
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Подгонка параметров электронных элементов
|
|
|
|
Лазерная обработка пленок
Пленки тонкие 100 нм …. 10 мкм
Толстые 10 мкм ….100 мкм
¾ размерная обработка (подстройка элементов)
¾ поверхностное испарение (для пьезоэлементов)
¾ рекристаллизация и отжиг(подгонка сопротивления без разрушения пленки)
Пленки Cr, Al, Ag, th = 500 Ǻ; q = 7…9 Вт/см2; τи = 0.3 … 3 10-7 с
lmin ≈ 1,4 мкм для τи = 10-7 с.
Подгонка пленочных резисторов испарением. (до 0,01% от Rном)
Незащищенную пленку можно нагреть и окислить, тем самым уменьшить сопротивление до ±1% от Rном
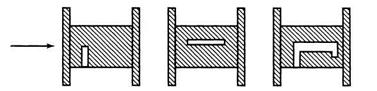
а б с
Варианты лазерной подгонки резисторов:
а — Y-рез; б — Х-рез; с — L-рез
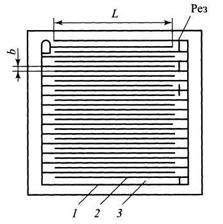
Щелевой пленочный конденсатор:
1 — левая обкладка; 2 — правая обкладка; 3 — подложка-диэлектрик

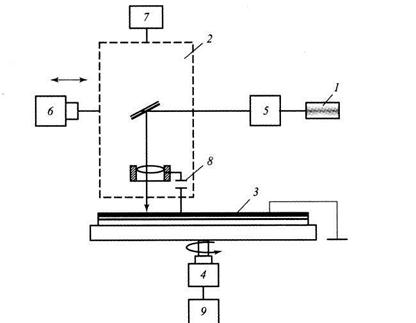
Рис. 10.5. Схема установки для лазерной цифровой записи
Металлическое покрытие толщиной 5... 10 нм. Шаг дорожки 1,5 …2,0 мкм, (погрешность 0,05 …0,1 мкм) Поперечный размер питов 0,4 … 0,6 мкм. Мощность лазера до 40 мВт, частота следования импульсов до 30 Мгц,
Наинизшим порогом записи обладает висмут.
Laser Micro - focus on Fine Solutions
Precision down to the µm range
Fine welding, fine cutting and material ablation
The increasing miniaturization in electronics, semiconductor manufacturing and medical technology is opening up unique opportunities for the use of lasers. Especially in areas in which traditional material processing meets its limitations, lasers, with their excellent focusing and the resulting small heating zone, are finding new opportunities for employment. The great flexibility and reproducibility of the laser and its ease of automation, render it ideal it for use in the areas of automotive technology and of tool and mold making. And even more unusual materials like gold, diamonds or titanium can be processed with high quality. This advantage is especially appreciated in the areas of jewelry and dental technology.
Opto-electronics
Lasers are provided with many opportunities for use in the manufacture of opto-electronic components. Because of the minimal warming zone, the small diameter of the welding spot, and the adjustable energy, the laser is a manufacturing tool of choice.
The spectrum of applications ranges from spot welding of plug and multiplexer units, to welding seams on gas-proof housing covers with modern galvanometer-controlled deflector-head technology. Extremely fine cutting, in the range of a few µm is also feasible. Rofin/Baasel Lasertech have optimized part of their product range especially for the manufacture of opto-electronic components.
Lithium Batteries
This application requires a helium-proof welded seam. Welding with laser and galvanometer scanner has clear advantages over micro-plasma welding, for instance. Laser processing has hardly any thermal effect on the material, so destruction of the insulator is also avoided
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 564; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!