
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Distance
|
|
|
|
Time
Methods for Reducing External Exposure
Radiation exposure from external sources can be decreased in any one of the four ways listed below, or by an appropriate combination of them.
- Decreasing the length of time spent near a source of radiation.
- Allowing the source to decay before approaching it.
- Increasing the distance between the source and yourself.
- Absorbing the radiation in shielding material placed between the source and yourself.
In addition, access to radiation areas can be controlled, and areas routinely surveyed and sign-posted to identify areas where higher than normal fields exist.
Radiation exposure can be controlled by limiting the length of time a person spends in a radiation area. If the radiation dose rate is known and a person wishes to limit the dose they receive, the maximum length of time that they can spend in the area is calculated as follows:
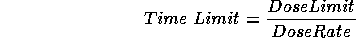
The units of time and dose must be consistent for these calculations. Some examples are shown below.
- The radiation equivalent-dose rate (often called the radiation field) in an area is
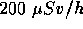 . If a person is to receive a dose no greater than
. If a person is to receive a dose no greater than 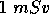 how long can he spend in the area?
how long can he spend in the area?
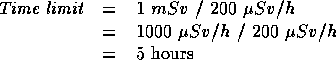
- For how long may a person work in a field of
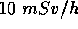 if their dose is to be less than
if their dose is to be less than 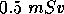 ?
?
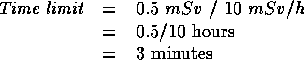
- A person is to work in a mixed field consisting of
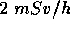 of gamma radiation,
of gamma radiation, 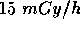 of beta radiation,
of beta radiation,  of fast neutrons and
of fast neutrons and 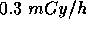 of slow neutrons. How long can he work for without exceeding a whole body dose of
of slow neutrons. How long can he work for without exceeding a whole body dose of 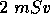 ?
?
The first step is to convert all these to mSv/h using the appropriate values of the radiation weighting factor.
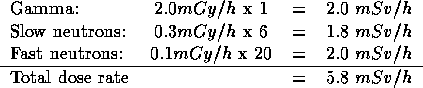
then:
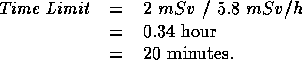
In the last example the skin equivalent dose is not included, because it is subject only to the 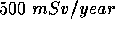 limit for deterministic effects.
limit for deterministic effects.
Work to be done in radiation fields should be completed as quickly as possible without compromising normal safety practices. The job should be planned before it is started. This is to ensure that efficient procedures are developed which will result in the lowest possible exposure to personnel. Work in very high radiation fields should not only be planned, but practiced on a similar set-up in the absence of radiation. In this way mistakes which may lead to unnecessary exposures can be averted. It is especially important to ensure that all tools needed for the job are available at the job site so that little time (and hence dose) is used in waiting for the appropriate tools to be found.
Increasing the distance between a person and the source of radiation can result in a considerable reduction of exposure. The manner in which the intensity of radiation decreases as you move away from the source depends on the absorption of the radiation by air and on the size and shape of the source relative to the distance from which it is viewed.
Alpha particles will only travel a few centimeters in air and most beta particles will be absorbed after travelling a meter or so. Absorption by the air is the more important factor in reducing the intensity of these particles as distance from the source is increased.
|
|
|
Gamma and neutron radiation is not effectively scattered by air and so geometric factors determine their intensity as a function of the distance from the source.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-06-27; Просмотров: 270; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!