
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Topic: elementary dynamic links
|
|
|
|
SUMMARY OF LECTURE № 9


1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
Logarithmic characteristics of the open-loop systems are used in the synthesis of automatic control systems. The transfer function of the open-loop system is presented as a set of elementary dynamic links.

Classification of links is produced, by the form of the transfer function. For this, consider open-loop system of automatic control. We will use early adopted signs/

Here: 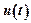 – input value;
– input value;  – output value;
– output value;  – disturbance action.
– disturbance action.
Are known to the properties of any of the automatic control can be described using the static and dynamic characteristics.
Recall that the static characteristics of real objects are nonlinear.
In general, they have the form:
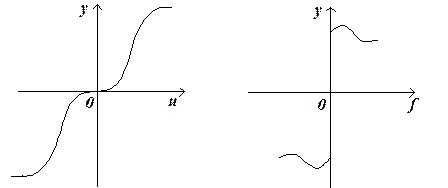
Fig. 9.1 – Static characteristics
To dynamic characteristics they include time and frequency characteristics.
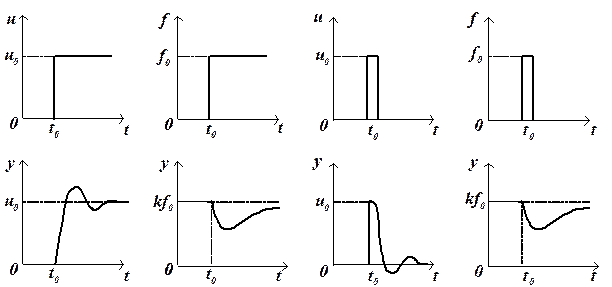
| а) reaction to a stepped controlling action | b) reaction to a stepped disturbance action | c) reaction to a impulse controlling action | d) reaction to impulse disturbance action |
Fig. 9.2 – Time domain characteristics
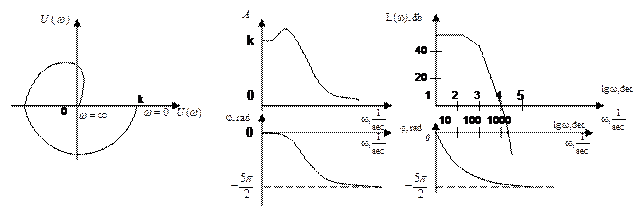
 Fig. 9.3 – Frequency response
Fig. 9.3 – Frequency response
Nonlinear characteristics are linearized. In this case, they use linearization attributes:
1. Accuracy –  .
.
2. The operating point.
3. Range of the input signal variation 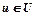 .
.
4. Range of the output signal variation 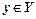 .
.
5. The structure of the equation.
6. Evaluative values of the coefficients – 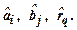
7. The time scale – 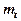 .
.
The structure of the linear mathematical model in a general form is as follows:

Important note: the initial conditions are nonzero: 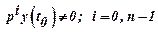
Make changes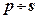 , move on to the operator equation:
, move on to the operator equation:

Introduce the signs:
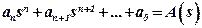 ;
;
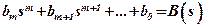 ;
;
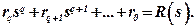
Given this, we get:
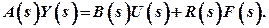
Therefore:
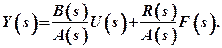
Redenote:
 и
и 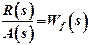
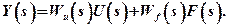
We expand polynomials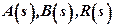 , using the theorem of Bezout (remember it from the school course!), get:
, using the theorem of Bezout (remember it from the school course!), get:
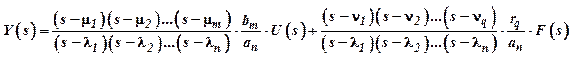
Here:
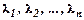 – zeros of a polynomial
– zeros of a polynomial 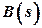 ;
;
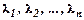 – polynomial’s pole
– polynomial’s pole 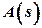 ;
;
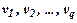 – zeros of a polynomial
– zeros of a polynomial 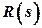 ;
;
Let 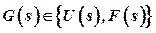 , then
, then 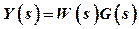
In general, the transfer function 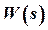 can be represented as follows:
can be represented as follows:
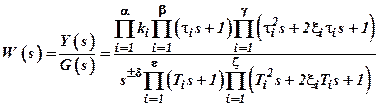 ;
;
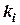 – the transient coefficient;
– the transient coefficient; 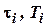 – time constants;
– time constants; 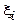 – degree of damping.
– degree of damping.
Using this expression, write down the transfer functions of the elementary links:
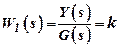 - lagless links;
- lagless links;
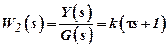 – force links of the 1st order;
– force links of the 1st order;
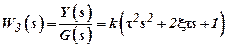 – force links of the 2nd order;
– force links of the 2nd order;
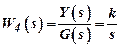 – integrating links;
– integrating links;
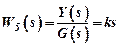 – differentiator;
– differentiator;
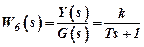 – aperiodic links;
– aperiodic links;
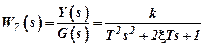 – oscillatory links.
– oscillatory links.
2. CALCULATION CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ELEMENTARY DYNAMIC LINKS
Consider the lagless element:
On the example of the two-stroke potentiometric sensor we design the calculation characteristics of the lagless element.
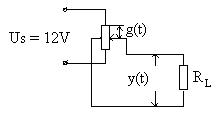 Fig. 9.4 – Scheme of a two-stroke potentiometric sensor
Fig. 9.4 – Scheme of a two-stroke potentiometric sensor
|
Let 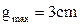 , then , then 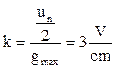
|
Using this information, we can construct a static, time and frequency responses.
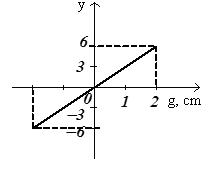
Fig. 9.5 – Static characteristic
Note: the model is fundamentally poorer then original!
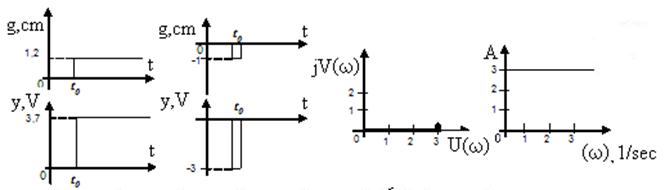
а) reaction to a stepped b) reaction to impulse c) Nyquist diagram d) AFC
controlling action disturbnse action
Fig. 9.6 – Dynamic characteristics
Please, try to set the calculated static and dynamic
characteristics for the rest of the transfer functions of the elementary
 links!
links!
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-13; Просмотров: 532; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!