
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Economic profit in TRTC-model and in MRMC-model
|
|
|
|
Free Entry
In the long run the entry of new competition – or the exist of unprofitable firms from the industry, to go into other trades – is one of the most important aspects of competition and is thus one of the four characteristics of the P-competitive structure.
Free entry means that new companies can set up in business to compete with established companies whenever the new competitors feel that the profits are high enough to justify the investment. This is, first and foremost, a legal condition. That is, in a "perfectly competitive" market there are no government restrictions on the entry of new competition. This legal status is often called by the French phrase "laissez faire", meaning "let them make (whatever they want to make for sale)". But it could also be a practical condition. For example, if no-one could set up in business without enormous capital investments, that might prove an effective limit on the entry of new competition – especially if, for some reason, the capital cannot be raised by borrowing or issuing shares.
 According to graphical interpretation maximum Economic Profit occurs at output level Q*, the greatest vertical distance between TR and TC. On the Figure 2 the quantity Q* can provide such level of profit.
According to graphical interpretation maximum Economic Profit occurs at output level Q*, the greatest vertical distance between TR and TC. On the Figure 2 the quantity Q* can provide such level of profit.
a and b points are break-even points – as under corresponding quantity there is neither profit nor losses (TR=TC).
Then, the areas before a - break-even point and after b - break-even point shows losses of producer.
The angle of slope of TR line and the angle of slope TC curve are equal under Q*. That means that coefficients ΔTC/ΔQ=ΔTR/ΔQ. But as it is the same that MR=MC, the rule of profit maximization for perfect competitor is: MC=MR=P.
Another way to illustrate it is to use average and marginal costs graph.
On this graph economic profit is shown as an EP area.
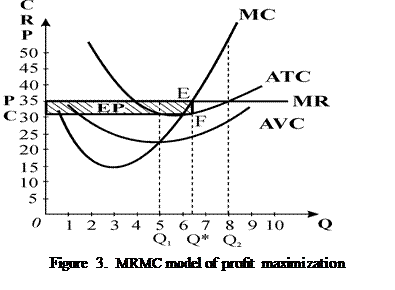 The point of MR and MC intersection shows the optimal level of output Q* under definite price P.
The point of MR and MC intersection shows the optimal level of output Q* under definite price P.
And as the firm is “price taker” in this case it will regulate the output according to profit maximization rule all the time. But the result can vary because of the costs level.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 1310; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!