
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
American regional features
|
|
|
|
British regional features
• Northern /u/ in cut, much, love
• Scottish /u/ in soot, took, book
• /a/ in bad, bath /hw/ in which, where /x/ in Loch Ness, Loch Lomond
• /q/ in licht trilled /r/ in murder
• Irish /r/ in all positions: river
• clear /1/ in people, milk
All the regional types of British accents are characterized by a narrower (compared with RP) pitch range which gives the effect of more levelled-out, monotonous speech. The most common pitch patterns are level and rising-falling. The former is especially common for Irish speech, while the latter is a feature of Scottish intonation. In big cities, such as Edinburgh in Scotland and Cardiff in Wales, educated people show a specific combination of Gaelic (Celtic by origin) and English intonation patterns when they start a tone group with a very high rise-falling tone and then drop to a mid-level continuation. Russian learners of English also do the same in reading an English text but manage to drop their pitch level still lower, to the very bottom of the pitch range, then rise again. The fine perturbations of pitch show, as we can see, habitual norms in speech melody. RP is unique in having a very wide pitch range and smoothly, gradually descending pitch pattern, at least in reading and formal speech. Regional speech is described as monotone because of its narrow pitch range.
Southern a*-vocalization after a vowel, as in river (Americans say that the second r is gone with the wind);
Monophthongization of the diphthong [ai] which is unmarked before a voiced consonant as in side, tide [sa:d, ta.d] but is socially marked before a voiceless:
light, sight [lat, sat]; Southern drawl in that [osaat]; /i/ in men, ten [mm, tin].
Other regional features are stereotyped in American spelling by their citizens:
New York open [a]: N00 Yawk Tawk;
Boston vocalised r in Pahk the cah in Hahvahdyahd;
Afro-American dental plosives instead of dental fricatives: dese, dose, Itinkso. However the most recent quantitative research based on telephone survey (called Telsur) for "The Phonological Atlas of North America" completed by William Labov at the University of Pennsylvania gives an overview of the U.S.A. map of regional accents today. The data corroborated the basic division into North, Midland and South previously made on the basis of lexical differences along the East Atlantic coast. It also showed that the West is not only a residual area in which northern, midland and southern features mix and disappear but also an area with a specifically advanced stage of cot — caught merger (70% of the lexicon as compared to 21% in Pennsylvania, for instance).
The most astounding finding is that the vowel systems of the North and the South are developing in different directions, and that the pronunciation of vowels in big cities is more different today than it was fifty years ago. The two trends are called the Northern Cities Shift and the Southern Vowel Shift because there are principal rotations that caused the systems' shifts. The North has retained the initial tense long high and mid vowels, while the South has started laxing them.
In the Northern Cities Shift (NCS) the rotation starts with raising the /ге/vowel in cad, then the fronting of/o/ in codto its position, followed by lowering and fronting of/o:/ in cawed, then backing of /л/ in cud and /e/ in Red, the final stage is lowering and backing of/i/ in kid. The NCS spreads as far as the boundary between the North and North Midland and stops at that (see Figure 12).

Figure 12. The Northern Cities Shift
The Southern Vowel Shift (SVS) involves the system of long vowels and diphthongs at the first stages: first /ai/ is pronounced as /a/ in hide, the next step is /ei/ in made moving backward and lowering, the next stages 3 and 4 involve tensing of short vowels which results in short /i/ and long /v./ exchanging their positions in kid and keyed, the sound /e/ in Ked occupying the position of /ei/ in made; long tense back vowels, /u:/ in cooed and the diphthong /ou/ in code are fronting, while long tense vowels of cord and card are gliding to a closer and more backward position (see Figure 13).
SVS spreads gradually over the South and partly over South Midlands. The most salient regional distinctive features reflect the first stages of the shifts:
• Northern [ae] becomes more front and high in cat, bat, carry;
• [e] becomes more back and lowered, i.e. centralized: less, nest;
• the Southern monophthong [a] in side, tide and sight, light, as well as [i] before nasals in men, ten have been mentioned already (see above).
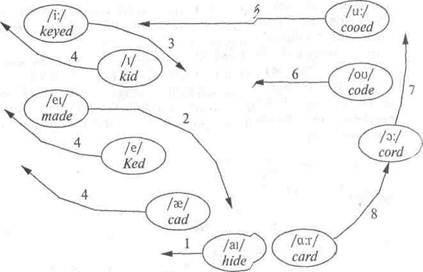
Figure 13. The Southed Shifi
General Canadian (Gen Can) shares a few features with the North of the U.S.A., such as raising of /ae/ in cad and such a characteristic of Northern Midland and the West as the cot — caught merger.
General Australian (Gen Aus) shares a few features with London popular speech (Cockney). The most salient vowel characteristic is /ai/ in day, take. Within the country they also distinguish, besides Gen Aus, Cultivated Australian and Broad Australian. Cultivated Australian is closer to RP than General Australian. Broad Australian is applied to a heavy local accent, most often of people in the countryside, the part of the land often referred to as "the Bush".
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 1233; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!