
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Give the title to the text
|
|
|
|
Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Give the title to the text.
Explain why iron and zinc are used.
5. What is the voltage output of cells in use nowadays?
6. What does the value of the output depend on?
7. What is the relation between the size of the electrodes and the current capacity?
The capacity of a capacitor is measured in farads. A capacitor has a capacity of one farad when a charge of one coulomb increases the potential between its plates by one volt.
The capacity depends on four things:
first, the higher the voltage used to charge the capacitor the more energy it will store;
second, the larger the size of plates and the greater their number the more energy will be stored;
third, the closer are the positive and negative plates the greater is the charge;
fourth, some insulators store greater charge than others.
1. What does the capacity of a capacitor depend on?
3. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Wattmeter
A wattmeter is used to measure the value of power. It is connected to the circuit directly. A wattmeter consists of coils: two fixed coils and a coil which moves in the magnetic field produced by the fixed coils. Wire used for the coils must have a high resistance; the fixed coils are in series with the load, the moving coil is connected across the line in series with a resistance. When a wattmeter is used, the readings on its scale show the value of power being used.
1. What is the wattmeter used for?
2. What does it consist of?
3. In what way are the elements connected?
4. What do the readings on the scale show?
-116-
4. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Rheostat
A rheostat is a resistor whose resistance value may be varied. Thus, a rheostat is a variable resistor.
It is used to change the resistance of circuits, and in this way to vary the value of current.
A rheostat consists of a coil and a switch. Take into consideration that wire used for the coil must have a very high resistance. When a rheostat is used its terminals are connected in series with the load. The switch is used to change the length of the wire through which the measured current passes. The resistance may be changed to any value from zero to maximum.
The longer the rheostat wire used in the circuit, the greater is the resistance.
1. What type of resistor is a rheostat?
2. What is a rheostat used for?
3. In what way does a rheostat vary the value of current?
4. What elements does a rheostat consist of?
5. In what way are the terminals connected with the load?
6. What is the function of the switch?
5. Read the text and find in it the answer to the question that follows it.
Voltage Values
Voltages up to about 250 V are called low. The common electric lighting circuit operates either at about 127 or 200 V, and the voltage used on the main circuit of large houses is usually the same. One can get an electric shock, when one touches an uninsulated wire of such a circuit.
|
|
|
Voltages above 250 V are high voltages. They are used in industry. Medium-powered motors are usually operated at 380 V. Large motors are supplied by voltages of from about 500 up to 6,000 V.
What have you read about?
6. Read the text and find in it the answer to the question that follows it.
High-Frequency Current
Alternating current with frequency of 50 c/s is widely used in industry. Therefore this frequency is called an industrial frequency and the current, an industrial frequency current.
- Ill-
During sound transmission, current flowing in telephone wires changes with the frequency of sound oscillations, which ranges from 50 to 10,000 c/s. The currents of such frequencies are called audio- or low-frequency currents.
Radio transmission is based on the use of alternating currents with frequencies of hundreds, thousands, millions and even tens of million cycles per second. These currents called high-frequency currents are produced by means of an oscillatory circuit consisting of a coil and a capacitor. Moving along the turns now in one direction now in another, the electric charges oscillate in an oscillatory circuit.
By what means are high-frequency currents obtained?
7. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
HV Power Transmission
A high-capacity hydrogenerator produces an a.c. current at 22,000 V. The current with the potential difference of 220,000 V is produced by means of the transformers at a step-up station and then transmitted over the power lines.
The current potential difference is lowered to medium 6,600 V at the main step-down substation at the end of the line. From here the power is transmitted to the next substations. Transformers stepping the voltage down from 6,600 V are installed at those substations.
Due to voltage conversion, alternating current is used widely in industry. Direct current for battery charging for trams, trolleybuses and electric locomotives is changed from alternating current by means of rectifiers.
1. Where is the current potential difference lowered?
2. Where is the main step-down substation installed?
8. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Meters
One of the important things that an engineer should take into consideration is "how much?" How much current is this circuit carrying? What is the value of voltage in the circuit? What is the value of resistance? In fact, to measure the current and the voltage is not difficult at all. One should connect an ammeter or a voltmeter to the circuit and read off the amperes and the volts.
Common ammeters for d. с measurements are the ammeters of the magneto-electric system. In an ammeter of this type an armature coil rotates between the poles of a permanent magnet; but the coil turns only through a small angle. The greater the current in the coil, the greater the force, and, therefore, the greater the angle of rotation of the armature. The deflection is measured by means of a pointer connected to the armature and the scale of the meter reads directly in amperes.
When the currents to be measured are very small, one should use a galvanometer. Some galvanometers detect and measure currents as small as 10'nof an ampere per 1 mm of the scale.
|
|
|
A voltmeter is a device to be used for measuring the potential difference between any two points in a circuit. A voltmeter has armatures that move when an electric current is sent through their coils. The deflection, like that of an ammeter, is proportional to the current flowing through the armature coil.
A voltmeter must have a very high resistance since it passes only very small currents which will not disturb the rest of the circuit. An ammeter, on the other hand, must have a low resistance, since all the current must pass through it. In actual use the ammeter is placed in series with the circuit, while the voltmeter is placed in parallel with that part of the circuit where the voltage is to be measured.
In addition to instruments for measuring current and voltage, there are also devices for measuring electric power and energy.
1. What is the above article about?
2. What is a voltmeter used for?
9. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it. Negative Transconductance Oscillator
A negative transconductance oscillator consists of a pentode with the screen and suppressor grids coupled together. The screen is more positive than the plate. The cathode supplies electrons to both the screen and the plate. If the screen voltage rises, this increase is transferred over to the suppressor. It becomes more positive than before. A large quantity of electrons passes to the plate and a small quantity of electrons passes to the screen. Thus, the screen current is reduced. A negative resistance characteristic is produced in the screen circuit at the terminals.
A tuned circuit is connected to the terminals and in this way oscillations are produced.
1. In what way is the screen current reduced?
2. What does negative transconductance oscillator consist of?
- 118-
- 119-
| 9—1796 |
10. Read the text and find in it the answer to the question that follows it. What are the Names of Oscillators?
Many types of oscillator circuits are used nowadays. Their tube types, tank circuits, and feedbacks are different.
Examine the diagrams given below. What are the names of the oscillators? To answer this question read the following texts.
1. The Electron-coupled Oscillator uses a multi-grid vacuum tube with a cathode and two grids operating in common. In this device the plate circuit load is coupled to the oscillator through the electron stream. The diagram shows a tetrode variant using a series-fed oscillator.
2. The Dynatron Oscillator uses the negative resistance characteristic of a tetrode tube to eliminate the resistance of its tank circuit in order to keep oscillations.
3. The Blocking Oscillator uses a plate transformer to provide the feedback voltage.
4. A Multivibrator is a form of oscillator using two RC-controlled triodes.
5. The Tuned Plate - Tuned Grid oscillator has parallel or resonant circuits in both plate and grid circuits. The necessary feedback is supplied by the plate-to-grid interelectrode capacitance.

|
| d) e) Fig. 20 - iac - |
Name the five oscillators in Fig. 20.
11. Read the text and find in it the answer to the question that follows it.
Solar Energy
The Sun radiates to our planet great amounts of energy. This energy input fuels all our biological processes and is the original source for hydropower, wind power, and fossil fuel resources. Environmentally and economically, the Sun is our greatest energy source. Why then is the direct use of solar energy so limited for industrial, domestic, commercial, and transportation purposes?
First, solar energy arrives in small quantities - only about one kW per square meter; second, it does not arrive at all during night hours. Third, it is very difficult to transform it into useful energy forms except low-grade heat.
Why is the direct use of solar energy limited nowadays?
|
|
|
12. Read the text and find in it the answer to the question that follows it.
Superconductivity
In the electric generating field, as well as in the electric-transmission and storage-technology areas, considerable attention is focused on the use of superconductivity conductors. Cooling an electric conductor to temperatures close to absolute zero (-273C) results in the conductors' losing their resistance to electric current. Accordingly, their ohmic losses also drop greatly. Current densities of tens of millions amperes per sq cm can be tolerated in such conductors.
Cryogenic technology being now mastered, one can foresee the possibility of supercooling not only generators but also underground transmission lines and storage coils.
Are these statements true or false?
a) Conductors can never lose their resistance to the flow of electric current.
b) Generators and underground transmission lines can be supercooled.
13. Read the text and find in it the answer to the question that follows it.
Metals Used as Conductors
The use of electricity depends upon a means of conducting it from its source to the point where it is to be used. Copper has been used as a conductor since the beginning of the industry and no proper substitute has been found. Only one metal, silver, is more efficient, but it has too high cost to be extensively used.
-iai-
 Aluminium, because of its lightness, is used in common practice for transmission lines where long spans are necessary. It has, compared to other metals, a conducting capacity of about 60 per cent of that of copper.
Aluminium, because of its lightness, is used in common practice for transmission lines where long spans are necessary. It has, compared to other metals, a conducting capacity of about 60 per cent of that of copper.
Why cannot silver be extensively used?
14. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Switchboard
Switchboard is an assemblage of switches, controlling or indicating devices mounted upon a frame for the purpose of control or an inspection of an electric path, circuit or system of circuits. Usually it is a metal frame carrying vertical slabs with switches, controlling handles and indicating or controlling instruments mounted thereon in an electric central station or distributing centre.
1. What is described in the text?
2. Where is the device used?
15. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Dynamo
Dynamo is a common device for converting mechanical energy into electric energy. This process depends on the fact that if an electrical conductor moves across a magnetic field, an electric current flows in the conductor.
Usually a dynamo includes an electromagnet, called the field magnet, between the poles of which a suitable conductor, usually in the form of a coil, called the armature, is rotated. The mechanical energy of the rotation, in the form of a current in the armature, is thus converted into electric energy.
1. What device is described in the text?
2. What types of the device do you know?
16. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Test Blocks Types B-4 and B-6
The types B-4 and B-6 test blocks with test plugs are designed as multipole connectors in the circuits of protective relays and measuring instruments.
The test blocks provide an easy and safe checking and replacement of relays and instruments during operation without breaking connections in wiring and on terminal blocks.
The test blocks are made in several versions which differ in the number of poles and in the way of wire connection.
Design. The test blocks consist of two units: the base and the removable cover.
While testing, the cover is removed and is replaced by the test plug which is inserted into the base and is electrically connected to the circuit for testing purposes.
|
|
|
Technical data. Rated voltage: 250 V; rated current: 5 A. Test voltage: 2 kV, a.c. 50 c.p.s. Transient stability: 300 A. The insulation resistance at ambient temperatures of 20±5°C should be not less than 2 megohms at relative humidity up to 80%, and not less than 2 megohms at relative humidity of 95%.
Mounting. Test blocks are mounted on the front panel. Before mounting, blocks should be provided with current-carrying pins.
Operating conditions. The blocks are designed for indoor use in stationary installations at ambient temperature and relative air humidity which are indicated. The blocks are produced in three types of designs: 1. conventional; 2. export; 3. tropicalized. Ambient temperatures for the blocks of the first type of design are from -20 up to +35; for blocks of the second type - from -10 up to +35, and for the third type - from -10 up to +55. As to relative air humidity, it is also different for different types of devices. For the first type it is 80% at 20±5°C; for the second type it is also up to 80% in the same range of temperatures, and for the third type it is 95% at 40°C.
The test blocks are not to be used a) in an atmosphere containing current-conducting dust or gases which damage metals and insulation; b) where shock and vibration can take place; c) in an explosion-hazardous atmosphere.
The delivery set includes a) base; b) cover; c) fastenings for mounting blocks and connections of wires.
Order form. When ordering, state the type of the block, kind of wire connection and number of units. For example, ORDER: Test block type B-6 for back connection - 3 pes (=pieces).
1. What are the main characteristics of test blocks types B-4 and B-6?
2. When are the test blocks described not to be used?
-iaa-
9*
-ia-
17. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Compressed-gas-insulated Transmission
Transmission lines in which compressed gas is used as insulator have a number of advantages. The main advantages are simplicity of construction and low cost.
What is the construction of compressed-gas-insulated transmission lines? It is rather simple. They comprise a number of phase conductors; each phase conductor is placed inside a tube and centered by means of circular spacers. The tube space is filled with compressed gas - usually sulphur hexofluoride. Each tube in a 345-kV line has a diameter about 50 cm.
The system including compressed-gas-insulated transmission has the following advantages: its losses are rather low, they are considerably lower than those of cable transmission. Unlike cables, compressed-gas-insulated transmission system can be designed for ultra high frequencies. No external electric field appears in the system. The shunt capacitance is considerably less for a gas-insulated line than for a cable. A gas-insulated line can thus transmit power over larger distances than cable lines.
The system should be protected against metallic particles. In case metallic particles get into the system, they cause a fault - a dielectric breakdown.
1. Does the system described have any advantages? What are they?
2. What gas is the space filled with?
3. Why should the system be protected?
18. Read the text and find in it the answers to the questions that follow it.
Starting Resistors Types 50-51
The electrical block resistors are generally used in starting and regulating installations for motors of any type and power.
Starting resistors have the capacity to support very high temperature variations, to which they are subjected due to their operating duty, without alteration or distortion.
Resistors consist of silicon sheet-steel or of special cast iron elements. Said elements are grouped in an assembly by means of steel rods interlocked by bolts in order to obtain rigid assemblies. These units are suitable for use in any type of machine and operate under high vibration conditions. For protection purposes, the resistor units are assembled in sheet-steel cases supplied with ventilation slits.
Starting resistors have a number of advantages; they are unbreakable, light, rigid; they can withstand, without variation, vibration and shocks. They are also easily detachable; their elements are interchangeable. Resistors are intended for operation in an ambient temperature of up to 300°C.
1. What device is described in the article?
2. What is the device used for?
3. What elements does it consist of?
4. What are the advantages of the device?
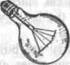
19. Study Fig. 21 and complete the sentences stating what metals are used for producing the devices a-e.
What Metals Are Used in Making Electrical Devices?
1. Alnico is an alloy of iron, aluminium, nickel, and cobalt used in
making....

|

|
| a) meter pointer b) permanent magnet c) battery cell |
|
| d) lamp e) heater element Fig.21 |
2. Phosphor bronze springs are used to produce....
3. Tungsten is used in....
4. Nickel and cadmium are used in... rechargeable.
5. Nichrome is high-resistance alloy of nickel and chromium used for....


-185-
20. Arrange the paragraphs of the text in the logical order.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-08; Просмотров: 4632; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!