
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Solution the system ( 7.1) by method of Jordan-Gauss
|
|
|
|
The goal of this method is to lead an augmented matrix of system 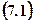 to diagonal form. It’s easy to make by using a table.
to diagonal form. It’s easy to make by using a table.
Table 1. The first 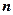 columns of the table are columns of the coefficients of the unknowns, next column is a column of constant terms. And the last column (check column) is column whose elements are equal to the sums of elements of each rows.
columns of the table are columns of the coefficients of the unknowns, next column is a column of constant terms. And the last column (check column) is column whose elements are equal to the sums of elements of each rows.

|  
| … | 
| 
| 
|
Table 2. (and all subsequent) Consecutively choose diagonal elements distinct from zero. We will call this element a key element and row and column at the intersection of which is the key element, key row and column respectively. Rewrite the key row without changes. All elements of key column we will replace by the rule of rectangular (see §6).
Remark: 1) All zeros rows are deleting;
2) Equal or proportional rows, except for one, are deleting;
3) Row in a form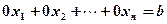 , where
, where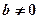 , shows that the system has no solution.
, shows that the system has no solution.
Using the last table we rewrite a system in traditional form. If the system has been reduced to a diagonal form, we obtain a unique solution. If the number of equations less then number of unknowns, the system has free unknowns and an infinite set of solutions. In this case we will leave basic unknowns (whose coefficients were key elements) on the left-hand side of equations and other unknowns (free unknowns) we will transfer to the right-hand side of equations.
It gives us a general solution of the system. By assigning any values to the free unknowns, we will get particular solution. Among particular solution we select basic solution in which free unknowns are assigned to zeros.
| ## | ENGLISH | RUSSIAN | |
| 1. | augmented | расширенный | |
| 2. | compatible (incompatible) | совместная (несовместная) | |
| 3. | infinite | бесконечный | |
| 4. | general | общий | |
| 5. | particular | частный | |
| 6. | basic | базисный | |
| 7. | discard | отбросить |
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-15; Просмотров: 360; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!