
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Variants of English
|
|
|
|
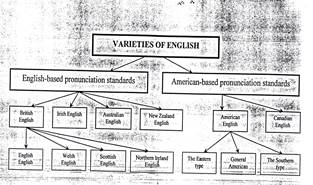
Nowadays two main types of English are spoken in the English-speaking world: British English and American English.
According to British dialectologists (P. Trudgill, J. Hannah, A. Hughes and others), the following variants of English are referred to the English-based group: English English, Welsh English, Australian English, New Zealand English; to the American-based group: United States English, Canadian English. Scottish English and Ireland English fall somewhere between the two, being somewhat by themselves.
According to M. Sokolova and others, English English, Welsh English, Scottish English and Northern Irish English should be better combined into the British English subgroup, on the ground of political, geographical, cultural unity which brought more similarities - then differences for those variants of pronunciation.
32. Spread in English/
English is spreading throughout the world far more rapidly than any other language; however, the level of sentimental attachment or genuine liking for English falls far short of the level of necessity-based desire to learn it. There is a possibility that the spread of English is decreasing: given some rapid economic or military change around the world, there could be a concomitant separation of peoples' attachment to English. In many countries, local authorities are engaged in language planning to foster the positive image of the national language for many functions for all people, and simultaneously to foster the spread of English in its function--a difficult set of co-occurring goals. As the spread of English makes the rest of the world increasingly bilingual, the Anglophone world remains predominantly monolingual. There is substantial bilingual education in the United States, but it is primarily non-transitional; the level of functional bilingualism in the Anglo world is very low. The survival of America as a democratic civilization depends upon the survival of a pluralistic mythology through greater balance between English and the other languages in the U.S. It is the responsibility of CATESOL and all the TESOL's to work toward such a balance. (EJS)
33.English-based pronunciation standarts of English.
British E Pronunciation Standards and Accents(BEPS) comprise English English(EE), Welsh English(WE), Scottish English(ScE) and Northern Ireland English(NIE).
EE: roughly speaking the non-RP accents of E may be grouped like this:
1. Southern accents
1)Southern accents (Great London, Cockey, Surray, Kent, Essex, Hertfordshire, Buckinghamshire);
2)East Anglia accents (Lincolnshire, Norfolk, Suffolk, Cambridgeshire, bedfordshire, Northamptonshire, Leicestershire);
3)South-West accents (Gloucestershire, Avon, Somerset, Wiltshire).
2. Northern and Midland accents.
1) Northern accents (Northumberland, Durham, Cleveland)
2) Yorkshire accents:
3)North-West accents (Lancashire, cheshire)
4)West Midland (Birmingham,Wolverhampton)
34. Received Pronunciation A pronunciation model is a carefully chosen and defined accent of a language. In the nineteenth century Received Pronunciation (RP) was a social marker, a prestige accent of an Englishman. "Received" was understood in the sense of "accepted in the best society". The speech of aristocracy and the court phonetically was that of the London area. Then it lost its local characteristics and was finally fixed as a ruling-class accent, often referred to as "King's English". It was also the accent taught at public schools. With the spread of education cultured people not belonging to upper classes were eager to modify their accent in the direction of social standards. A more broadly-based and accessible model accent for British English is represented in the 15th (1997) and the16th (2003) editions – ВВС English. This is the pronunciation of professional speakers employed by the BBC as newsreaders and announcers. Of course, one finds differences between such speakers - they have their own personal characteristics, and an increasing number of broadcasters with Scottish, Welsh and Irish accents are employed. On this ground J.C. Wells (Longman Pronunciation Dictionary, 33rd edition - 2000) considers that the term BBC pronunciation has become less appropriate. According to J.C. Wells, in England and Wales RP is widely regarded as a model for correct pronunciation, particularly for educated formal speech.
|
|
|
35.Changes in the standart.
Considerable changes are observed in the sound system of the present day E, which are most remarkable since the well-known Great Vowel Shift in the Midle E period of the language development. The RP of recent years is characterized by a greater amount of permissible variants compared to the `classical` type of RP described by Jones and Armstrong.
The phenomenon is significant both from the theoretical and practical point of view. The variability concerns mainly vowels. Most of E. vowels have undergone definite qualitative changes. The qualitative distinctions manifest new allophonic realization of the vowel phonemes. Ch.Barber comes to the conclusion that a definite trend towards centralization is observed in the quality of E vowels at present.
Changes of wovel quality:
1.According to the stability of articulation:
a) Two historically long vowels [I:], [u:] have become diphthongized and are often called diphthongoids: the organs of speech slightly change their articulation by the very end of pronunciation, becoming more fronted.
b) there is a tendency for some of the existing diphthongs to be smoothed out, to become shorter, so that they are more like pure vowels.
2. According to the horizontal and vertical movements of the tongue. The tendency is marked by the centering of both front and back vowels.
3.Combinative changes.
4.Changes in lenth.
Changes in Consonant quality
1. Voicing and Devoicing. Increase in tendency for devoicing. As soon as the oppositional of voiced – voiceless is neutralized in the final position, the fortis/lenis character of pronunciation has become the relevant feature of consonants.
2. Loss of [h].
3. [hw] insteed of [w] in why, what, when.
4. Loss of final [n –носової].
5. Glottal stop [?] like in the batmen [t] is absent – [bae? Man]
6. Palatalized final [k] is stronger in words like `week`.
7. Linking and intrustive [r] is not heard in such phrases as `far away`.
8.Combinative changes. Softening of the [tj] [dj], [sj].
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-31; Просмотров: 2978; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!