
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Find these African countries on the map and name their capitals
|
|
|
|
Africa
Read and translate this text
Practise reading the following words
Words and word combinations to the text
Lesson 11 Africa
Make up all possible types of questions to the text 10.9
10.11 Speak on:
1. geographical position of Asia
2. its flora and fauna
3. population
4. agriculture and industry
10.12 Get ready to speak about any Asian country you like. Make use the following:
1. Geographical position (be located, lie off, longitude, latitude, size, be separated from, be washed by, etc.)
2. Climate and relief (damp, humid, mild, continental, temperature, volcano, plateau, mountain, etc.)
3. Economy (branches of industry, produce, manufacturing, be rich in, agriculture, etc.)
4. State system (constitutional monarchy, empire, parliament, federation, election, consist of, etc.)
to embrace – охватывать
confluence – слияние
to crack – раскалывать(ся), давать трещину
shift – сдвиг, смещение
fault – разлом
trench – узкая продольная длина, впадина
lava – лава
to pour out – извергаться
freshwater lake – пресноводное озеро
hydrology – гидрология
to affect – влиять, воздействовать
astride – по обе стороны
to modify – изменять(ся)
big-game – крупный зверь
to roam – бродить
savanna – саванна
reserve – заповедник
suppler – поставщик
diamonds – алмазы
cobalt – кобальт
copper – медь
chromium – хром
platinum – платина
bauxite – боксит
manganese – марганец
tin – олово
processing plants – перерабатывающие заводы
developing nations – развивающиеся страны
Cape of Good Hope, Madagascar, Sahara, Sub-Saharan Africa, Mountain Kenya, Mountain Kilimanjaro, Syria, Mozambique, Nyasa, Tanganyika, Nile, Congo, Benguela Current, Mozambique Current, Uganda, Tansania, South Africa, Zaire, Zambia
Africa is the second largest continent on Earth, embracing one fifth of its land area and occupying 30,217,000 square kilometers, some 2 percent of which is inland water. The continent is bounded on the north by the Mediterranean Sea, on the west by the Atlantic Ocean, and on the south by the confluence of the Atlantic and the Indian oceans off the Cape of Good Hope. There are a number of islands associated with Africa, the largest of those, lying to the southeast, is Madagascar.
Africa’s great area includes a variety of landforms and climates. The vast desert lands of the Sahara separate North Africa from the continent – central lands and southern Africa, which together are called Sub-Saharan Africa. Much of Africa’s interior consists of plateaus and hilly uplands. In southern and eastern Africa, high mountains surround the plateaus near the coast. The plateaus in eastern Africa were long ago cracked by a shift in the land that created a huge fault. When the land shifted, a series of deep trenches formed between the cracked surfaces. Lava poured out and built up higher plateaus, sometimes topped volcanic peaks. Mountain Kenya and Mountain Kilimanjaro in eastern Africa are two of the volcanic peaks formed when the land shifted.
The series of trenches extend all the way from Syria in the Middle East to Mozambique in the southern Africa. Together the trenches form the Great Rift Valley. In some places, the trenches are about 60 km wide and 450 m deep. Two of Africa’s largest lakes, Nyasa and Tanganyika, lie in Great Rift trenches. Lake Tanganyika, 676 km long, is the longest freshwater lake in the world. Africa’s hydrology is dominated by the Nile and the Congo river basins, which together drain nearly one-fourth of the continent’s area.
Africa’s climate is greatly affected by its position astride the equator. Temperatures are high for most of the year in the northern and the southern tropical zones, but they are modified by elevation in the mountains and by the influence of ocean currents on the coasts – e.g., the cooling Benguela Current (southwest) and the warming Mozambique Current (southeast). Only 6 percent of the African continent is arable while nearly one-fourth is forested or wooded. The continent is well known for its wide variety of animal life. Big-game animals are found roaming the savanna regions. Some of the world’s finest national parks were established as game reserves in Kenya, Uganga, Tansania, South Africa, and other countries.
African countries have abundant minerals resources. They possess some of the world’s richest deposits of certain minerals, gold and diamonds are among the most important. Zaire and Zambia supply most of the cobalt and copper used throughout the world. Other minerals important to the modern nations include chromium, platinum, bauxite, iron ore, tin and manganese, oil. Many countries have not yet developed the technology to use these resources efficiently. Africa still has few manufacturing industries and the governments try to set up more processing plants. Economists classify all the countries of Africa, except South Africa as developing nations. But there are definite signs of the economic growth of the African nations.
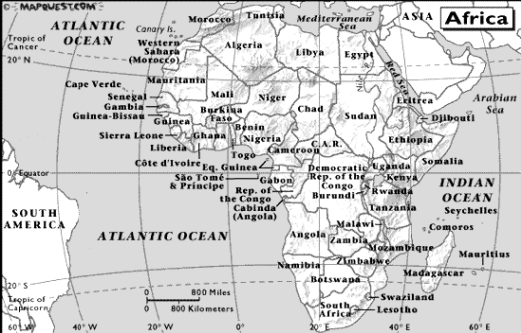
Алжир – Algeria – Algiers
Ангола – Angola – Luanda
Бенин – Benin –
Ботсвана – Botswana –
Буркина-Фасо – Burkina Faso –
Бурунди – Burundi –
Габон – Gabon –
Гамбия – Gambia –
Ганна – Ghana –
Гвинея – Guinea –
Гвинея-Бисау – Guinea-Bissau –
Джибути – Djibouti –
Египет – Egypt –
Заир – Zaire –
Замбия – Zambia –
Западная Сахара – Western Sahara –
Зимбабве – Zimbabwe –
Камерун – Cameroon –
Кабо-Верде – Cape Verde –
Кения – Kenya –
Коморские острова – Comoros –
Конго – Congo –
Кот-д’Ивуар – Côte d’Ivoire –
Либерия – Liberia –
Ливия – Libya –
Лесото – Lesotho –
Маврикий – Mauritius –
Мавритания – Mauritania –
Мадагаскар – Madagascar –
Марокко – Morocco –
Малави – Malawi –
Мали – Mali –
Мозамбик – Mozambique –
Намибия – Namibia –
Нигер – Niger –
Нигерия – Nigeria –
Руанда – Rwanda –
Сан-Томе и Принсипи – Sāo Tomé & Principe –
Свазиленд – Swaziland –
Сейшельские острова – Seychelles –
Сенегал – Senegal –
Сомали – Somalia –
Судан – Sudan –
Сьерра-Леоне – Sierra Leone –
Танзания – Tanzania –
Того – Togo –
Тунис – Tunisia –
Уганда – Uganda –
Центральная Африка – Central African Republic –
Чад – Chad –
Экватор. Гвинея – Equatorial Guinea–
Эритрея – Eritrea –
Эфиопия – Ethiopia –
Южная Африка – South Africa –
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-01-03; Просмотров: 434; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!