
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Application Management Lifecycle
|
|
|
|
Operational Models
An Operational Model is the specification of the operational environment in which the application will eventually run when it goes live. This will be used during testing and transition phases to simulate and evaluate the live environment. This is a way of ensuring that the application can be sized correctly and the required environmental conditions can be documented and understood by all. The Operational Model should be defined and used in testing during the Service Design and Service Transition phases respectively (see Service Design and Service Transition publications).
The lifecycle followed to develop and manage applications has been referred to by many names, including the Software Lifecycle (SLC) and Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). These are generally used by Applications Development teams and their Project Managers to define their involvement in designing, building, testing, deploying and supporting applications. Examples of these approaches are Structured Systems Analysis and Design Methodology (SSADM), Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM), Rapid Application Development (RAD), etc.
ITIL is primarily interested in the overall management of applications as part of IT service s, whether they are developed in-house or purchased from a third party. For this reason, the term Application Management Lifecycle has been used, as it implies a more holistic view.
This should not replace the SDLC, which is still a valid approach used by developers, especially by third-party software companies. However, it does mean that there should be greater alignment between the development view of application s and the ‘live’ management of those applications.
This is more difficult in large-scale purchased applications, such as e-mail, since the developers do not typically interact individually with their application’s user s. However, the basic lifecycle still holds true in that the application needs requirement s, design, customization, operation and deployment. Optimization is achieved through better management, improvements to customization and upgrades.
The Application Management Lifecycle is illustrated as follows:
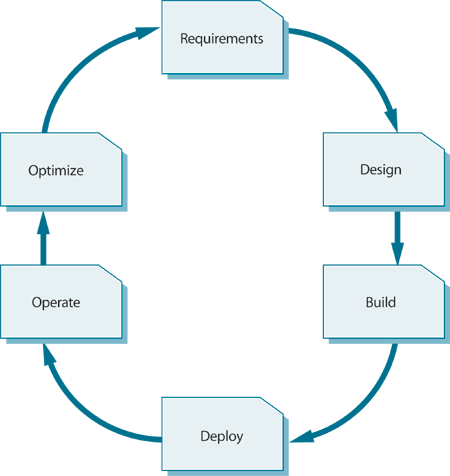
Figure 6.5 Application Management Lifecycle
ITSM processes and Applications Development processes have to be aligned as part of the overall strategy of delivering IT services in support of the business.
Applications Development and Operations are part of the same overall lifecycle and both should be involved at all stages, although their level of involvement will vary depending on the stage of the lifecycle.
Relationship between the Application Management and Service Management Lifecycle s
The Application Management Lifecycle should not be seen as an alternative to the Service Management Lifecycle. Applications are part of services and have to be managed as such. Nevertheless, application s are a unique blend of technology and functionality and this requires a specialized focus at each stage of the Service Management Lifecycle.
Each stage of the Application Management Lifecycle has its own specific set of objective s, activities, deliverable s and dedicated teams. Each stage also has a clear responsibility to ensure that their outputs match up to the specific objectives of the Service Management Lifecycle. Different aspects of Application Management are covered in detail in each of the ITIL publications, as follows:
- Service Strategy: Defines the overall architecture of applications and infrastructure. This will include defining the criteria for developing in-house, outsourcing development, or purchasing and customizing applications. Service Strategy will also assist in defining the Service Portfolio (including applications) which also includes information about the Return on Investment of applications and the services they support. Thus high-level requirement s are set during this phase.
- Service Design: Helps to establish requirements for functionality and manageability of applications and works with Development teams to ensure that they meet these objectives. Service Design covers most of the Requirements phase and is involved during the Build phase of the Application Management Lifecycle.
- Service Transition: Application Development and Management teams are involved in testing and validating what has been built and deploying it operationally.
- Service Operation: This covers the Operate phase of the Application Management Lifecycle. These processes and structures are discussed in detail in this publication.
- Continual Service Improvement: Covers the Optimize phase of the Application Management Lifecycle. Continual Service Improvement measures the quality and relevance of applications in operation and provides recommendations on how to improve applications if there is a clear Return on Investment for doing so.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 525; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!