
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Combined functions
|
|
|
|
Organizational structure variables
Hybrid organization structures
It is unlikely that IT Operations Management will be structured using only one type of organization structure. Most organizations use a technical specialization, with some additional activity - or process-based departments.
The type of structure used and the exact combination of technical specialization, activity-based and process -based departments will depend on a number of organizational variables.
The exact criteria chosen and the resulting organizational structure will depend on a number of variables, which may include:
- The nature of the business
- Business requirement s and expectations
- The technological and technical architecture
- The stability of the current IT Infrastructure and the availability of skills to manage it
- The governance of the organization (i.e. the way in which authority is assigned and decisions are made – as well as any formal governance framework that is used, such as COBIT or SOX)
- The legislative, political and socio-economic environment of the organization
- The type and level of skills available to the organization
- The size, age and maturity of the organization
- The management style of the organization
- Dependence on IT for business-critical activities, processes and function s
- The way in which IT participates in the value network (i.e. the way IT interacts with the business and its partners, supplier s and customer s)
- The relationship between IT and its vendors.
For a more complete description of how these factors influence organizational design, please refer to the ‘Organizational Development’ section of the Service Strategy publication.
One last type of organization should be discussed. This structure incorporates IT Operations, Technical and Application Management departments into a single structure. This is sometimes the case where all groups are co-located in a single data centre. Here, the Data Centre Manager takes responsibility for all Technical, Application and IT Operations Management.
This type of organization structure is illustrated in Figure 6.10.
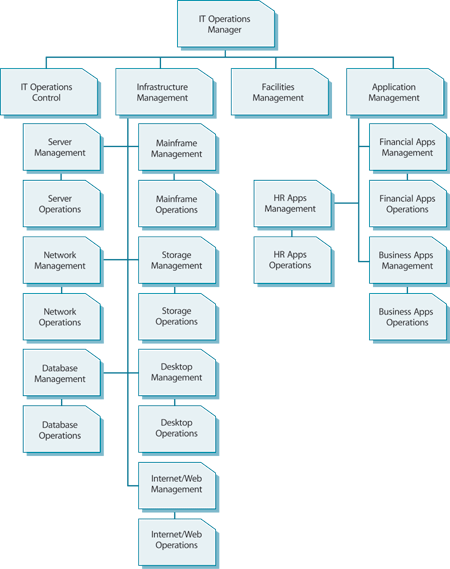
Figure 6.10 Centralized IT Operations, Technical and Application Management structure
In this structure, IT Operations Management is responsible for the Technical and Application Management function s, which in turn are responsible for managing their own operational activities. Each department is able to delegate some of these activities to the Operations Control department.
The advantages of this organization structure are:
- There is greater consistency and control between the more tactical and more operational Technical Management activities
- It is easier to enforce the performance standard s and technical architecture s that are created in Service Design, since the people who were involved in design are managing the activities of the people who are executing those activities
- As there is no duplication between location or activity, this structure is often more cost-effective.
The disadvantage of this organization structure is:
- The scope of this structure makes it very difficult to manage effectively in large organizations or in organizations with multiple Data Centres.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 456; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!