
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Glossary
|
|
|
|
Axon – a long appendix of a neural cell (neuron) that transfers the impulse of nervous excitation.
Aplysia – sea gasteropoda mollusc one of the species of which – Aрlysia californica – is a favourite object of research carried out by American biologists.
A posteriori (lat. - empyrical) – experiental.
A priori (lat. – prior) – experience independent, preceding the experience.
Ganglion – a cluster of tens to thousands neurons.
Gestalt ( German – Specimen) – one of the central concepts of Gestalt psychology, which can be in the simplified way called mental image.
Collaterals – here – axon branching.
Cochlear nuclei – the nuclei of auditory system of the brain, which are called so due to the neural relationship with ductus cochlearis of the inner ear.
Crick Francis Harry Compton (born in 1916) – English biophysicist and geneticist, the Nobel prize winner. In 1953, in co-operation with G. Watson, created a model of DNA structure (double helix) that gave a start to molecular genetics. Transactions on decoding a genetic code and neurophysiology.
Lateral inhibition – (Lat.: latus – side) inhibition of neighboring neurons from the side of excited neuron, for example, in the retina. Results in more contrast difference between the state of a group of excited neurons and the neighboring unexcited ones.
Melanin – black, dark brown or yellow pigment that is formed as a result of polimerization of tyrosine (one of amino acids of the organism) oxidation products. It is intensively formed in the skin at irradiation by sun or UV rays. Higher content of melanin strengthens pigmentation of the organism, while the absence of melanin causes albinism.
Mitochondrions – microbodies possessing their own genome being similar to that of procaryotes. Mitochondrions are the energy centers of the cell. Using the energy of nutrients, they attach additional phosphate groups to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and turn it into the energy-saturated adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that is then used for all energy needs of the cell.
Обратное преобразование Фурье – в данной работе рассматривается как переход от образа F(р, q) в области пространственных частот к образу f(x, y) в пространственной области по правилу:
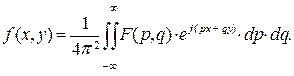
Органеллы – морфологические образования внутри клетки (ядро, митохондрии, хлоропласты и др.).
Перехваты Ранвье – зазоры между шванновскими клетками, покрывающими отростки нейронов многих животных. Шванновские клетки заполнены жироподобным изолирующим веществом – миелином, благодаря чему электрически изолируют длинные участки нервного волокна от окружающих тканей. Процесс перемещения нервного импульса вдоль нейрона заключается в перескоках процесса возбуждения от одного перехвата Ранвье к другому.
|
|
|
Преобразованная материя – это неживая материя, не способная к информационному формированию структур с передачей им наследственной информации молекулярного уровня, но получившая под воздействием разумных существ другие недоступные неживой материи свойства.
Прямое преобразование Фурье или просто преобразование Фурье (спектральный анализ) – в данной работе рассматривается как переход от образа f(x, y) в пространственной области к образу F(р, q) в области пространственных частот по правилу:
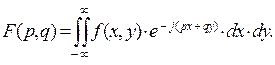
Ранвье перехваты – см. перехваты Ранвье.
Рибосомы – молекулярные агрегаты, которые на основе информации, представленной тройками (“триплетами”) нуклеотидов РНК, соединяют отдельные аминокислоты в цепочку, далее самостоятельно сворачивающуюся в молекулу белка. Рибосомы являются, пожалуй, наиболее сложными из известных молекулярных агрегатов. Они построены из нескольких типов белков и имеют внутренний каркас из нитей РНК различной длины. Такие РНК принято называть рибосомными и обозначать рРНК. В хроматине ядрышка находятся лишь многократно размноженные кластеры генов трёх наиболее длинных нитей рРНК с показателями седиментации (оседания в растворе) 5,8S; 18S и 28S. Кроме того,
Fourier inversion – here, considered as transition from the pattern F(р, q) in the domain of spatial frequencies to the pattern f(x, y) in the spatial domain, according to the rule:
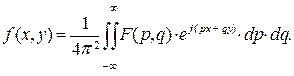
Organelles – morphological formations inside a cell (nucleus, mitochondrions, chloroplast, etc.).
Ranvier nodes – gaps between Schwann cells covering the neuron appendices of many animals. Schwann cells are filled with fatty insulating substance – myeline, due to which the long parts of the neural fiber are isolated from surrounding tissues. The process of the neural impulse movement along the neuron includes hopping of excitation process from one Ranvier node to another.
Transformed matter – lifeless matter being uncapable of information formation of structures with transfer the hereditary information of molecular level to them, but having acquired other properties, unavailable in the lifeless matter, under the influence of sentient beings.
|
|
|
Direct Fourier transform or simply Fourier transform (spectral analysis) – here, considered as transition from the pattern f(x, y) in the spatial domain to the pattern F(р, q) in the domain of spatial frequencies, according to the rule:
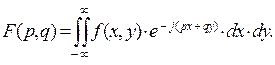
Nodes of Ranvier – see Ranvier nodes.
Ribosomes – molecular aggregates that, basing on the data presented by triplets of RNA nucleotides, bind the separate amino acids into a chain that is then reduced to a protein molecule. The ribosomes are, perhaps, the most complicated of the known molecular aggregates. They are composed of several types of proteins and have the inner frame of RNA threads of different length. Such RNAs are usually called ribosomal RNA and denoted as rRNA. The nucleus chromatine contains only multiply reproduced clusters of genes of three longest rRNA threads with sedimentation indications (sedimentation in the solution) 5,8S; 18S and 28S. Besides, the peripheral nucleus chromatine contains the genes 5S rRNA.
в периферийном хроматине ядра располагаются гены 5S рРНК.
Синапс – информационный контакт между двумя нейронами. Существуют электрические и химические синапсы. В подавляющем большинстве случаев нейробиолог сталкивается с химическими синапсами, представляющими собой две мембраны (принадлежащие разным нейронам), разделённые так называемой синаптической щелью. Сигнал переносится через синаптическую щель с помощью молекул вещества, называемого нейромедиатором.
Таламус – отдел мозга, содержащий много ядер и исключительно важный с точки зрения обработки сенсорной информации.
Терабит – единица количества информации, равная 1012 бит.
Фаза – параметр, определяющий координату мгновенного состояния процесса во времени, „привязывающий” его к другому мгновенью, принятому за начало отсчёта. Обычно фаза измеряется в долях периода процесса, например, в радианах или угловых градусах. Фотографическая эмульсия сама по себе не способна отсчитывать время (тем более, в диапазоне фемтосекунд, равных 10–15с, которыми измеряется период световой волны). Поэтому в голографическом способе регистрации изображений используется „привязка” фаз светового пучка, несущего полезное изображение („предметного пучка”), путём одновременного освещения той же светочувствительной поверхности вторым, строго упорядоченным пучком лучей, характеристики которого хорошо известны. Его называют „опорным пучком”. Картина интерференции предметного и опорного пучков во всех подробностях отражает опережение или отставание световой волны предметного пучка относительно опорного (фазы которого являются как бы началом отсчёта) в каждой точке светочувствительной поверхности. Именно эту картину интерференции и фиксирует фотослой.
|
|
|
Фракталы – область математики, использующая, в частности, пространства с дробной размерностью, и требующая больших объёмов вычислений. Исследование фракталовстало возможным только после появления электронных вычислительных машин.
Функция корреляции – в данной работе рассматривается как функция взаимной корреляции двух образов, например, образа f(x, y) и h(x, y):
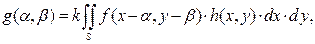 где S означает интегрирование по поверхности образа h(x, y).
где S означает интегрирование по поверхности образа h(x, y).
Synapse – information contact between two neurons. There are electrical and chemical synapses. In most cases the neurobiologist faces the chemical synapses that are two membranes (belonging to different neurons) separated by a so-called synaptic slot. The signal is transferred through a synaptic slot, using the molecules of the substance that is called neuromediator.
Thalamus – segment of the brain, containing many nuclei and being of great importance in terms of sensory information processing.
Terabit – unit of information, equalling to 1012 bits.
Phase – a parameter determining the coordinate of the instant state of the process in time, which “associates” it with another instant moment being taken as reference time. Usually, the phase is measured in fractions of the process period, e.g. in radians or arc (angular) degrees. The photoemulsion itself is unable to count the time (especially, in the range of femtoseconds equalling to 10–15 s, which measure the period of the light wave). Therefore, the holographic method of image recording uses the “associating” of the phases of the light beam carrying the available image (“object beam”) by means of concurrent illumination of the same photo-sensitive surface by another, strictly ordered, bundle of rays the characteristics of which are well known. It is called the “reference beam”. The picture of interference of the object and reference beams in all details reflects the advance or delay of the object beam light wave relative to the reference one (teh phases of which are considered the reference time) in each point of the photo-sensitive surface. It is precisely the picture of interference that is recorded by the film.
Fractals – field of mathematics, which uses, specifically, the spaces with fractals and requires large scope of computations. Analysis of fractals has become possible only with electronic computers.
Correlation function – here, considered as the function of mutual correlation of two patterns, e.g. the patterns f(x, y) and h(x, y):
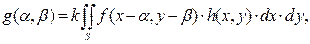
where S is integration on the surface of the pattern h(x, y).
Частотная плоскость голографического коррелятора является той областью вычислительного пространства, где входное изображение представлено в виде распределения сигналов пространственных частот, т.е. где каждой координате на плоскости соответствует определённая частота. Пространственные частоты, о которых здесь идёт речь, описывают характеристики изображений и измеряются числом штрихов или, точнее, пар линий (чёрной и белой, с синусоидальным профилем распределения поглощения света) на единицу длины. Не следует путать их с используемыми в электротехнике частотами колебаний, измеряемыми числом циклов в секунду.
|
|
|
Шванновские клетки – см. перехваты Ранвье.
Эндоплазматический ретикулум – мембранная система внутри клетки, на поверхностях которой закреплены молекулярные агрегаты и ферменты, обеспечивающие, в частности, синтез белков.
Эффекторные органы, системы – то же, что исполнительные органы и системы организма.
Frequency plane of holographic correlator is the region of computational space where the input image is represented as distribution of signals of spatial frequencies, i.e. a certain frequency corresponds to each coordinate on the plane. Here, spatial frequencies describe the characteristics of images and are measured by the number of strokes or, more exactly, by a pair of lines (black and white, with sinusoidal profile of the light absorption distribution) per unit length. They should not be confused with the vibration frequencies used in electrical engineering, which are measured by number of cycles per second.
Schwann cells – see Ranvier nodes.
Endoplasmic reticulum – membrane system inside the cell on the surfaces of which the molecular aggregates and enzymes enabling, particularly, the protein synthesis are fixed.
Effector organs, systems – the same as executive organs and systems of the organism.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-06-04; Просмотров: 536; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!