
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Key principles. Requirements to Content of the protocol
|
|
|
|
PURPOSE OF THE WORK
REQUIREMENTS TO CONTENT OF THE PROTOCOL
LABORATORY ASSIGNMENTS
HOME ASSIGNMENTS
CHECK-UP QUESTIONS
2.3.1. What functions are fulfilled in node points of a network?
2.3.2. What purpose are switches used in data networks for?
2.3.3. Explain the arrangement and the principle of the switch operation.
2.3.4. In which ways is the switching function realized in switches?
2.3.5. What are «Virtual networks» (network groups)? For what purposes are they created?
2.3.6. What features do intellectual switches have?
2.3.7. Explain the difference of MDI and MDI-X ports.
2.3.8. What is the assignment of ports indication?
2.3.9. How is the set-up of the intellectual switch executed?
2.4.1 Study key principles.
2.4.2 Prepare answers to check-up questions.
2.4.3 Result the generalized scheme of the switch construction, architectures of switching elements in the report of laboratory work.
2.5.1 Enter A system from the computer connected to the switch through COM-port, and install connection by means of tip program (tip com1).
2.5.2 In the laboratory task five computers will be involved. In an initial status all of them belong to one network. Make sure that there are links between all computers by means of ping command. Receive IP - addresses of computers from a teacher.
2.5.3 Divide available quantity of computers into virtual networks as follows:
1. Computers 1 and 2 belong to VLAN2
2. Computers 3 and 4 belong to VLAN3
3. Computer 5 is the common server, and belongs to both VLANs.
2.5.4 Make sure that there are links within each VLAN, there is no link between computers from different VLANs, and there is link of computers from both VLANs with the common server. Numbers of computers connection ports to the switch from a teacher.
2.5.5 Set up port 5 for the operation in a full-duplex mode with the control of a full-duplex flow.
2.5.6 Set up port 6 for the operation in a half-duplex mode with the control of a half-duplex flow.
2.5.7 Show the results of your work to the teacher then restore manufacturing switch settings.
2.6.1 The name of laboratory work.
2.6.2 Purpose of the work.
2.6.3 Results of home assignments.
2.6.4 Short description of the work done.
2.6.5 Conclusions about the work done.
2.6.6 Date, the signature of a student, the remark of a teacher.
LABORATORY WORK №3
THEME: ACTIVE NETWORK EQUIPMENT BRIDGES-ROUTERS
Studying principles of the bridge and router operation, the network screen and acquiring practical skills of main modes operation and maintenance.
Practically in all cases, whether it is one computer or set of computers interconnected in a local area network, there is necessity to use external wide-area networks to apply to Internet resources and to exchange information with other local area networks. To do this, such active network equipment as modems, bridges and routers, network screens are used.
As it is known, modems are intended to convert digital signals into analogue ones with their successive transmission across telecommunication lines, and also to restore an initial digital signal at reception. As there is a variety of different media through which data exchange is performed, many types of modems are created. Depending on coordination of data transfer, modems can be divided into on two big categories:
- Synchronous;
- Asynchronous.
Asynchronous modems can lose to 25 % time for transmission and reception negotiation. Synchronous modems use accessible link speed more effective and provide faster communications than asynchronous modems.
Remote bridge. It is the bridge intended for data transfer of one local segment through a wide-area network to other local segment. It builds the table of MAC-ADDRESSES on the basis of the traffic passing through it and on the basis of it makes solution – to transfer frames to a remote segment or not. If usual bridges do not almost find applications today the remote ones are applied rather often. They do not need to be configurated and this property proves to be very useful at remote offices where there is no qualified serving staff.
Bridge. It works at a data link level. It’s a medium of frames transmission on the basis of the physical address between two segments using, as a rule, identical protocols of physical and link levels. Thus, bridges provide the extension of a network, which does not demand program modifications on workstations operating in local segments. All servers working in segments use unique addresses when interacting and do not have to distinguish obviously servers of an own segment and servers of other segments. Bridges care of it. The bridge should know, which addresses of the data link level (MAC-ADDRESS) belong to each segment to define which frames to skip, and which ones to return to its segment. For this purpose it has a scheme of operation with addresses. If some segments are linked by several bridges, each bridge should have the table of passing paths through bridges as well. To provide the operation in conditions when frames arrive faster, than they can be transferred, the bridge should have sufficient volume of the buffer.
Unlike the switch the router supports protocols not only physical and data link levels, but also network one. Network layer protocols provide collection of the information about topology of connections between logical networks and construction of tables of routing with paths to all logical networks known to a router. (Methods of paths definition, optimal after the given criteria are considered in following section). On the basis of routing tables the router fulfils transmission of packages from one network to another and can make of solution for choice of the most rational path of an information transfer in difficult topology (topology with closed loops).
It has some physical interfaces, including, various network technologies, and can also provide economic access to territorial networks as it isolates the local traffic more effectively. If the router is capable to support some protocols of a network layer, it is named a multiprotocol router.
The range of functional tasks of a router also includes buffering, filtering and a fragmentation of packages. Therefore it is a typical computer with one or even several processors and with complicated software of real time. Since each package is handled by a router separately, its productivity considerably loses to productivity of the switch. There can be a bottleneck, hindering the traffic passing if it is set at the kernel level.
The server computer can fulfill the router role in the case is the network layer of its operating system supports transmission of packages. Universal OS of Unix or Windows include the program unit providing setup of the mode “router”.
Association of two remote local area networks by means of two Zyxel Prestige 128L modems (see Figure 3.2.1).
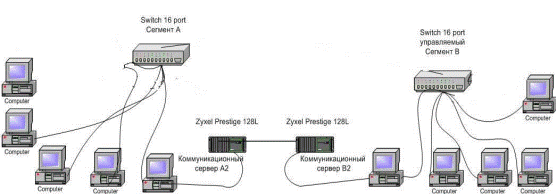
Figure 3.2.1 – Example of a remote local area network
Common description of Zyxel Prestige 128L bridge-router. Prestige 128L Zyxel model of a company-manufacturer represents the bridge-router for the physical dedicated symmetric digital line. Having united in itself the function of a router, a bridge and a network screen, Prestige 128L possesses variety of functions which provide flexible network solutions for the access to the Internet, interconnections of local area networks of large corporations subsidiaries and connection of remote individual users.
Prestige 128L functionality includes:
- Support of protocols of TCP/IP and Novell IPX stacks and transparent translation of protocols (in a bridge mode).
- Connection at 64 Kbit/with or 128 Kbit/s speed on a cooper pair of 0,4 mm section for a distance to 5,5 km.
- 2B1Q line code.
- The spectrum of a signal to 80 kHz.
- Support of the data link level protocol of «point-point» PPP connection.
- Static and dynamic assignment of IP-addresses.
- Network Address Translation, NAT.
- Routing according to RIP-2 protocol (the advanced version of RIP protocol).
- The network screen filtering packages according to different tags (type of the protocol of higher level, number of the destination port of the transport layer etc.).
In Figure 3.2.2 there is the back panel of the device.
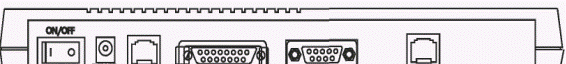

Figure 3.2.2 – The back panel of the device
Inscriptions on the panel have the following sense:
- ON/OFF – the power supply toggle-switch;
- POWER – the power supply plug;
- ETHERNET – the plug for connection of a local area network of Ethernet 10Base-T standard (telecommunication RJ-45 plug);
- AUI – the plug for connection of a local area network of Ethernet 10Base-5 standard;
- TERMINAL – the plug for connection of the control terminal (the Console port RS-232);
- LINE – the plug for a dedicated line (WAN port).
Prestige front panel looks like the following (Figure 3.2.3).
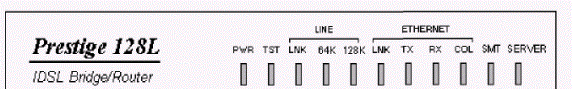

Figure 3.2.3 – The front panel of the device
Names and descriptions of light-emitting diodes of the Prestige front panel:
- PWR – the given light-emitting diode lights up at once, as soon as Prestige is connected to the power supply and switches in position «I» (on).
- TST – the light-emitting diode blinks, if Prestige functions properly.
- Line: LNK – this light-emitting diode shows, that the leased line (WAN port) is connected, to Prestige and it is initialized successfully.
- 64К and 128К – the light-emitting diode 64К shows, that the speed of a line is 64К. A light-emitting diode 128К shows, that the speed of a line is 128К.
- Ethernet: LNK – the given light-emitting diode shows, that Prestige is connected to a LAN through Ethernet interface.
- ТХ and RX – light-emitting diodes (Transmit) of transmission and reception (Receive) show the LAN traffic presence.
- COL – shows collision presence by transmission on a LAN.
- SMT – shows, that Prestige it is connected to the control terminal through RS-232 port.
- SERVER – shows, that Prestige sets synchronization to the leased line.
Setup of Zyxel Prestige 128L bridge-router. Before start device setup, it is necessary to start program Hyper Terminal on the controlling terminal ( see the start path in Figure 3.2.4).
Figure 3.2.4 – The start path program Hyper Terminal
Further it is necessary to enter setup of Hyper Terminal program (see Figure 3.2.5)
To set a connection name (any quantity of characters).
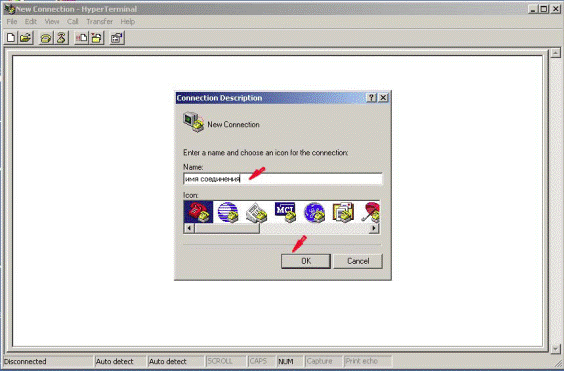
Figure 3.2.5 – Hyper Terminal start program
Select COM1 port from the dropping out list “Connect using:”
Select from the dropping out list “Bits per second:» speed of connection – 9600kb/s.
Select from the dropping out list “Flow control”: flow management – Hardware.
After execution of above mentioned operations we get to a window of link with SMT (System maintenance terminal) a-firmware to handle Zyxel Prestige 128L.
At power up Prestige will make some internal tests and initializes IDSL line. After initialization Prestige asks to press the Enter key to continue as follows in the Figure 3.2.6.
When pressing ENTER, Prestige will display registration and ask to type the password, as shown in Figure 3.2.7. The password is 1234. Press Enter after password input.
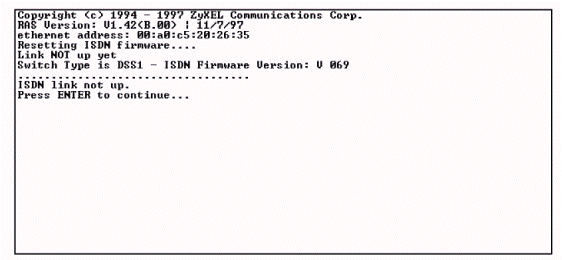
Figure 3.2.6 – Hyper Terminal start program

Figure 3.2.7 – Hyper Terminal start program
Then you will get to the main menu (Fig. 3.2.8).
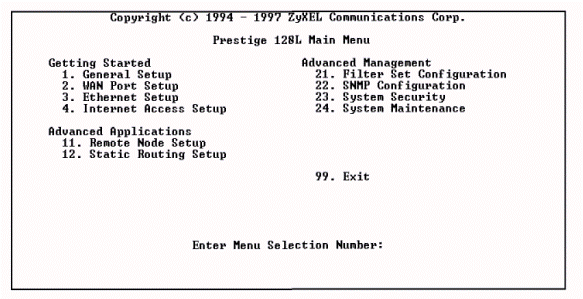
Figure 3.2.8 – Prestige main menu
As at first we set up the bridge for so to operate in a bridge mode we will be interested only in settings up concerning data link and physical levels.
When the modem is set up in a router mode for operation we will not be interested only in setting up concerning data link and physical levels, but also in network one.
Let's use 1, 2, 3 and 11 items of the main menu (see Table 3.2.1).
Table 3.2.1 – Main SMT menu
| N | Manu name | Description |
| General Setup | Customization of the common parameters and inclusion of Routing for certain protocols and transmission on the bridge. | |
| WAN Port Setup | IDSL configuration | |
| Ethernet Setup | Ethernet configuration | |
| Remote Node Setup | Customization of a remote node for connection of Local area networks, including connection to the Internet. Prestige supports four remote nodes. |
| Attention!!! All operations generated in a terminal window are instantly transferred to the modem, i.e. you «are» in the modem operating system already. It»understands» only pressing the keys of thekeyboard. Further familiarize attentively with rules of input of commands and data. - Transition to other menu.To transit to the necessary submenu, enter its number under the current menu and press the Enter key - Return to the previous choice.To return to the previous menu, press Escape key. A unique exception is the main menu where the unique way of return is to input 99 for an output from SMT. - Cursor movement.Being in the menu, to transit to the next field, press the Enter key (carriage return). To move in fields it is possible to use keys with arrows Upand Downfor the transition to the previous and following choices accordingly. - Information input.There are two types of filled to be fields. It is necessary to enter the demanded information in the field of the first type. The field of the second type gives the possibility of a choice from the several preinstalled values. In the second case, exhaustive search of possible values is carried out by means of a key of SPACE BARblank. - Mandatory fields.Some SMT fields are important for configuration Prestige. In the given fields the sign «?» is put down initially, showing that the information should be entered without failure before storing of the menu. - N/A Fields. There is N/A in some SMT. It means, that the given option is unavailable. - Configuration storage.It is possible to store the configuration by pressing the ENTERkey when a message appears: Press ENTERto confirm or ESC to cancel: Storing of screen data, returns as a rule to the previous menu. |
Menu 1 – General Setup. The given menu contains management and common system information. Enter 1 to the main menu for access to menu 1 – «General Setup» (Fig. 3.2.9).

Figure 3.2.9 – Menu 1 – «General Setup»
1 System Name –Select a descriptive name for Prestige (for the identification purposes), Jet1. The name can include to 8 alphanumeric characters. Blanks in the name are not allowed. The dash sign «–» and sign to underline «_» are allowed.
2 Location – Enter geographical Prestige layout (to 31 characters), e.g., Odessa_ONAT.
3 Contact Person Name – Enter the person’s name, who is responsible for Prestige (to 8 characters), e.g., Ivan_Ivanych. Location fields and Contact Person are not mandatory.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 495; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!