
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Fig. 3. Frequency Modulation
|
|
|
|
TEXT 1. Frequency and Phase Modulation
UNIT 5
1. Выучите следующие слова и выражения:
amount [ə'maunt] - величина, количество
wide-band FM (WBFM) - широкополосная частотная модуляция
narrow band FM (NBFM) - узкополосная частотная модуляция, УЧМ
application[ˌæplɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n] применение, использование, употребление, приложение, применимость
resilience [rɪ'zɪlɪən(t)s] - устойчивость(к внешним воздействиям), упругость
amplification[ˌæmplɪfɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n] - усиление
linear ['lɪnɪə] — линейный
2. Прочитайте и устно переведите текст:
The modulation techniques can be broadly divided into two basic categories: amplitude modulation and angle modulation. The angle modulation can be further divided into two more categories: frequency and phase modulations.
The basic principle behind frequency modulation (FM) is that the amplitude of an analog baseband signal can be represented by a slightly different frequency of the carrier. This is a method of impressing data onto an alternating-current (AC) wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave.
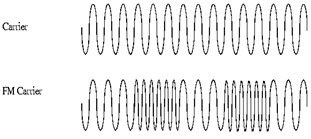
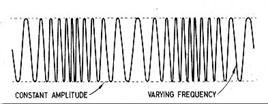
When the audio signal is modulated onto the radio frequency carrier, the new radio frequency signal moves up and down in frequency. The amount by which the signal moves up and down is known as the deviation and is normally quoted as the number of kilohertz deviation. As an example the signal may have a deviation of ±3 kHz. In this case the carrier is made to move up and down by 3 kHz.
Broadcast stations in the VHF portion of the frequency spectrum between 88.5 and 108 MHz use large values of deviation, typically ±75 kHz. This is known as wide-band FM (WBFM). These signals are capable of supporting high quality transmissions, but occupy a large amount of bandwidth. Usually 200 kHz is allowed for each wide-band FM transmission. For communications purposes less bandwidth is used. Narrow band FM (NBFM) often uses deviation figures of around ±3 kHz. It is narrow band FM that is typically used for two-way radio communication applications. Having a narrower band it is not able to provide the high quality of the wideband transmissions, but this is not needed for applications such as mobile radio communication.
There are several advantages of frequency modulation.
One particular advantage of frequency modulation is its resilience to signal level variations. The modulation is carried only as variations in frequency. This means that any signal level variations will not affect the audio output, provided that the signal does not fall to a level where the receiver cannot cope. As a result this makes FM ideal for mobile radio communication applications including more general two-way radio communication or portable applications where signal levels are likely to vary considerably. The other advantage of FM is its resilience to noise and interference. It is for this reason that FM is used for high quality broadcast transmissions.
Another advantage of frequency modulation is associated with the transmitters. It is possible to apply the modulation to a low power stage of the transmitter, and it is not necessary to use a linear form of amplification to increase the power level of the signal to its final value.
It is possible to use non-linear RF amplifiers to amplify FM signals in a transmitter and these are more efficient than the linear ones required for signals with any amplitude variations. This means that for a given power output, less battery power is required and this makes the use of FM more viable for portable two-way radio applications.
Phase modulation is similar in practice to FM. When the instantaneous phase of a carrier is varied, the instantaneous frequency changes as well, and vice versa. But PM tends to require more complex receiving hardware and there can be ambiguity problems in determining whether, for example, the signal has changed phase by +180° or -180°. Although PM is used for some analog transmissions, it is far more widely used as a digital form of modulation where it switches between different phases. This is known as phase shift keying, PSK, and there are many flavours of this.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 819; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!