
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Что нельзя отнести к причинам кризисного состояния окружающей среды в России?
|
|
|
|
Test
Тема 34. Надзор и контроль за соблюдением законодательства о труде
Тест 1. Виды надзорных и контрольных функций, использующиеся при осуществлении его соответствующими органами:
а) коллегиальный;
б) предварительный;
в) предупредительный;
г) текущий;
д) последующий.
Тест 2. Комитеты по охране труда создаются в организациях с численностью работников:
а) более 10;
б) более 50;
в) более 100;
г) более 3.
Тест 3. При производственной деятельность работодателя представляющей опасность для жизни и здоровья работников и населения:
а) организация подлежит ликвидации;
б) организация подлежит реорганизации;
в) деятельность организации может быть приостановлена;
г) деятельность организации может быть изменена соглашением сторон.
Тест 4. При осуществлении надзора за исполнением законов на территории Российской Федерации органы прокуратуры не вправе:
а) принимать меры, направленные на устранение нарушений;
б) привлекать виновных к ответственности;
в) проводить проверки исполнения законов;
г) вмешиваться в оперативную деятельность поднадзорных объектов.
Тест 5. Последующий надзор и контроль осуществляется при разрешении трудовых споров и выявлении:
а) вновь допущенных нарушений;
б) ранее допущенных нарушений;
в) возможных нарушений;
г) при рассмотрении обращений организаций и граждан.
1. The kind of phonetic notation used by explanatory dictionaries in the USA
a. transliteration
b. allophonic transcription
c. Webster’s respelling system
d. the transcription of the International Phonetic Association (IPA)
2. The form of pronunciation most commonly described in books on the phonetics of British English and traditionally taught to foreigners
a. General American
b. Scottish Standard English
c. Cockney
d. Received Pronunciation
3. The type of English Pronunciation where rolled [r] (of the Russian type) is used in all positions
|
|
|
a. Southern English
b. Received Pronunciation
c. Standard Scottish Pronunciation
d. BBC English
4. The most wide spread type of educated American speech
a. Received Pronunciation
b. General American Pronunciation
c. Southern American Pronunciation
d. BBC English
5. Voiced consonants are
a. [p, t, k]
b. [f,  , s]
, s]
a. c [b, d, g, v, 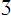 , z, ð,
, z, ð, 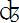 ]
]
c. [  ,
, 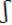 , h]
, h]
6. Voiceless consonants are
a. [f,  , s, p, t, k,
, s, p, t, k,  ,
, 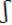 , h]
, h]
b. [ 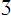 , z,
, z, 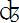 ]
]
c. [ð, l,  ]
]
d.[b, d, g, v]
7. According to the view originated by L.V.Sherba the phoneme is
a. a physical object
b. a mentalistic image
c. a functional, material and abstract unit
d.an abstract idea
8. Two major classes of sounds traditionally distinguished by phoneticians in any language
a. capital
b. consonants and vowels
c. lexical and grammatical
d. high and low
9. They defined language as “the immediate actuality of thought”
a. Austin Powers and Mick Jagger
b. Beavis and Butt-Head
c. Quentin Tarantino and Gregg Araki
d. K. Marx and F. Engels
10. The four components of the phonetic system of language (phonemic, syllabic, accentual and intonational) all constitute its
a. spelling
b. distribution
c. pronunciation
d. history
11. Noise consonant sounds produced with a complete obstruction which is slowly released and the air escapes from the mouth with some friction
a. sonorants
b. affricates
c. rolled
d. glottal
12. According to the work of the vocal cords noise consonants may be
a. voiced and voiceless
b. round and square
c. large and narrow
d. iron and copper
13. According to the degree of noise English and Russian consonants are divided into two classes
a. noise consonants and sonorants
b. round and square
c. large and narrow
d. iron and copper
14. Consonants made with the tip of the tongue projected between the teeth
a. alveolar
b. interdental
c. glottal
d. labial
15. Consonants articulated in the glottis
a. glottal
b. lingual
c. labial
d. dental
16. Consonants made by the lips
a. unicentral
b. palatalized
c. bicentral
d. labial
17. Consonants articulated with the tip against the upper teeth ridge
a. alveolar
b. palatalized
c. bicentral
d. unicentral
18. A word or a group of words characterized by a certain intonation pattern and completed from the point of meaning
a. equinox
b. confusion
c. an intonation group
d. a mocking word
19. The first philologist to found the branch of phonetics which is concerned with the study of the purely linguistic aspect of speech sounds
a. I.A. Baudouin de Courtenay
b. L. Bloomfield
c. D. Jones
d. L. Hjelmslev
20. The founder of the Copenhagen linguistic Circle
a. L. Bloomfield
b. L. Hjelmslev
c. D. Jones
d. I.A. Baudouin de Courtenay
21. The majority of alphabetic transcriptions used in teaching foreign languages are based on
a. the transcription of the International Phonetic Association (IPA)
b. allophonic transcription
c. transliteration
d. Webster’s respelling system
22. The kind of phonetic notation used by explanatory dictionaries in the USA
a. Webster’s respelling system
b. allophonic transcription
c. transliteration
d. the transcription of the International Phonetic Association (IPA)
|
|
|
23. The form of pronunciation most commonly described in books on the phonetics of British English and traditionally taught to foreigners
a. Received Pronunciation
b. Scottish Standard English
c. Cockney
d. General American
24. The type of English Pronunciation where rolled [r] (of the Russian type) is used in all positions
a. Standard Scottish Pronunciation
b. Received Pronunciation
c. Southern English
d. BBC English
25. The most wide spread type of educated American speech
a. General American Pronunciation
b. Received Pronunciation
c. Southern American Pronunciation
d. BBC English
26. Voiced consonants are
a. [b, d, g, v, 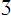 , z, ð,
, z, ð, 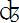 ]
]
b. [f,  , s]
, s]
c. [p, t, k]
d. [  ,
, 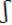 , h]
, h]
27. Voiceless consonants are
a. [f,  , s, p, t, k,
, s, p, t, k,  ,
, 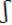 , h]
, h]
b. [ 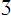 , z,
, z, 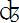 ]
]
c. [ð, l,  ]
]
d. [b, d, g, v]
28. According to the view originated by L.V.Sherba the phoneme is
a. a functional, material and abstract unit
b. a mentalistic image
c. a physical object
d. an abstract idea
29. Two major classes of sounds traditionally distinguished by phoneticians in any language
a. consonants and vowels
b. capital and
c. lexical and grammatical
d. high and low
30. They defined language as “the immediate actuality of thought”
a. K. Marx and F. Engels
b. Beavis and Butt-Head
c. Quentin Tarantino and Gregg Araki
d. Austin Powers and Mick Jagger
31. The four components of the phonetic system of language (phonemic, syllabic, accentual and intonational) all constitute its
a. pronunciation
b. distribution
c. spelling
d. history
32. Noise consonant sounds produced with a complete obstruction which is slowly released and the air escapes from the mouth with some friction
a. affricates
b. sonorants
c. rolled
d. glottal
e.
33. According to the work of the vocal cords noise consonants may be
a. voiced and voiceless
b. round and square
c. large and narrow
d. iron and copper
34. According to the degree of noise English and Russian consonants are divided into two classes
a. noise consonants and sonorants
b. round and square
c. large and narrow
d. iron and copper
35. Consonants made with the tip of the tongue projected between the teeth
a. interdental
b. alveolar
c. glottal
d. labial
36. Consonants articulated in the glottis
a. glottal
b. lingual
c. labial
d. dental
37. Consonants made by the lips
a. bicentral
b. palatalized
c. labial
d. unicentral
38. Consonants articulated with the tip against the upper teeth ridge
a. alveolar
b. palatalized
c. bicentral
d. unicentral
39. A word or a group of words characterized by a certain intonation pattern and completed from the point of meaning
a. an intonation group
b. confusion
c. equinox
d. a mocking word
40. The first philologist to found the branch of phonetics which is concerned with the study of the purely linguistic aspect of speech sounds
a. I.A. Baudouin de Courtenay
b. L. Bloomfield
c. D. Jones
d. L. Hjelmslev
41. The founder of the Copenhagen linguistic Circle
a. L. Hjelmslev
b. L. Bloomfield
c. D. Jones
d. I.A. Baudouin de Courtenay
42. The extreme form of the physical conception was propounded by
a. D. Jones
b. L. Bloomfield
c. L. Hjelmslev
d. I.A. Baudouin de Courtenay
43. According to V.A.Vassilyev there are two large groups of consonants
a. occlusive and constrictive
b. round and square
c. large and narrow
a. d)iron and copper
44. The prevalent principle of English orthography
a. conservative
b. morphological-derivational
c. monographemic
d. chaotic
45. The predominant principle of Russian orthography
a. a)morphological-derivational
b. b)conservative
1. c)chaotic
2. d)distorted
46. The musical word stress is typical for
a. Russian
b. English
c. Vietnamese
d. German
47. Recurrence of stressed syllables at more or less equal intervals of time in a speech continuum
|
|
|
a. speech rhythm
b. loudness
c. monologue
d. dialogue
48. A set of symbols for each phoneme of the language
a. respelling
b. respelling
c. alphabet
d. phonemic transcription
49. A set of symbols for each phoneme of the language representing modifications of their allophones
a. alphabet
b. Webster’s respelling system
c. allophonic transcription
d. transliteration
1.Слабо развитое законодательство и право в сфере взаимодействия общества и природы;
2. Дефекты организации государственного управления природопользованием и охраной окружающей среды;
3. Дефицит финансирования программ и мероприятий по охране окружающей среды;
4.Дефицит специалистов – экологов;
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-31; Просмотров: 576; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!