КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Lesson 2. Task 1. a)Differentiate between the following words
|
|
|
|
Task 1. a) Differentiate between the following words.

| These two adjectives are often confused. Economical refers to the cost of things. Something is economical if it provides good value for the amount of money you spend on it: It was more economical to hire the vehicles than to buy them. In its most common sense, economic only appears before nouns and its meaning is connected with the word economy and the subject of economics. It is connected with trade, industry and development of wealth of a country, an area or a society and is used mainly when describing their financial situation: We observe the region’s gradual economic recovery. The government initiated unpopular economic reforms. Less commonly, economic is used to mean “making enough profit” or as a synonym of economical to describe something that costs less money or uses less time, materials or effort. In these senses the word can appear before or after the noun. |
b) Explain the usage of the above adjectives in the following sentences.
1. Economic means “concerning economics”. 2. Economical is commonly used to mean “thrifty, avoiding waste”. 3. He’s rebuilding a solid economic base for the country’s future. 4. Small cars should be inexpensive to buy and economical to run. 5. The government’s economic policy is aimed at developing entrepreneurial culture. 6. It’s more economical to go by bus. 7. Many organizations must become larger if they are to remain economic. 8. The book gives some valuable ideas for economical housekeeping. 9. Though unpopular among citizens, Poland’s radical economic reforms achieved their goal. 10. Economical use of time may make you more productive. 11. The pace of economic growth is picking up. 12. She is a very economical cook. 13. Critics say that the new system may be more economic but will lead to a decline in programme quality. 14. Experts try to predict economic and social consequences of the forthcoming elections. 15. Economy goods are available in very large quantities at economical costs. 16. They gave up a large house for economic reasons. 17. If you don’t like to spend money unnecessarily, you may simply be economical, which means that you manage your finances wisely and avoid any unnecessary expenses. 18. Exports account for two-thirds of our economic activity. 19. We are looking for the most economical production methods. 20. He blamed the drop in sales on the global economic crisis.
Task 2. a) The words below often occur after “ECONOMIC”.
|
b) Which of the above word-combinations means:
1. Економічне диво;
2. економічний простір;
3. економічна грамотність;
4. економічна відсталість; економічне відставання;
5. економічна самостійність; економічне самозабезпечення;
6. економічний покупець, раціональний покупець (такий, що звертає увагу на ціну, якість, розмаїття товарів і простоту прийняття рішень щодо покупки);
7. господарник, хазяйський (дбайливий) керівник (керівник, який здійснює політику економічно ефективного управління, тобто досягнення максимально високих результатів при мінімальних ресурсних затратах);
8. економічний мігрант (той, хто переїжджає з однієї країни чи місцевості до іншої, аби покращити власний рівень життя); “ковбасний емігрант” (термін, який у колишньому Радянському Союзі вживався щодо емігрантів, які залишали країну не з політичних міркувань, а радше будучи невдоволеними власним рівнем життя через тотальний дефіцит, зокрема й продуктів харчування)?
с) Make up sentences with the above word combinations.
Task 3. Study the etymology of the word “ECONOMY”.
| Etymology: | ECONOMY | |
| 1) from Greek oikonomia (“household management”), based on oikos “house” + nemein “manage” via Latin → | ||
| 2) → French15th century économie (“management of material resources”) | ||
| Current senses of “economy” date from the 17th century. |
Task 4. a) The words below often occur with “ECONOMY”.
|
b) Which of the above word-combinations means:
1. (used especially in newspapers) a country whose economy is growing very fast;
2. a period when you try to spend less money than usual; an organized effort to reduce costs and avoid wasting money;
3. a temporary situation when businesses grow very fast, the prices of shares and homes, etc. rise and employment increases;
4. business activity or work that is done without the knowledge of the government or other officials so that people can avoid paying tax on the money they earn;
5. goods that are cheaper than normal goods usually because you are buying larger quantities;
6. most powerful countries of the West;
7. something that seems to save money but will really make you spend more;
8. the cheapest seats on a plane; the cheapest class of air travel; the part of a plane where people with the cheapest tickets sit?
c) In the sentences below find the English equivalents of the following terms:
· псевдо економія;
· тіньова економіка;
· товари за зниженою ціною;
· економ-клас, туристичний клас;
· західна держава; західна економіка;
· спекулятивна економіка (“економічна булька”);
· кампанія за економію; боротьба за режим економії;
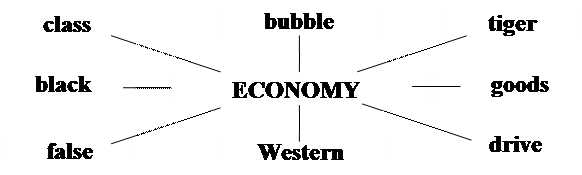
· економіка країн, які динамічно розвиваються; економіка країн-“тигрів” (таких як Сінгапур, Тайвань чи Південна Корея).
1. I always fly economy class.
2. They’re on an economy drive.
3. We were in a bubble economy.
4. Buying cheap tools is false economy.
5. Fares start from €597 for economy class.
6. Singapore’s tiger economy is still expanding steadily.
7. Economy goods are commonly sold through the Internet.
8. Experts believe the black economy is 40% the size of the official economy.
9. There are a lot of opinions about why the Western economy has flourished.
10. The central bank failed to put up interest rates and a bubble economy developed.
Task 5. a) Differentiate between the following word combinations.

| ECONOMIC GOODS | ECONOMY GOODS |
| Services or physical objects that can command a price in the market; anything that people want and are willing to pay a price for, rather than something that is available freely. Економічний товар; економічні блага. | Goods that are cheaper than normal goods usually because you are buying larger quantities. Дешеві товари. |
Task 6. a) Make up words using the productive word-building flexions (Table A) and the stems (Table B).
Table A
| re- | -ment | -th | -ity | -tion | -sion | -ness | -ship |
Table B
| 1.able; | 7.depress; | 13.advance; |
| 2.hard; | 8.oppress; | 14.develop; |
| 3.grow; | 9.prosper; | 15.stagnate; |
| 4.stable; | 10.achieve; | 16.backward; |
| 5.recess; | 11.difficult; | 17.transform; |
| 6.strong; | 12.novation; | 18.construction; |
b) Learn some other word-building patterns.
| To take off | → | take-off |
| (злетіти; швидко піднятися – про фондову кон’юнктуру або курс цінних паперів); | (швидкий підйом; швидке зростання); | |
| to swing up | → | upswing |
| (коливатися вгору); | (підвищення економічної кон’юнктури); | |
| to turn up | → | upturn |
| (піднімати(ся) вгору); | (підвищення; зростання (економіки, благополуччя, цін і т.п.); поліпшення (умов); початок економічного підйому); | |
| to turn down | → | downturn |
| (збавляти, зменшувати); | (економічний спад; спад ділової активності; зниження, зменшення). |
Task 7. Match items in column A with their antonyms in column B.
| A | B |
| 1. economic transformations; | a) economic lag; |
| 2. economic backwardness; | b) economic crisis; |
| 3. economic achievements; | c) economic upturn; |
| 4. economic development; | d) economic strength; |
| 5. economic difficulties; | e) economic progress; |
| 6. economic depression; | f) economic hardship; |
| 7. economic recovery; | g) economic successes; |
| 8. economic upswing; | h) economic oppression; |
| 9. economic stability; | i) economic renaissance; |
| 10. economic collapse; | j) economic reconstruction; |
Task 8. Open the brackets using the right word.
1. The Great Depression was a worldwide economic (downturn / upswing) starting in most places in 1929 and ending at different times in the 1930s or early 1940s for different countries.
2. The economic crisis of 1929-1933 was the largest and most severe economic (boom / depression) in the 20th century.
3. The Great Depression originated in the United States; historians most often attribute the start to the stock market (crash / take-off) of October 29, 1929, known as Black Tuesday.
4. The (development / depression) had devastating effects in virtually every country, rich and poor.
5. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with banking panics, and many (recessions / advancements) coincided with these panics.
6. The late-2000s (development / recession) has changed to a sharp drop in international trade, rising unemployment and slumping commodity prices.
7. The United States is in an economic (strength / crisis) that may already be the worst since the Great Depression.
8. One thing seems clear: the recent period of unparalleled economic (growth / oppression) and prosperity has come to an abrupt end in most of the world.
Task 9. a) What happens to an economy? Distribute the following word combinations into three groups according to their meaning:
A. Positive state of the economy – growth and progress;
B. Negative state of the economy – crisis and stagnation;
C. Recovery of the economy after a period of stagnation.
| 1. economic lag [læg] | 20. economic progress [`prəugres] / [`prα:gres] |
| 2. economic turn [tə:n] | 21. economic recovery [rı`kAv ə ri] |
| 3. economic crisis [`kraısıs] | 22. economic recession [rı`se∫ən] |
| 4. economic boom [bu:m] | 23. economic downturn [`dauntə:n] |
| 5. economic chaos [`keıOs] / [`keıα:s] | 24. economic successes |
| 6. economic upturn [`Aptə:n] | 25. economic stagnation |
| 7. economic growth [grəuθ] / [grouθ] | 26. economic prosperity |
| 8. economic revival [rı`vaıvəl] | 27. economic difficulties |
| 9. economic disaster [dı`zα:stə] / [dı`zæstər] | 28. economic renovation |
| 10. economic collapse [kə`læps] | 29. economic depression |
| 11. economic stability [stə`bıləti] | 30. economic oppression |
| 12. economic strength [streŋkθ] | 31. economic renaissance [rı`neısənts] / |
| 13. economic take-off | [ֽrenə`sα:nts] |
| 14. economic troubles | 32. economic development |
| 15. economic upswing [`Apswıŋ] | 33. economic advancement |
| 16. economic rebound [`ri:baund] | 34. economic achievements |
| 17. economic renewal [rı`nju:əl] | 35. economic backwardness |
| 18. economic advance | 36. economic reconstruction |
| 19. economic hardship | 37. economic transformations |
b) Match the terms in column A with the respective Ukrainian equivalents in column B.
| A | B |
| 1.economic lag 2.economic turn 3.economic chaos 4.economic boom 5.economic rebound 6.economic collapse 7.economic hardship 8.economic oppression 9.economic renaissance 10.economic backwardness | a) перелом в економічному розвитку; перехід до економічного підйому або падіння; b) економічна (господарська) відсталість; c) економічний крах; розвал економіки; d) перехідний період в економіці; e) відставання в економіці; f) економічне пригнічення; g) економічне відродження; h) економічні труднощі; i) економічний хаос; j) економічний бум; |
Task 10. Characterize the current state of Ukraine’s economy using appropriate terms from Task 9. Give your reasons.
Task 11. Read and translate the passage.
An economic indicator (or business indicator) is a statistic about the economy. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance.
Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries, such as unemployment, housing starts, Consumer Price Index (a measure for inflation), industrial production, bankruptcies, Gross Domestic Product, retail sales, stock market prices, and money supply changes. Economic indicators are primarily studied in a branch of macroeconomics called “business cycles”.
An economic boom occurs when real GDP grows faster than the trend rate of economic growth (in the UK, the trend rate is around 2.5% per year).
Vocabulary Notes:
1. Economic performance – економічний показник; економічний результат;
2. earnings report – рахунок прибутків та збитків (компанії);
3. housing start – початок будівництва житлового будинку;
4. Consumer Price Index – індекс споживчих цін; індекс цін на споживчі товари;
5. Gross Domestic Product – валовий внутрішній продукт;
6. stock market price – курс цінних паперів на фондовому ринку;
7. money supply – грошова маса.
Task 12. a) Match the terms in column A with their definitions in column B:
| A | B |
| 1. GDP (Gross Domestic Product) 2. GNP (Gross National Product) 3. recession 4. economic boom 5. consumer price index (CPI) | a)a sudden increase in trade and economic activity; a period of wealth and success; b)the total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country in one year; c)in the US and some other countries, a list of the prices of some ordinary goods and services which shows how much these prices change each month, used to measure the rate of inflation; d)a difficult period in the economy of a country or group of countries, when there is less trade and industrial activity than usual and more people are unemployed; a period of general economic decline, specifically decline in GDP for two or more consecutive quarters; e)the total value of all the goods and services produced within a nation in a particular period including the income from investments in foreign countries. Basically, it measures the value of goods and services that the country’s citizens produced regardless of their location; |
b) Translate into Ukrainian:
1. Tourism contributes about 5% of GDP.
2. GDP grew by 0.5 per cent in the fourth quarter.
3. Today farming produces only about 2-4% of GNP.
4. The economy is now officially in recession.
5. The manufacturing sector is recovering slowly from last year’s recession.
6. The economic boom was fuelled by easy credit.
7. The consumer price index rose 0.3 per cent in May.
Task 13. Think and answer.
1. When does an economic boom occur?
2. What can cause an economic downturn?
3. What makes economies fall into stagnation?
4. Whose responsibility is it to shake the country out of stagnation?
5. What is to be done in this country to do away with its economic lag?
Task 14. a) Make the difference between the following words.

| In many cases you can use any of these words: a rapid increase / growth / rise; · Growth is often uncountable and is used especially to talk about size: population growth is much more typical than “population increase / rise”. It is also more often used to talk about something positive: the growth in earnings / employment / demand. · Increase and rise are often used to talk about more negative things: an alarming increase / rise in violent crime. · Increase is more general than rise, used for things that increase by themselves or that are increased deliberately by somebody. · Rise is used more for things that happen to rise, rather than for deliberate increases. Price rises are seen from the point of view of the people buying things, not selling them. Businesses announce price increases; customers feel the effects of price increases / rises. |
b) Make up sentences with the above words.
Task 15. Practice reading the following words.
| 1. to accept [ək`sept] 2. actually [`ækt∫u ə li] 3. aware [ə`weə] 4. basic [`beısık] 5. to cause [kO:z] 6. command [kə`mα:nd] / [kə`mænd] 7. competing [kəm`pi:tıŋ] 8. concept [`kOnsept] / [`kα:nsept] 9. consistently [kən`sıst ə ntli] 10. to consume [kən`sju:m] / [kən`su:m] 11. consumption [kən`sAm p ∫ən] 12. deficits [`defəsıts] 13. to distribute [dı`strıbju:t] 74% / [`dıstrıbju:t] 26% 14. economy [ı`kOnəmi] / [ı`kα:nəmi] 15. entire [ın`ta ı ə] / [ın`taıər] 16. to figure (out) [`fıgə] / [`fıgjər] 17. foremost [`fO:məust] / [`fOr:moust] 18. generally [`Genər ə li] | 19. immediate [ı`mi:diət] 20. an increase [`ıŋkri:s] 21. to influence [`ıntfluənts] 22. to intensify [ın`tentsıfaı] 23. mechanism [`mekəֽnız ə m] 24. necessarily [ֽnesə`ser ə li] 25. recognition [ֽrekəg`nı∫ən] 26. to rivet [`rıvıt] / [`rıvət] 27. subsidizing [`sAbsıdaızıŋ] 28. to suggest [sə`Gest] / [səg`Gest] 29. supply [sə`plaı] 30. thus [ðAs] 31. tuition [tju`ı∫ən] / [tu`ı∫ən] 32. user [`ju:zə] / [`ju:zər] 33. various [`veəriəs] / [`veriəs] 34. widespread [`waıdspred] 35. within [wıð`ın] 36. worry [`wAri] |
Task 16. Read the text.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 608; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!