volatile. The information is accessed using one or more read/write heads which may contain one or more recording transducers. A disk drive spins the disk at high speed and reads its data or writes new data onto it. Magnetic storage takes these forms:
· Floppy disk, used for off-line storage. A floppy disk drive uses 3.5 inch diskettes which can only hold 1.44 MB of data; it's often called A: drive and is relatively slow.
· Hard disk, used for secondary storage. Most PCs have one or two internal hard disks, usually called C: or D: drive, which can hold gigabytes of data. It's used to keep the operating system, the programs and the files easily available for use. When you format a disk, or prepare it for use, its surface is divided into concentric circles called tracks. Each track is further divided into a number of sectors. The computer remembers where information is stored by noting the track and sector numbers in a directory.
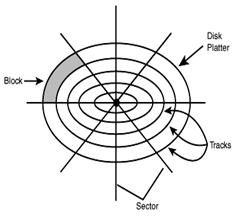
| · A portable hard drive is an external unit with the drive mechanism and the media all in one sealed case. You can use it to make a backup, a spare copy of your files, or to transport data between computers. · Magnetic tape data storage, used for tertiary and off-line storage. The average time required for the read/write heads to move and find data is called access time; it is measured in |
milliseconds (ms). Don't confuse 'access time' with 'transfer rate', the rate of transmission of data from the disk to the CPU (e.g. 15 Mb per second).
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 620; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!