
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
EXERCISES. Answer the following questions:
|
|
|
|
Answer the following questions:
1. Why does the media relate to economic data and the implications for the individuals and businesses?
2. What aspects of the economy's operation are statistics available to show?
3. What do statistics show?
4. What are sources of data on the economy in the UK?
5. What is the GNP?
6. Why should statistics be treated with some caution?
/NIT 7. HOW TO MEASURE ECONOMIC ACTIVITY
I — 4-789

 II. Suggest Ukrainian equivalents:
II. Suggest Ukrainian equivalents:
Important items; economic data; a prime example; the adverse effects; householders; statistics are available to show; available resources of labour; at full capacity; key industries; key data; the value of a nation's output; the Treasury; building societies; they should be treated with some caution; trend (find it in 3 sentences)
III. Replace the parts in italics by synonyms:
• a large number of
• the operation of the world's major economies
• headlines relate to
• the implications for individuals and businesses
• by highlighting the adverse effects on businesses
• these resources are being under-utilised
• figures give an indicator of
• changes have great significance for
• numerous
• additionally
• economic statistics are presented in many forms.
IV Fill in the gaps with the words and expressions from the text.
1. The headlines in newspapers often_____ economic data and___ for individuals and
businesses.
2. The statistics tell us whether the economy is working______ using all or nearly all,_____
resources of labour, machinery and other factors of production or whether these
resources are being____.
3. Economists use the term____ to describe the value of a nation's output during a year.
4. Although these statistics can be_____ in assisting managers, they should_____ with____
when___ the future trend of the economy.
V Economic Performance. The sentences below are extracts from a newspaper report on economic performance. Choose the correct explanation for the words in bold from a, b, c.
1. Retail sales continued to grow in March, confirming the trend begun in the pre-
Christmas boom, according to Paul Figg, of IMA Consultants.
a) sales in the shops
b) sales of clothes
c) factory prices
2. Consumer demand will help economic growth, forecast at 4% for the year.
a) price rises
b) jobs
c) total national income
3. Higher consumption of imported goods could result in a worsening trade deficit.
a) decline in trade
b) negative balance of value of exports and imports
c) inflation
4. Uncertainty in the industrial job market is creating a lack of consumer confidence.
a) employment in manufacturing
b) spending in the shops
c) feel-good factor in ordinary people
5. Manufacturing output is lower and exports have almost halved.
a) building new factories
b) industrial production
c) employment in factories
6. There is a problem of excessive stock levels which means there are no new jobs.
a) goods waiting to be sold
b) strikes
c) high prices
42 PART I. ECONOMICS
There is an economic slowdown in most major export markets.
a) countries which normally export to this country
b) countries which normally buy from us
c) Stock Exchanges.
VI. Financial Performance. Match the words in the box with these definitions.

|
1. The condition of not being able to pay one's debts.
2. To cancel out a bad effect or condition.
3. A list of investments owned by a bank or investor.
4. To put at risk or in danger.
5. Funds put up by the shareholders of a company.
6. Property or equipment owned by a company.
7. A promise or guarantee.
8. Controlling, according to rules and regulations.
9. To wear away or disintegrate.
10. The difference between income and costs which causes a minus figure.
11. Origin or starting point.
12. The amount of money coming into the company in a financial year.
VII. Explain the following in English:
Media; householders; mortgages; trade balance; wages; salary; building societies.
■:T 7. HOW TO MEASURE ECONOMIC ACTIVITY

 UNITS. NATIONAL INCOME
UNITS. NATIONAL INCOME
DISCUSSION 1. What do you know about national income?
2. Do you know how to measure national income?
reading NATIONAL INCOME
F. Scott Fitzgerald: "...You know, Ernest, the rich are different from us..."
Ernest Hemmingway: "...Yes, I know. They have more money than we do..."
National Income is the sum of all the incomes obtained from the production of goods and services by a country's economy over a period of time, usually one year. National Income is therefore the value of a flow of economic activity, and is not a value of a country's stock of wealth. Wealth and income are different.
National Income figures are used:
• to measure the standard of living in a country;
• to compare the economic performance of different countries;
• to measure the rate of growth or decline in economic activity from one period to the next;
• to assist the central government with its economic planning.
National Income can be measured in three ways. This is because eco
nomic activity can be seen as two related circular flows - a circular flow of
income and expenditure and a related circular flow of productive services
going into firms from households to produce goods and services, which
households then buy.
n
PART I. ECONOMICS
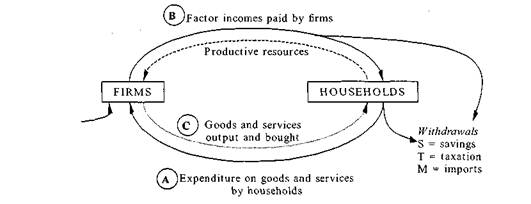
 CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME
CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME
|
| Injections I = investment G = government spending X = exports |
 Withdrawals from the circular flow consist of:
Withdrawals from the circular flow consist of:
• Savings. If households save some of their income, they don't spend it on goods and services.
• Taxation. If a government taxes income or expenditure, money is diverted from firms or households to the government.
• Imports. If households or firms buy goods from abroad, the payments go to foreign suppliers and out of the country's own circular flow of income.
Injections into the circular flow consist of:
• Investment. This is investment in plant, machinery and other fixed assets by firms. This injects funds into the circular flow of income.
• Government spending. Spending by government also injects money into the circular flow of income. It acts in the opposite way to taxation. Broadly speaking, governments raise money from taxes (withdrawal) and spend the money they have raised (injection).
• Exports. These generate earnings from abroad, which flow into the national economy. Goods must be produced for export, and so exports increase the volume (and value) of output by the economy.
The three methods of calculating National Income are based on three aspects of these circular flows. A An expenditure approach calculates GDP as the total expenditure on
goods and services produced during the year by the country's economy. В An income approach calculates GDP as the total income earned by factors of production. It includes some "imputed income" and excludes transfer incomes. C An output approach calculates GDP as the value of output production by each industry. Value is measured as "added value" which is the value of output produced by the industry minus the cost of raw materials, components and services etc. purchased from supplier firms. This is necessary to avoid double counting. The total value of all industrial output calculated in this way gives us GDP
Each method should produce the same total National Income, but errors and omissions in gathering statistics mean that each method produces slightly different totals.
UNIT 8. NATIONAL INCOME
VOCAB U LARY stock - запас
NOTES wealth - багатство
to decline - погіршуватися,
зменшуватися
to divert - відводити, відхиляти,
відвертати
fixed assets - основні засоби imputed income - нарахований дохід transfer income - трансфертний дохід omission - пропуск totals - підсумок
 EXERCISES I. Answer the following questions:
EXERCISES I. Answer the following questions:
1. What is National Income?
2. What National Income figures are used for?
3. How National Income is measured?
4. What are the components of withdrawals/injections?
5. What methods of calculating National Income do you know?
II. Match the synonyms.
A buyer, to desire, to make profits, to take care (of), о supply, to conduct transactions, interest, considerable, a purchaser, to allow, benefit, to get profits, variety, to manufacture, to arrange a deal, to provide (with), significant, to look after, tendency, lack, intervention, to permit, diversity, to produce, interference, tend, to wish, absence.
III. Types of Profits. Match the terms with definitions and translations. Learn the terms.
| 1. PROFIT | a) • The comeback: profits and income from transactions or investments. • The profit or income from money invested. | а) Дохід на вкладений капітал за цінними паперами, звичайно в процентах. |
| 2. RETURNS | b) • Return, monetary or otherwise, for human effort. • The after-tax profits of a company attributable to its ordinary shareholders. • Payment received for work done or from money invested by a person or an organisation. | Ь)Прибуток,доходи, виторг, заробітна плата. |
| 3. INCOME | c) • Payment to a worker, either in kind or in cash, apart from his or her wages. • Value received as of right. | с) Прибуток, вигода, допомога. |
| 4. GAINS | d) • The amount of money arising from a transaction or series of transactions. • The money received from selling something. | d) Надходження, виторг, доходи. |
| 5. REVENUE | e) • Alternative term for profit. • A term used to describe profits of an irregular or nonrecurrent nature. | є) Прибуток, дохід, виграш. |
| 6. EARNINGS | f) • Return on an investment, taking into account the annual income and the capital value of the investment, usually expressed as a percentage. • The amount, expressed normally as a percentage on the capital invested, of income created by an investment. | f) Дохід за цінними паперами,видобуток, виробіток. |
| 7. BENEFIT | g) • Money received from any transaction or sale, or money received by the government in the form of taxation. | g) Доходи (державні). |
| 8. PROCEEDS | h) • Money, goods or services received from any activity. • The inflow of wealth accruing to an individual or a business over a period of time. • Money (in the form of WAGES or SALARY or PROFIT) received from work done, or (as INTEREST) from money invested or (as RENT) from property owned. | h) Доходи, надходження, виторг. |
PART I. ECONOMICS
| -. YIELD | і) • Surplus money, after all expenses have been met, generated by a firm or enterprise in the course of one accounting period. • A surplus of the revenues of a trading concern over its costs. The amount of money arising from a transaction or series of transactions. | і) Перевищення надходжень над витратами, позитивна різниця між ціною продажу та купівлі цінних паперів або продуктів. |
IV Match the antonyms.
То sell, advantage, high prices, to spend money, to decline, flexible, to go out of business, to save money, disadvantage, low prices, worst, to buy, credible, variety, best, uniformity, inflexible, to stay out of the way, incredible, available, to meddle with other people's business, unavailable, to stay in business, to level off.
V Learn the following definitions and compose sentences of your own with them.
| Market prices | - prices actually paid. |
| Factor cost | - values at the cost of the factors of production. These are market prices minus indirect taxes (e.g. VAT - Value Added Tax) plus any subsidies paid by the government to producers. |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | - the value of all economic activity created within the country during the period in question, at market prices or factor cost. |
| Gross National Product (GNP) | - GDP plus net property income from abroad (or minus, if it is a negative value, with payments abroad exceeding income from abroad). |
| Net National Product (NNP) | - National Income. This is GNP minus an estimated value for the consumption of the nation's fixed assets (depreciation). |
| Imputedncome | - {умовно нарахований дохід) income, which does not exist as monetary income, but which has been given a value in order to assess National Income. Imputation is the process of "inventing an economic transaction'.' For example, there is an imputed income for "rent" which relates to the use of owner-occupied homes by their owner/occupiers. |
| Transfer incomes | - are payments that are made to someone, where the recipient does not make any contribution to output in return (e.g. retirement pensions, social security benefits, etc.). They are payments, which involve the transfer of wealth, rather than a reward for creating new economic wealth. They are excluded from the income statistics and they are not income earned from economic activity. |
VII.
VIII.
Managing Exchange Rates. The sentences below describe different economic factors affect each other. Complete the spaces with words or phrases from the box.
balance of payments deficit interest rates exports
building societies exchange rates unemployment consumer spending
When banks and (1)____ offer credit, or cheap loans at low (2)_____, consumer spending
rises and (3)____ go up. High (4)____ creates pressure to increase wages. High consumer
spending also creates more demand for imports. This causes problems for the (5)_______.
Imports also cost more when the exchange rate is high. A high exchange rate also means
lower (6)____. Together these factors can make a worse balance of payments (7)______ and
higher inflation. Higher inflation usually leads to higher (8)_______.
Express your attitude towards the following proverbs and sayings.
• Money begets money. • Money is the root of all evil.
• Money has no smell. • Muck and money go together.
Writing Practice. Make a short summary about national income from the above text. Use the opening phrases from Appendix 1.
UNIT 8. NATIONAL INCOME
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 1191; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!