
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Screen Features
|
|
|
|
| Size | Desktop screens are usually 15 - 23 in. by diagonal measurement. (This is how TV screens are measured, too.) Larger sizes are available, at a significantly higher cost. Prices are dropping, but you still have to have the space for a bigger screen. | |||||||||||||||
| Resolution | Determines how clear and detailed the image is. Pictures on a screen are made up of tiny dots. 1 dot on screen = 1 pixel (from "picture element") The more pixels per inch, the clearer and more detailed the picture. One measure of this is the dot pitch, the distance between the dots that make up the picture on the screen. However, different manufacturers measure differently. Most measure from dot center to the center of the nearest same color dot. Some measure from the center of a dot to an imaginary vertical line through the center of the nearest dot of the same color, giving a smaller number for the same dots as the previous method. Some monitors use skinny rectangles instead of dots and so must use a different method altogether. So, dot pitch has become less useful as a measure of monitor quality. A dot pitch of.28 is very common and.26 should be good for nearly all purposes, however it is measured. | |||||||||||||||
| Refresh Rate | CRT screens: How often the picture is redrawn on the monitor. If the rate is low, the picture will appear to flicker. Flicker is not only annoying but also causes eye strain and nausea. So, a high refresh rate is desirable. 60 times per second is tolerable at low resolutions for most people. 75 times per second or more is better and is necessary for high resolutions. (Does not apply to LCD screens) | |||||||||||||||
| Type | Old types = CGA, EGA, VGA
New systems now come with super VGA with a picture size of 800 x 600 pixels (as a minimum) and 16 million colors | |||||||||||||||
| Color |  The number of colors displayed can vary from 16 to 256 to 64 thousand to 16.7 million. The more colors, the smoother graphics appear, especially photos.
The number of colors available actually depends more on the video card used and on how much memory is devoted to the display. It takes 8 bits to describe 1 pixel when using 256 colors. It takes 24 bits per pixel when using 16 million colors. So a LOT of memory is needed to get those millions of colors. Video cards now come with extra memory chips on them to help handle the load. The number of colors displayed can vary from 16 to 256 to 64 thousand to 16.7 million. The more colors, the smoother graphics appear, especially photos.
The number of colors available actually depends more on the video card used and on how much memory is devoted to the display. It takes 8 bits to describe 1 pixel when using 256 colors. It takes 24 bits per pixel when using 16 million colors. So a LOT of memory is needed to get those millions of colors. Video cards now come with extra memory chips on them to help handle the load.
| |||||||||||||||
| Reverse video | example: 
| |||||||||||||||
| Cursor/ Pointer | The symbol showing where you are working on the screen, like: 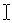 and and 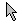 In the olden days of just DOS, there were few choices for the cursor. The invention of the blinking cursor was a tremendous event. Really! Under Windows there are a huge number of basic to fantasy cursors to choose from. In the olden days of just DOS, there were few choices for the cursor. The invention of the blinking cursor was a tremendous event. Really! Under Windows there are a huge number of basic to fantasy cursors to choose from.
| |||||||||||||||
| Scrolling | Moving the lines displayed on the screen up or down one line at a time |
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 398; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!