
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Vowel digraph syllable
|
|
|
|
R-controlled syllable
Consonant-le syllable
Open syllable
Vowel-consonant-e syllable
Closed syllable
Theory
The Syllable. Word Stress
Test
Suggest one-word/phrase answers to the following statements/questions:
| № | Question | Answer |
| Are Linking R and intrusive R the same? | ||
| Assimilation can be progressive and … | ||
| … is a phenomenon whereby similar consonant or vowel sounds in a word become less similar. | ||
| … means the addition of one or more sounds to a word | ||
| What phenomenon is observed when tuna oil is pronounced [tjunər ɔɪl]? | ||
| Epenthesis may be divided into … types | ||
| Excrescence means the addition of a … | ||
| Anaptyxis means the addition of a … | ||
| What phenomenon is observed when Thomson → is pronounced Thompson? | ||
| Linking R and intrusive R are linking phenomena involving the appearance of the … consonant |
Answer the following questions:
a) What is epenthesis?
b) Tell the difference between excrescence and anaptyxis.
c) Provide examples of assimilation (not less than five).
d) Provide examples of dissimilation (not less than five).
e) Tell the difference between linking R and intrusive R.
11.1 The syllable as an integral part of the word. Types of syllables in English
Words can be cut up into units called syllables. Humans seem to need syllables as a way of segmenting the stream of speech and giving it a rhythm of strong and weak beats, as we hear in music. Syllables exist only to make speech easier for the brain to process. A word contains at least one syllable. The syllable is a basic unit of speech studied on both the phonetic and phonological levels of analysis. No matter how easy it can be for people and even for children to count the number of syllables in a sequence in their native language, still there are no universally agreed upon phonetic definitions of what a syllable is. A syllable is a word or part of a word that has one vowel sound.
The Six Syllable Types:
11.2 The syllable formation theories. Basic rules of syllabification in English. Nature of word stress
There are different points of view on syllable formation which aге briefly the following: The most ancient theory states that there are as many syllablies in a word as there are vowels. This theory is primitive and insufficient since it does not take into consideration consonants which also can form syllables in some languages, neither does it explain the boundary of syllables. The expiratory theory states that there are as many syllables in a word as there arc expiration pulses. The borderline between the syllables is, according to this theory, the moment of the weakest expiration. This theory is inconsistent because it is quite possible to pronounce several syllables in one articulatory effort or expiration,e.g. seeing / 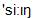 /. The sonority theory states that there are as many syllables in a word as there are peaks of prominence or sonority.
/. The sonority theory states that there are as many syllables in a word as there are peaks of prominence or sonority.
|
|
|
The definition of the syllable from the functional point of view existing in modern linguistics tends to single out the following features of the syllable:
1) syllable formation (складоутворення);
2) syllable division/separation (складоподіл).
In English the syllable is formed: 1. by any vowel alone or in combination with one or more consonants – not more than 3 preceding and not more than 4 following it, e.g. are [a:], we [wi:], it [it], sixths [siksθs].
2. by a word final sonorants [n], [1], [m] immediately preceded by a consonant: e.g. rhythm ['rið(e)m], garden ['ga:d(e)n].
The English sonorants [w], [j] are never syllabic as they are always syllable-initial.
Thus vowels and sonorants are syllable-forming elements and every word, phrase or sentence has as many syllables as it has syllabic elements.
According to the placement of vowels and consonants the following types of syllables are distinguished:
Table 1
| Placement of VOWELS | Placement of CONSONANTS |
| open: the V is at the end, such a S is articulated with the opening of the mouth by the end: e.g. they, wri-ter | covered at the beginning:the C is at the beginning of the syllable: e.g. tie |
| closed: which end in C, at the end of such a S the mouth is closed: e.g. hun-dred, hat | covered at the end: the C is at the end of a S: e.g. on |
The presentation of a syllable structure in terms of C and V (canonical forms) gives rather numerous combinations which can be grouped into 4 structural types of syllables:
Table 2
| 1. Fully open | V ore, or |
| 2. Fully closed (V between C) | CVC fat CCVC place CVCC fact CCCVCC street CVCCC facts CVCCCC sixths [siksθs] |
| 3. Covered at the beginning (one C or a sequence of C precede a vowel) | CV too CCV spy CCV traw |
| 4. Covered at the end (one C or more complete the syllable) | VC on VCC act VCCC acts |
Syllables can be also designated
1. by the position in the word: from the beginning – INITIAL (початковий), MEDIAL (серединний), FINAL фінальний/кінцевий) or from the end – ULTIMATE (останній), PENULTIMATE (передостанній/другий від кінця), ANTEPENULTIMATE (третій від кінця);
2. by the position in relation to stress: PRETONIC (переднаголошений), TONIC (наголошений), POSTTONIC (післянаголошений). (Any syllable which is not tonic is ATONIC/ненаголошений):
e.g. tre- men- dous
initial medial final
antepenultimate penultimate ultimate
pretonic tonic posttonic
Now we shall consider three very important functions of the syllable:
1) constitutive function (конститутивна функція). It lies in its ability to be a part of a word or a word itself;
2) distinctive function (смислорозрізнювальна / дистинктивна функція). In this respect the syllable is characterized by its ability to differentiate words and word-forms, that is ['nai-treit] nitrate – ['nait-reit] night-rate;
3) identificatory function (ідентифікативна функція): the listener can understand the exact meaning of the utterance only when the correct syllabic boundary is perceived:
|
|
|
an aim – a name
mice kill – my skill
an ice house – a nice house
peace talks – pea stalks
plate rack – play track
Sometimes the difference in syllabic division might be the basic ground for differentiation sentences in such minimal pairs as:
I saw her eyes. – I saw her rise.
I saw the meat. — I saw them eat.
11.3 Word stress
Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel. Signals: pitch of voice (level), sonority of sound (vowel quality: strong, weak; stressed syllables have strong vowels – pot, Tom, office, odd, man – weak: potato, official, addition, woman), duration in time (length – syllables are extra long when they are prominent) – together they make syllables sound louder. Degrees of stress: primary, secondary (partial), weak. Stress may be semantically contrasted (verb – noun – adjective). Modify of stress: photogragh-photographer-photographic.
Orthographically identical word-pairs in English differentiated by word-stress as nouns (penultimate stress) or verbs (ultimate stress):
Table 2
| abstract accent addict address affect afix annex collect combat commerce | commune compound compress conine conlict contest contrast convict defect desert | detail digest discard discharge discount discourse escort envelope exploit export | extract fragment import impact impress incline increase insert insult intern | object outrage perfume pervert present project produce progress protest rebel | recess record reill refuse segment survey subject suspect torment transfer transport |
increase [' inkr is] [in'kri:s]
insult [' insʌlt] [in'sʌlt]
impress ['impres] [im'pres]
inlay ['inlei] [in'lei]
transport ['træsnspɔ:t] [træns'pɔ:t] or [trəns'pɔ:t]
torment ['tɔ:ment] [tɔ:'ment] or [tə'ment]
combine ['kɒmbain] [kəm'bain]
conduct ['kɒndʌkt] [kən'dʌkt]
contrast ['kɒntra:st] [kən'tra:st]
11.4 Functions and tendencies of the English stress. Typology of accentual structure
The numerous variations of English word stress are systematized in the typology of accentual structure of English words worked out by G.P. Torsuev [1960]. He classiies them according to the number of stressed syllables, their degree or character (the main and the secondary stress). The distribution of stressed syllables within the word accentual types forms accentual structures of words, e.g. the accentual type of words with two equal stresses may be presented by several accentual structures: 'well-'bred, 'absent-minded or 'good-looking. Accentual types and accentual structures are closely connected with the morphological type of words, with the number of syllables, the semantic value of the root and the prefix of the word.
The accentual types are:
I. This accentual type marks both simple and compound words. The accentual structures of this type may include two and more syllables, e.g. 'father, 'possibly, 'mother-in-law, 'gas-pipe.
II. The accentual type is commonly realized in compound words, most of them are with separable preixes, e.g. 'radio-'active, 're'write, 'diso'bey.
III. and IV. The accentual types are met in initial compound abbreviations like 'U'S'A, 'R'S'V'P.
V. The type is realized both in simple and compound words, very common among compound words, e.g. 'hair-,dresser, 'sub,structure.
VI. The accentual type marks a great number of simple words and some compound words as well. In simple words the stresses fall onto:
|
|
|
the prefix and the root: 1.,maga'zine;
the root and the suffix: 2.,hospi'tality;
the prefix and the suffix: 3.,disorgani'zation.
VII. The type includes rather a small number of simple words with the separable prefixes, e.g. 'mis,repre'sent.
VIII. The type is found in a very small number of words, usually simple words with the stresses on the prefix, the root and the suffix, e.g.,indi,viduali'zation.
IX. The type is met in rare instances of compound words with separable prefixes, e.g. 'un'sea,worthy.
X. The type is represented by rare instances of simple and compound words, e.g. 'soda-,water,bottle.
XI. The type is found in rare instances of compound words consisting of the three components, e.g.,ginger'beer-,bottle.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-31; Просмотров: 1150; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!