
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
The theoretical part
|
|
|
|
The programmatic complex "FactSage" (version 6.4) was drawn on for the thermodynamics design of high temperature renewal of substance slag dumps [11]. The process was designed, where repairer was the hard carbon. Data about composition of slag, used in the process of design as initial, shown in the table 1. The array of the used data about composition of slags was got from literary sources and became the result of generalization of own analyses of composition slag dumps of Zlatoust metallurgical plant (Chelyabinsk area, Russian Federation). Some data about chemical and phase composition of these slags are driven to [8].
The FeO’s content makes the 15 masses slag (base composition is the second column of table 1). The magnetic separation is used for processing of slags, lowering maintenance gland in the slag, certain interest presents that, how lowering of maintenance of iron will affect on the result of restoration processes. The design was conducted for two compositions of slag with the lowered maintenance of FeO (third and fourth columns).
The simulations were performed for the temperature range 750-1650 ° C in step of 5 ° C at the pressure of the gas phase of 1 atmosphere. Thermodynamic calculation was performed on 100 g of slag. Simulations assumed that the system introduced deliberately excessive amounts of carbon (graphite). According to preliminary calculations, 100 g of slag elected enough to take 10 g of carbon.
Table 1 - Compositions of slags, used in the process of simulation
| Component of slag | Base compo-sition mass.% | Slag impoverished on Fe. mass, % | Slag strongly impo-verishhed on Fe. mass, % | Known results of experimental study. Mass, % |
| FeO | 15.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 | 3.72–43.88 |
| SiO2 | 25.50 | 27.00 | 28.5 | 17.7–26.6 |
| CaO | 30.00 | 31.76 | 33.53 | 21.9–47.4 |
| MgO | 11.40 | 12.07 | 12.74 | 6.2–18.5 |
| Al2O3 | 8.00 | 8.47 | 8.94 | 4.1–9.8 |
| MnO | 3.20 | 3.39 | 3.58 | 2.14–5.00 |
| Cr2O3 | 3.50 | 3.71 | 3.91 | 1.6–11.3 |
| TiO2 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.12 | 0.23–2.75 |
| V2O5 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.12–0.36 |
| NiO | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.05–0.34 |
| Cu2O | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | less 0.05 |
| CaSO3 | 1.06 | 1.12 | 1.18 | 0.07–0.35 (content of sulfur) |
| Ca3P2O8 | 1.00 | 1.06 | 1.12 | 0.04–0.41 (content of phosphorus) |
| Sum |
Для моделирования использованы базы FSstel, FToxid, FactPS. Выбор растворов из общего их количества осуществлялся в процессе предварительного моделирования методом исключения из списка фаз переменного состава тех, которые не проявляют себя в качестве существующих. В ходе расчёта допускалось существование в системе всех веществ из использованных баз за вычетом дублирующихся (приоритетный порядок – FSstel, FToxid, FactPS) и являющихся компонентами избранных растворов (это исключение производится в автоматическом режиме). Помимо этого из списка чистых веществ исключен CaTiO3 (поскольку это вещество является основой перовскитного раствора и не исключёно из списка автоматически).
|
|
|
The basic results of the conducted calculations are presented as dependences of the masses of components and compositions of the studied phases on the temperature for comfort of analysis.
Consider the simulation results of the renewal of basic slag composition.
Dependences of the masses of the basic condensed phases on the temperature are presented on the picture 1. The small amount (less 2 g.) of CaTiO3, sulfide of manganese, phosphate of calcium and FeV2O4 can be in the system.
Metallic fusion can appear already at temperatures 1070-1080 °С ensues from the picture 1. His amount with the increase of temperature grows (some falling down at temperatures about 1200 °C, but after again increasing) gradually. The liquid slag arises up in the system at the temperature about 1270 °C. His amount quickly grows and arrives at the maximum at the temperature about 1460 °C. The last hard oxide phase disappears at the same temperature in the system. Obviously, that to this temperature plenty of hard oxide phases will prevent to formation of the consolidated metallic fusion (to the association of drops of liquid metal), in spite of the fact that the fars of metallic fusion appear in the system at substantially less temperatures.
Substantial interest presents composition of metallic fusion appearing in the system. To estimate changes what be going on in this composition, allows the picture 2. The table of contents of iron in fusion maximally arrives at the size the about 90 mass %. according to the presented data in the period of origin of metallic fusion. The table of contents of iron falls with the increase of temperature, as other elements are restored and fill up by itself metallic fusion (it is chrome and manganese). The stake of cut-in in the metal carbon increases with the height of temperature.
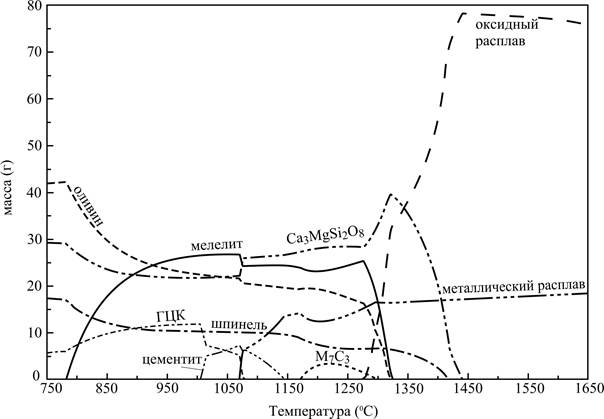
Figure 1 - Mass of condensed phases depending on temperature
Two groups can be distinguished by the nature changes of maintenance of minor admixture elements in composition a metal.
1) Nickel, phosphorus, copper and vanadium, maintenance of that (as well as maintenance of chrome) to the temperature 1350 °С goes out on the practically permanent level.
2) Elements maintenance of that in composition the metal originally extraordinarily small, however with the height of temperature increases steadily. Silicon, titan, aluminum and magnesium behave to the last group. The content of silicon grow and by 1650°С go out on the level of the 2-3 masses, %.
Iron is the basic component extractive in the process of renewal in the metallic phase. Calculations show that if at subzero temperatures iron is contained in composition different oxide phases (and also in composition the austenite), after, in an interval 1020-1340 °C a noticeable amount of iron is in the system as carbidic solutions, after 1340 °C practically all mass of iron is in composition metallic fusion. Iron is restored and goes across in the complement of fusion practically fully at such temperatures. Nickel and copper behave also. 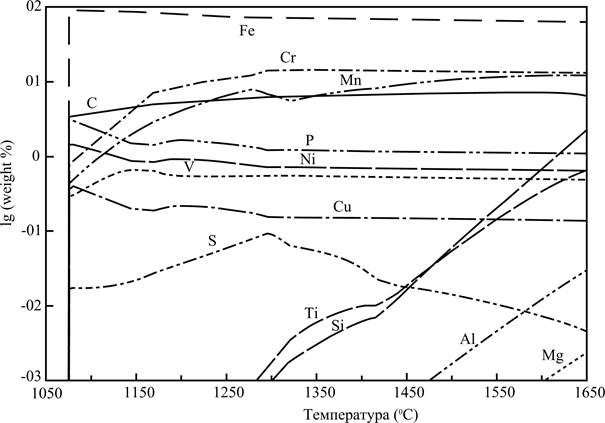
|
|
|
Figure 2 - composition of the liquid metal (mass fraction of components) depending on the temperature.
The manganese behaves other gates. The manganese is in the system as the solution of monooxides, solution of sulfide, in composition metallic fusion, and also as carbidic solutions to the temperature 1270 °C. Substantial part of manganese gets in slag fusion after 1270 °C, gradually restored and goes across in the complement of liquid metal with the height of temperature. The manganese is present in composition the slag in noticeable amounts to the high bound of the examined interval of temperatures. The content of manganese become noticeable and increases in the gas phase from temperatures about 1400 C. Design results show that on complete extraction of manganese in the complement of metallic fusion during renewal, expecting the carbon is not necessary. The noticeable amounts of manganese remain in composition the slag and gas even at maximal extraction of manganese in the metal.
Slag fusion presents most interest from all condensed oxide phases. It composition builds and presented, by oxides and sulfide components. Composition of slag changes with the height of temperature (due to renewal of heavy metals), but at the temperature an about 1470 °C maintenance of basic components (CaO, SiO2, MgO, Al2O3) go out on the permanent level - higher 41% CaO, about 33% SiO2, about 15% MgO and 9% Al2O3.
Composition of gas phase presents substantial interest. The design envisaged possibility of existence in composition the gas phase 95 substances. Gas composition is substantial from the point of view of ecological safety of process, taking into account the relatively large amount of appearing gas (about 10g. on 110g. of general mass of the system at the temperature 1500 °С)
Design of results are presented on the picture 3. Composition of gas phase is presented as denary logarithms of molefractions of components depending on the temperature.
Results designs specify on that in composition the gas phase carbon monoxide will prevail in all examined interval of temperatures. At temperatures necessary for formation of the consolidated metallic fusion (1450-1500 °С), maintenance another, except CO, components of gas phase less 1%. Large majority of components of gas phase is in it composition in quite negligible quantities.

Рисунок 3 – Состав (десятичные логарифмы мольных долей) газовой фазы
Оценить, как скажутся на основных параметрах процесса уменьшение содержания в шлаке железа позволяют рисунки 4 и 5.
Данные, представленные на рисунке 4, позволяют заключить, что обработка шлака с пониженным содержанием железа позволит получить меньшее количество металлического расплава, но при этом не скажется принципиально на его результативности.
Данные рисунка 5 позволяют оценить объёмы газообразных веществ, образующихся в процессе восстановления при различных температурах.
Представленная также на этом рисунке информация об изменении энтальпии системы в зависимости от температуры позволяет оценить затраты тепловой энергии, необходимые для приведения системы в состояние, при котором интересующие нас процессы становятся возможны. Для температуры 25 ºС энтальпии смесей равны DH0298(15%FeO) = –1218 kJ, DH0298(10%FeO) = –1266,3 kJ, DH0298(5%FeO) = –1315,7 kJ.
|
|
|
Согласно результатам моделирования, например, для перехода от состояния 110 г исходной смеси на основе базового состава при 25 ºС к состоянию системы при 1500 ºС потребуется порядка 300 кДж тепловой энергии. Проведённый расчёт не учитывает тепловые потери, которые неизбежно будут сопровождать высокотемпературный процесс, однако и данные, полученные для идеальных условий, могут быть полезны.

Рисунок 4 – Влияние состава шлака на массы некоторых фаз

Рисунок 5 – Объём газовой фазы и энтальпия реакционной массы в зависимости от состава шлака и температуры
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-29; Просмотров: 408; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!