
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Formation
|
|
|
|
The Caspian Sea, like the Black Sea, is a remnant of the ancient Paratethys Sea. It became landlocked about 5.5 million years ago due to tectonic uplift and a fall in sea level. During warm and dry climatic periods, the landlocked sea has all but dried up, depositing evaporitic sediments like halite that have become covered by wind-blown deposits and were sealed off as an evaporite sink[10] when cool, wet climates refilled the basin.[11] Due to the current inflow of fresh water, the Caspian Sea is a freshwater lake in its northern portions. It is more saline on the Iranian shore, where the catchment basin contributes little flow. Currently, the mean salinity of the Caspian is one third that of the Earth's oceans. The Garabogazköl embayment, which dried up when water flow from the main body of the Caspian was blocked in the 1980s but has since been restored, routinely exceeds oceanic salinity by a factor of 10.[2]
[edit]Geography
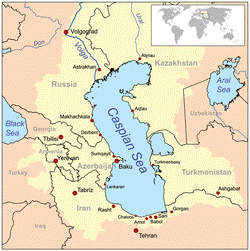

Map of the Caspian Sea, yellow shading indicates Caspian drainage basin. (Since this map was drawn, the adjacent Aral Sea has greatly decreased in size)
The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world and accounts for 40 to 44% of the total lacustrine waters of the world.[12] The coastlines of the Caspian are shared byAzerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkmenistan. The Caspian is divided into three distinct physical regions: the Northern, Middle, and Southern Caspian.[13] The North-Middle boundary is the Mangyshlak Threshold, which runs through Chechen Island and Cape Tiub-Karagan. The Middle-South boundary is the Apsheron Threshold, a sill of tectonic origin between the Eurasian continent and an oceanic remnant,[14] that runs through Zhiloi Island and Cape Kuuli.[15] The Garabogazköl bay is the saline eastern inlet of the Caspian, which is part of Turkmenistan and at times has been a lake in its own right due to the isthmus which cuts it off from the Caspian.
Divisions between the three regions are dramatic. The Northern Caspian only includes the Caspian shelf,[16] and is very shallow; it accounts for less than 1% of the total water volume with an average depth of only 5–6 metres (16–20 ft). The sea noticeably drops off towards the Middle Caspian, where the average depth is 190 metres (620 ft).[15] The Southern Caspian is the deepest, with oceanic depths of over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). The Middle and Southern Caspian account for 33% and 66% of the total water volume, respectively.[13] The northern portion of the Caspian Sea typically freezes in the winter, and in the coldest winters ice forms in the south as well. [17]
Over 130 rivers provide inflow to the Caspian, with the Volga River being the largest. A second affluent, the Ural River, flows in from the north, and the Kura River flows into the sea from the west. In the past, the Amu Darya (Oxus) of Central Asia in the east often changed course to empty into the Caspian through a now-desiccated riverbed called the Uzboy River, as did the Syr Darya farther north. The Caspian also has several small islands; they are primarily located in the North and have a collective land area of roughly 2,000 km2 (770 sq mi). Adjacent to the North Caspian is the Caspian Depression, a low-lying region 27 metres (89 ft) below sea level. The Central Asian steppes stretch across the northeast coast, while the Caucasus mountains hug the Western shore. The biomes to both the north and east are characterized by cold, continental deserts. Conversely, the climate to the southwest and south are generally warm with uneven elevation due to a mix of highlands and mountain ranges; the drastic changes in climate alongside the Caspian have led to a great deal of biodiversity in the region.[2]
The Caspian Sea has numerous islands throughout, all of them near the coasts. There are none in the deeper parts of the Sea. Ogurja Adais the largest island. The island is 37 km long, with gazelles roaming freely on it. In the North Caspian, the majority of the islands are small and uninhabited, like the Tyuleniy Archipelago, an Important Bird Area (IBA), although some of them have human settlements.
[edit]Hydrology


Caspian Sea near Aktau, Mangistau region,Kazakhstan.
The Caspian has characteristics common to both seas and lakes. It is often listed as the world's largest lake, although it is not a freshwater lake. The Caspian was once part of theTethys Ocean but became landlocked about 5.5 million years ago due to plate tectonics.[12]The Volga River (about 80% of the inflow) and the Ural River discharge into the Caspian Sea, but it has no natural outflow other than by evaporation. Thus the Caspian ecosystem is aclosed basin, with its own sea level history that is independent of the eustatic level of the world's oceans. The level of the Caspian has fallen and risen, often rapidly, many times over the centuries. Some Russian historians[ who? ] claim that a medieval rising of the Caspian, perhaps caused by the Amu Darya changing its inflow to the Caspian from the 13th century to the 16th century, caused the coastal towns of Khazaria, such as Atil, to flood. In 2004, the water level was −28 m, or 28 m (92 ft) below sea level.
Over the centuries, Caspian Sea levels have changed in synchrony with the estimated discharge of the Volga, which in turn depends on rainfall levels in its vast catchment basin. Precipitation is related to variations in the amount of North Atlantic depressions that reach the interior, and they in turn are affected by cycles of the North Atlantic Oscillation. Thus levels in the Caspian sea relate to atmospheric conditions in the North Atlantic thousands of miles to the northwest. These factors make the Caspian Sea a valuable place to study the causes and effects of global climate change.[ citation needed ]
The last short-term sea-level cycle started with a sea-level fall of 3 m (9.84 ft) from 1929 to 1977, followed by a rise of 3 m (9.84 ft) from 1977 until 1995. Since then smaller oscillations have taken place.[18]Environmental issues
The Volga River, the largest in Europe, drains 20% of the European land area and is the source of 80% of the Caspian’s freshwater inflow. Its lower reaches are heavily developed with numerous unregulated releases of chemical and biological pollutants. Although existing data are sparse and of questionable quality, there is ample evidence to suggest that the Volga is one of the principal sources of transboundary contaminants into the Caspian. The magnitude of fossil fuel extraction and transport activity constitute risks to water quality. Underwater oil and gas pipelines have been constructed or proposed, increasing potential environmental threats.[19]
Various islands in the Caspian have suffered extensive environmental damage due to oil production. Vulf, Azerbaijan has been affected by ecological damage because of the petrochemical industry. This has significantly decreased species of marine birds in the area.
The world’s first offshore wells and machine-drilled wells were made in Bibi-Heybat Bay, near Baku, Azerbaijan. In 1873, exploration and development of oil began in some of the largest fields known to exist in the world at that time on the Absheron peninsula near the villages of Balakhanli, Sabunchi, Ramana and Bibi Heybat. Total recoverable reserves were more than 500 million tons. By 1900, Baku had more than 3,000 oil wells, 2,000 of which were producing at industrial levels. By the end of the 19th century, Baku became known as the "black gold capital", and many skilled workers and specialists flocked to the city.
By the turn of the 20th century, Baku was the center of international oil industry. In 1920, when the Bolsheviks captured Azerbaijan, all private property – including oil wells and factories – was confiscated. Afterwards, the republic's entire oil industry came under the control of the Soviet Union. By 1941, Azerbaijan was producing a record 23.5 million tons of oil, and the Baku region supplied nearly 72% of all oil extracted in the entire USSR.[24]
In 1994, the "Contract of the Century" was signed, signaling the start of major international development of the Baku oil fields. The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan pipeline, a major pipeline allowing Azerbaijan oil to flow straight to the Turkish Mediterranean port of Ceyhan, opened in 2006.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-09; Просмотров: 462; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!