
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
The Rh Blood Group System
|
|
|
|
In the 1930s, researchers discovered the presence of a different surface antigen on human red blood cells. Soon after they injected rabbits with RBCs from rhesus monkeys, the rabbit serum contained antibodies that were directed against the monkey blood cells but that would also agglutinate some human RBCs. This indicated that a common antigen was present on both human and monkey red blood cells. The antigen was named the Rh factor (Rh for rhesus monkey). The roughly 85% of the population whose cells possess this antigen are called Rh +; those lacking this RBC antigen (about 15%) are Rh -. Antibodies that react with the Rh antigen do not occur naturally in the serum of Rh - individuals, but exposure to this antigen can sensitize their immune systems to produce anti-Rh antibodies.
Blood Transfusions and Rh Incompatibility If blood from an Rh + donor is given to an Rh - recipient, the donor's RBCs stimulate the production of anti-Rh antibodies in the recipient. If the recipient then receives Rh + RBCs in a subsequent transfusion, a rapid, serious hemolytic reaction will develop.
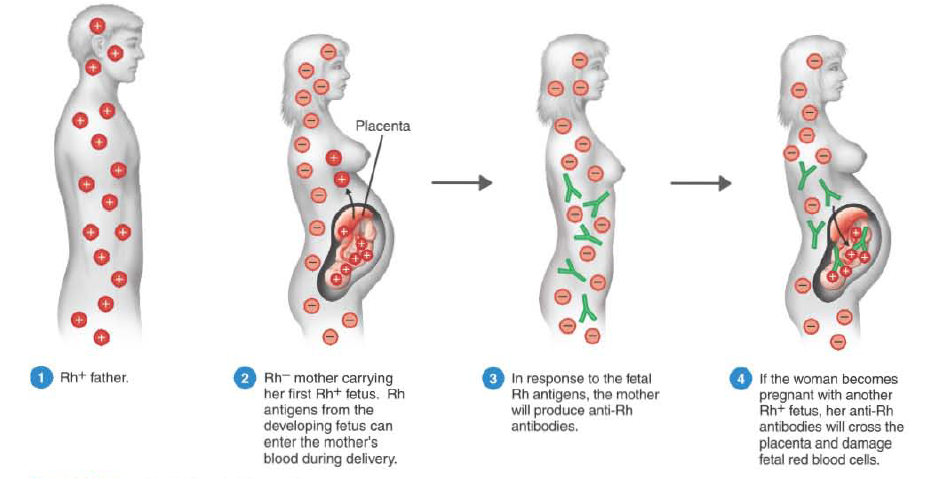
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn When an Rh - woman and an Rh + man produce a child, there is a 50% chance that the child will be Rh + (Figure 2). If the child is Rh +, the Rh - mother can become sensitized to this antigen during birth when the placental membranes tear and the fetal Rh + RBCs enter the maternal circulation, causing the mother's body to produce anti-Rh antibodies of the IgG type. If the fetus in a subsequent pregnancy is Rh +, her anti-Rh antibodies will cross the placenta and destroy the fetal RBCs. The fetal body responds to this immune attack by producing large numbers of immature RBCs called erythroblasts. Thus, the term erythroblastosis fetalis was once used to describe what is now called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDNB). Before the birth of a fetus with this condition, the maternal circulation removes most of the toxic by-products of fetal RBC disintegration. After birth, however, the fetal blood is no longer purified by the mother, and the newborn develops jaundice and severe anemia.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-06-04; Просмотров: 575; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!