
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Protocol of internetwork interaction of IP. Fragmentation of packets
|
|
|
|
The basis of a stack of the TCP/IP protocols is made by the protocol of internetwork interaction - Internet Protocol (IP).
The main functions of the IP protocol are:
- definition of a packet which is base concept and data transmission unit of the Internet network also IP packet is called the datagram;
- definition of the address scheme which is used in the Internet network;
- data transmission between channel level (level of access to a network) and transport level (in other words multiplexing of transport packets (datagrams) in frames of channel level);
- routing of packets on a network, i.e. transfer of packets from one gateway to another for the purpose of packet transfer to the recipient;
- fragmentation and assembly from fragments of packets of transport level.
The IP packet consists of header and the data field. The format of a packet is presented in Figure 5.2.8.
The header of a packet has the following fields:
- IP version field - specifies the IP protocol version. Now version 4 is everywhere used and transition to version 6 is prepared.
- (HLEN) - occupies 4 bits and specifies value of length of the header, measured in 32-bit words. Usually the header has length of 20 bytes (five 32-bit words) and has value 5 (0101).
- TYPE OF SERVICE is occupied by 1 byte and sets priority of a packet and a type of criterion of a choice of a route. The first three bits of this field form a subfield of a priority of a packet (PRECEDENCE). The priority can have values from 0 (a normal packet) to 7 (a packet of operating information). The established bit of D (delay) says that the route should be chosen for minimization of a delay of delivery of this packet, T bit - for maximizing capacity, and R bits - for maximizing reliability of delivery.
- TOTAL LENGTH - occupies 2 bytes and specifies total length of a packet taking into account header and the data field.
- IDENTIFICATION - occupies 2 bytes and it is used for recognition of the packets formed by fragmentation of an initial packet. All fragments should have identical value of this field.
- FLAGS - occupies 3 bits, it indicates possibility of fragmentation of a packet (the established bit of Do not Fragment - DF - forbids a router to fragmentize this packet), and also, whether this packet is an intermediate or last fragment of an initial packet (the established bit of More Fragments - MF says that the packet transfers an intermediate fragment).
- FRAGMENTATION OFFSET - occupies 13 bits, it is used for the showing in bytes of shift of the data field of this packet from the beginning of the general data field of the initial packet subjected to fragmentation. It is used at assembly/dismantling of fragments of packets by their transfers between networks with various sizes of the maximum length of a packet.
- TIME TO LIVE - occupies 1 byte and specifies a deadline during which the packet can move on a network. At the expiration of time of life the packet is cancelled.
- IP PROTOCOL- occupies 1 byte and specifies, what protocol of the higher level belongs a packet (for example, it can be TCP, UDP or RIP protocols).
|
|
|
- The checksum (HEADER CHECKSUM) - occupies 2 bytes, it is calculated on whole header.
- SOURCE IP ADDRESS and DESTINATION IP ADDRESS - have length - 32 bits.
- IP OPTIONS is unessential and it is used usually only when debugging network.
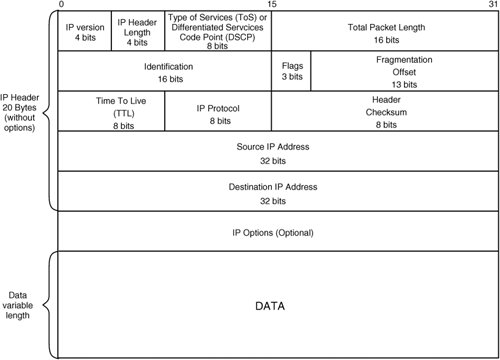
Figure 5.2.8 - Format of IP packet
The maximum length of the data field of a packet is limited to word length of the field defining this size, and is 65535 bytes, however during transfer on networks of various type the length of a packet is chosen taking into account the maximum length of a packet of the protocol of the bottom level that transfer IP packets. For example, if it is Ethernet frames, packets are chosen with maximum length of 1500 bytes which are placed in data field of Ethernet.
Protocols of transport level (TCP or UDP protocols) using network level for sending of packets, consider that the maximum size of the data field of an IP packet is equal 65535 and consequently can transfer to him the message of such length for transportation through a network. In the majority of types of local and global networks such concept as the maximum size of the data field of a frame or a packet in which the IP protocol should encapsulate its packet. This size is usually called the maximum unit of transportation - Maximum Transfer Unit, MTU. The Ethernet networks have value of MTU equal to 1500 bytes, the FDDI network - 4096 bytes, and the X.25 networks work with MTU in 128 bytes more often. To functions of IP level belong splitting of too long message into shorter packets with creation of the corresponding manage fields, the necessary fragments for the subsequent assembly enters into the initial message. This process is called as fragmentation.
Work of the IP protocol on fragmentation of packets in hosts and routers is shown in Fig. 5.2.9.
Let a computer connected to the network, which has an MTU of 4096 bytes, for example, the network FDDI. On admission to the IP-level computer a message from the transport layer the size of 5600 bytes, the IP protocol divides it into two IP-packet, setting the first sign of packet fragmentation and packet by assigning a unique identifier, such as 486.The first package size of the displacement field is equal to 0, while the second - in 2800. A sign of fragmentation in the second packet is zero, indicating that this is the last piece of the package. The total value of IP-packet is 2800 20 (the size of the header IP), that is2820 bytes, which fits in the frame data FDDI.
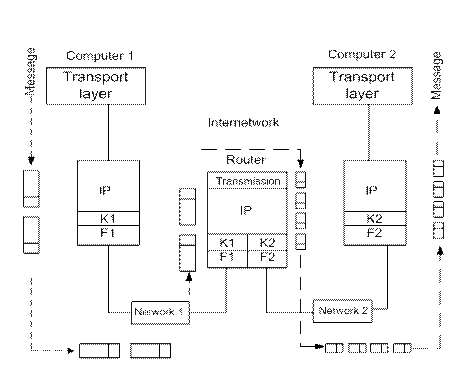
Figure 5.2.9 - Fragmentation of IP-packets for transmission between networks with different maximum packet size
K1 and F1 are channel and physical layers of the network 1, K2 аnd F2 are channel and physical layers of the network 2. Next, computer 1 transmits these packets to the link layer K1, and then to the physical layer of F1, which sends them to the router connected to this network.
The router sees the network address, which arrived two packages must be passed to the network 2, which has a smaller value of MTU, equal to 1500, is Ethernet network. The router retrieves the fragment transport from each package FDDI, and it still divides in half to fit each piece of data in the frame Ethernet. Then it creates new packages IP, each of which has a length of 1400 + 20 = 1420 bytes, which is less than 1500 bytes, so they are normally placed in the data field personnel Ethernet. As a result, the computer 2 via Ethernet comes to four IP-packets with a common identifier 486, which allows the protocol IP, running on the computer 2, the right to get the original message. If the package did not arrive in the order in which you have been sent, then the offset will specify the correct order of their association. With the arrival of the first fragment packet destination node starts a timer, which determines the maximum waiting time of arrival other fragments of the package. If the timer expires before the arrival of the last fragment, all received by this time discarded packet fragments, and the node that sent the original packet is sent an error message with protocol ICMP.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 1316; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!