
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
The two types of PDGFRs
|
|
|
|
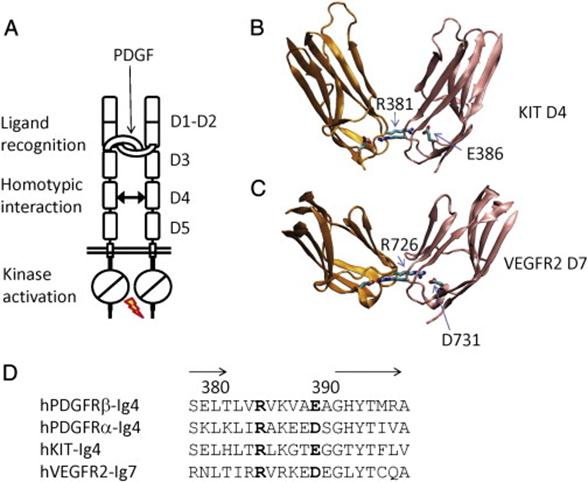
The extracellular region of the receptor consists of five immunoglobulin-like domains while the intracellular part is a tyrosine kinase domain. The ligand-binding sites are located to the three first immunoglobulin-like domains.
Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGF-R) are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of PDGF family. PDGF-R are important for regulation of cell proliferation, cellular differentiation, cell growth, development and many diseases including cancer. There are two forms of the PDGF-R, alpha and beta each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor is bound, PDGF-R form homo- or heterodimers.
The association between propeptide and mature growth factor domain in PDGF-A.
(B) Two residues in mature PDGF-A, W120 and N134, play organizing roles in the association of the propeptide with the mature domain.
(C) Ribbon model of the propeptide-loaded PDGF-A dimer, with the mature domains colored in green and cyan, whereas the propeptides colored in pink and magenta.
(D) The hydrophobic interaction pattern between PDGF-A propeptide and mature domain. The backbone of the propeptide is shown as ribbons, and the backbone of the mature domains is shown as coils. The interacting side chains are shown as sticks, colored according to their backbones.
(E) Sequence comparison between all four types of PDGFs shows that the two helices used in the interactions with mature growth factors domains are a common feature, and the hydrophobic residues for interactions are preserved.
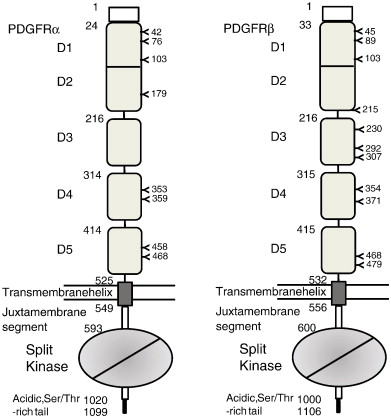
The starting numbers of the specific domains/segments in the coding sequences are marked left to the boundaries. Shown are all numbers for human PDGFRs. The positions of N-linked glycosylation are also marked. The lipid bilayer is represented by two straight lines. Note that D1 and D2 are integral modules, and the intracellular kinase domain is a split domain with an insert between N-terminal and C-terminal lobes.
PDGF-CC specifically interacts with PDGFR-αα and -αβ, but not with -ββ, and thereby resembles PDGF-AB.
PDGF-DD binds to PDGFR-ββ with high affinity, and to PDGFR-αβ to a markedly lower extent and is therefore regarded as PDGFR-ββ specific.
PDGF-AA binds only to PDGFR-αα, while PDGF-BB is the only PDGF that can bind all three receptor combinations with high affinity.
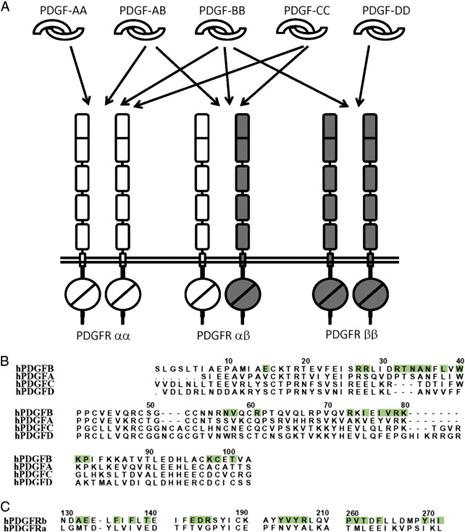
The specificity in PDGF:PDGFR recognition.
(A) The biochemically defined interactions between PDGF homodimers/heterodimers and the PDGFR homodimers/heterodimers. Note that there is no proof for pre-associated PDGFR dimers; therefore, the receptor dimers are just a result of ligand-driven clustering.
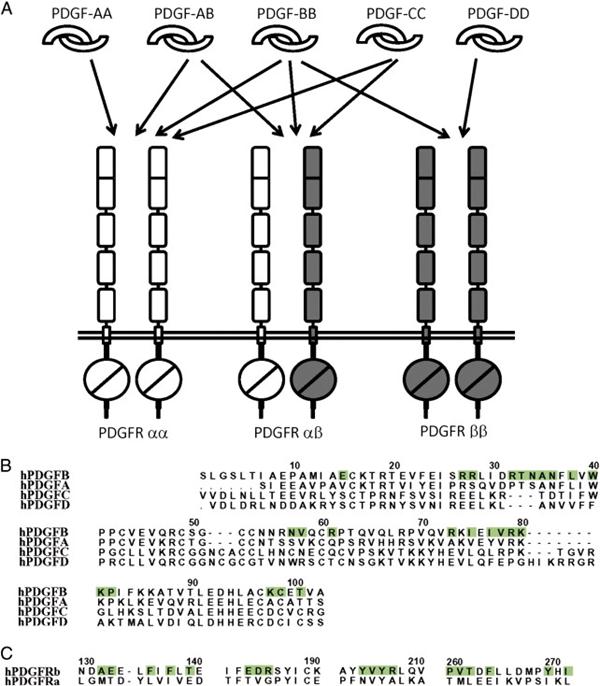
(B) Sequence comparison of PDGFs with the residues involved in PDGF-B:PDGFRβ interaction highlighted. This comparison shows that the hydrophobic residues used for the core of the PDGF:PDGFR interface are preserved, but the hydrophilic residues at the periphery of the interface have significant variations.
(C) Sequence comparison between the PDGFRs fragments used at the interface, with the PDGFRβ residues in ligand recognition highlighted. This comparison also shows that the hydrophobic nature of the ligand-recognition surface is preserved.
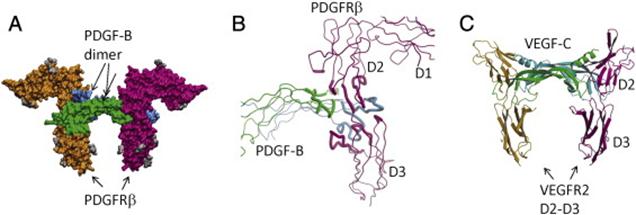
PDGF:PDGFR recognition.
(A) The surface model of the PDGF-B in complex with the D1–D3 domains of PDGFRβ. PDGF-B protomers are colored in green and cyan, and PDGFRβ is colored in magenta and orange. The N-linked glycans are colored in gray.
(B) The recognition involves the dimeric seam of PDGF-B, extending two arms clamping the D2–D3 boundary of PDGFRβ. Both PDGF-B and PDGFRβ are shown as tubes, and the interacting parts are shown as thicker tubes than the rest.
(C) PDGF:PDGFR recognition is reminiscent of VEGF:VEGFR recognition. Shown is the ribbon model of VEGF-C in complex with the D2–D3 domains of VEGFR2. Despite roughly equivalent structural elements involved, there are major differences including the interface chemistry, the domain orientations, and the length of the L1 loops.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-14; Просмотров: 465; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!