
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Addressing in IP-networks
|
|
|
|
Each computer in a network has addresses of three types:
- Physical (MAC-address) - the local address of node defined by technology by means of which the separate network is constructed in which this node is included. For the nodes included into local networks, it is MAC-address of the network adapter, for example, 11-A0-17-3D-BC-01. These addresses are appointed by producers of the equipment and are unique addresses as they are managed centralized. For all existing technologies of local networks MAC-address has a format of 6 bytes: the senior 3 bytes - the identifier of firm of the producer, and younger 3 bytes are appointed in a unique way by the producer.
- Network (IP address) - consisting of 4 bytes, for example, 109.26.17.100. This address is used at network level. It is appointed by the administrator during a configuration of computers and routers. The IP address consists of two parts: numbers of a network and node number. Number of a network can be chosen by the administrator randomly, or is appointed according to the recommendation of special division of Internet (Network Information Center, NIC). Node number in the IP protocol is appointed independently of the local address of node. The node can enter into some IP networks. In this case the node should have some IP addresses, on number of network links. Thus, the IP address characterizes not the separate computer or a router, but one network connection.
- Symbolical (DNS - name) - this address is appointed by the administrator and can consist of several parts - a name of the PC, a name of the organization, a domain name, for example - Genher, Maxx. Such address is used at application layer, for example, in the FTP or telnet protocols.
The stack of the TCP/IP protocols works with network (IP address) addresses. The IP address has length of 4 bytes and usually is written in the form of four numbers representing values of each byte in a decimal form, and divided by points, for example: 128.10.2.30 - a traditional decimal form of representation of the address, 10000000 00001010 00000010 00011110 - a binary form of representation of the same address.
The IP address consists of two parts: address of a network and number of a host (node). As a host we understand one computer connected to a network. There are 5 classes of IP addresses. These classes differ from each other by number of the bits which are taken to the address of a network and the address of a host in a network. These five classes are shown in Figure 5.2.7.
What part of the address belongs to network number and what to node number, is defined by values of the first bits of the address:
- If the address begins with 0, a network is of class A, and number of a network occupies one byte, other 3 bytes are interpreted as node number in a network. Networks of a class A have numbers in a range from 1 to 126. (Number 0 isn't used, and number 127 is reserved for the special purposes).
- If the first two bits of the address are equal 10, the network belongs to the class B and is a network of averages. In class B network address and the address of node take 16 bits each other, that is 2 bytes.
- If the address begins with sequence 110, it is a network of a class of C. The address of a network takes 24 bits, and node address - 8 bits.
- If the address begins with sequence 1110, it is the address of a class D and designates the special, group address - multicast. If in a packet as the address of destination is the class D address, all nodes to which this address is given should receive such packet.
- If the address begins with sequence 11110, it is the class E, it is reserved for future applications.
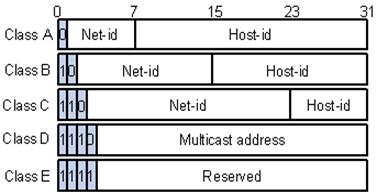
Figure 5.2.7 - Classes of IP-addresses
Ranges of numbers of IP-networks are given in the table 5.2.1:
Table 5.2.1 – Classes and ranges of IP-addresses
| Classes | Minimum address | Maximum address |
| A | 1.0.0.0 | 126.0.0.0 |
| B | 128.0.0.0 | 191.255.0.0 |
| C | 192.0.1.0 | 223.255.255.0 |
| D | 224.0.0.0 | 239.255.255.255 |
| E | 240.0.0.0 | 247.255.255.255 |
In the IP protocol there are some agreements on special interpretation of IP addresses:
- if IP-address consists only of binary zeroes, it designates the address of that node which has generated this packet;
- if in the field of number of a network is 0, by default it is considered that this node belongs to the same network, as node which sent a packet;
- if all bits of the IP address are equal 1, the packet with such destination address should be send to all nodes in the same network, as a source of this packet. Such sending is called as the limited broadcasting message.
- if in an address field of destination are only 1, the packet having such address, is sent to all nodes of a network with set number. Such sending is called as the broadcasting message (broadcast);
- the address 127.0.0.1 is reserved for the feedback organization when testing work of the software of node without real sending of a packet on a network. This address has the name loopback.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 537; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!