
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Basic stages of the machines making process
|
|
|
|
The basic technical-economical indexes of machines
General information of the machine building
Technical and economical indexes of the metallurgy processes
Raw materials and basic methods of metals production
General description of the metallurgy production
LECTURE №6
TECHNOLOGIES OF METALLURGY AND MACHINE BUILDING COMPLEXES AND THEIR TRENDS7. Technological processes of the parts production – Pr. Work
8. Trends of the metallurgy production and machine building complexes – Ind.work
1. Metallurgy is a branch of industry which engulfs the processes of getting metals from ores and other materials, of changing of their composition, structure and properties and giving the metal the certain form (finished good or half-machinned good).
The specific features of metallurgy are large production scales as compared to other industries and complication of technological cycle.
The mining and metallurgy complex plays a greate role for the industry of Ukraine. Ferrous metallurgy provides over 25 % of Internal Gross Outpoot and about of 43 % currency enterings of the country. It is the basic donor of the currency entering to budget. Metallurgy is the most export-oriented industry of Ukraine.
2. Pre-products (the raw materials) for the production of majority of metals are ore, fuel, flux and refractoriess.
Basic methods of the metals production are:
1).Pyrometallurgical (fire) method (cast iron, steel, copper etc.).
2). Electrometallurgy (steel,Al, Mg).
3). Hydrometallurgy (Zn, Ni, Co, Cr, Ag, Au).
4). Chemical and metallurgical method (Ti).
5). Powder metallurgy.
3. The kernel of metallurgy is a ferrous metallurgy – basis of mechanical engineering, building, defensive industry, articles of consumption; difficult and many-sided industry of economy.
The basic products of ferrous metallurgy are: cast iron, steel and some goods from it, ferro-alloys, powders of iron and its alloys.
Cast iron is produced by a pyrometallurgical method from iron ores in the blast furnaces.
The raw materials for the production of a cast iron are iron ores, fuel (coke) and fluxes.
For 1 t of the cast iron it is needed 1,7...2 t of ore, 500…700 kg of coke, 300...700 kg of flux, 2...3 t of the air blowing.
The basic products of blast-furnace production are: steelmaking iron (80%);cast iron (15…20 %);ferro-alloys (1...2 %); the by-products: slag (used in building and also for the production of mineral fertilizers); blast-furnace gas (used after cleaning from a dust for a heating of air in a metallurgical production).
A steel differs from a pig (cast) iron by the less content of a carbon and admixtures. Therefor sleelmaking involves processes which reduce the concentration of these elements.
On a chemical composition steels are divided on a carbon steel (90 %) and an alloyed steel.
Raw materials for a steelmaking process are: steelmaking iron, scrap, fluxes, oxidants, alloyed elements, ferro-alloys.
|
|
|
Energy sources: fuel oil; natural, blast-furnace and coke gas; electric energy, chemical energy.
The basic methods of steelmaking are:
1. Oxygen-converter method – consists in a blowing out of molten pig iron by oxygen. A method has a high productivity, small duration of process, low expense of metal, absence of fuel, low expense of elecroenergy as compared to another ways, lowered capital charges on building and service, low prime price etc. In the economic developed countries this method is the most popular today.
2. Marten method (An open-hearth furnace). The receipt of steel is carried out due to the use of fuel (mainly, gaseous). A method is universal but it has the substantial failings, foremost, a low productivity, a large duration of process, a large amount of fuel. Therefore it is out of use in many countries.
3. Production in electric furnace is a progressive method of receipt of steels based on the use of elecrtric energy. It is possible to get steels with minimum content of harmful admixtures of a high quality and with the special properties.
About 70 non-ferrous metals and more than 10 thousand of alloys on their basis are used in a modern technique.
Among all the non-ferrous metals alloys of aluminium, copper, titanium and magnesium have the most wide application in industry as a construction materials.
The production of aluminium, copper,titanium- magnesium products, nickel, lead, zinc is traditional in the structure of the non-ferrous metallurgy of Ukraine.
4. A level of development of the machine building industry of any country determines the state of all other industries and the whole economic position of the state.
In Ukraine the specific gravity of products of M.B.complex is 20 % in the general volume of the industry production.
The raw materials for the M.B. industry are the products of metallurgy.
The products of M.B. are machines, their complications, instruments.
Themachine is a mechanical device for the transformation of energy, materials or information.
Any machine consists of parts (primary indivisible element), units and mechanisms.
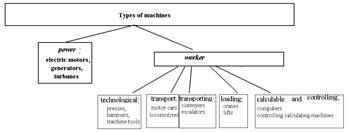
Fig.1 – Machines classification
5. The basic technical-economical indexes of machines are: ¨productivity, ¨ longevity, ¨ efficiency, ¨ economy, ¨ degree of automation, ¨ reliability, ¨ technologicalness of construction, ¨ repairness, ¨ prime price.
6. There are the followings stages of making of any machine: · production of the workpieces (half-finished goods); · production of the parts; · assembling of the parts into the units, mechanisms and the machine.
The general methods of the workpieces production are: casting, forging, stamping, welding etc.
¨ A casting process is the process of workpieces production by means of pouring the liquid metal into the special mould with the next solidification and removing from the mould. Casting processes are widly used for the production of a great variety of products (workpieces and parts).
About 50 % of the parts in mechanical engineering are made by casting; their cost makes about 15 % from the total cost of the machine.
The main advantages of the casting process are:
· It is possible to cast practically any material be it ferrous or nonferrous. The most cheap alloy is cast-iron (73 % of all the castings).
|
|
|
· Castings of any size (from 1 mm to 20 m) and weight (from 1 g to even up 400 t) can be made.
· It is possible to made the goods of shaped configuration (some of them can be got only by casting process).
· In some casting methods the finished goods (the parts) cab be produced.
· The economy of a metal.
A great problem of casting processes is ecological problem in a number of methods.
Casting technology can be realized by different methods, for exampl e:
1. Sand mould casting – the most widespread in industry (to 70...80% of castings) because of their universality, simplicity and low cost.
2. Special casting processes allow to get more high-quality goods, by greater exactness of sizes and volume of tooling. But the castings prime price is higher. Among these methods are: wax process – casting of smelted patterns (precision casting); permanent mould casting (gravity diecasting, chill casting) – a casting in the metal mould of multiple-use, filled by the metal under the action of gravity forces; diecasting (pressure casting) – molten metal injects into the metal mould at high pressures; centrifugal casting (the mould is rotated) etc.
Some methods of casting allow to get the prepared goods (parts) without the further tooling, for example, wax process, diecasting (pressure casting).
¨ Metal working processes (MWP) are the technological processes of production of the workpieces (half-finished goods) and finished products (parts) by deformation of materials in hot or cold condition.
These methods are generally economacal and in many cases improve the mechanical properties too. The production rate is very high in general.
About 90% of all of smelted steel and over 50% of nonferrous metals and alloys are processed by these methods.
1. Methods of receipt of piece goods. Forging process where the heated workpiece is deformed by periodic shots or static influence of universal instrument allows to receipt the heavy workpieces – forgings of weigh to 200…300 t. Method is mainly used in a single production. Stamping is a process of making goods by a special instrument – die. The got goods have a greater stability of sizes and shape, greater exactness, more high quality of surface as compared with the goods of forging. A stamping process also is more productive and can be used in mass production.
2. Methods of receipt of long-length workpieces.Rolling is a process where the metal is compressed between two rotating rolls. This is one of the most widely used of all the metal working processes (for production of rods, wires, pipes, rails) because of its high productivity and low cost.
¨ Welding is the technological process of joining of two or more elements to make a single part.
Along with metal working processes and casting production welding is a major technological process of M.B., basic advantages of which are the followings: economy of metal; realizing in the different positions and environments; possibility of receipt of connections of defferent metals and alloys, non-metal materials; wide range of sizes and mass of the got parts; making of the new typies of constructions/
There are more than 70th different processes incorporated by the general name of «welding».
The most popular in the world welding practice are the thermal methods. The most widespread sources of heat for welding are: electric arc, gases flame, plasma, electron beam, laser radiation.
A basic method of welding works in the economy of the industrially developed countries (more than 50 %) is an arc welding.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-07; Просмотров: 671; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!