
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Shielding Materials
|
|
|
|
Shelter
Special Medical Aspects
Shielding
Shielding is the most important method of protection from penetrating radiation. Of the three countermeasures against penetrating radiation, shielding provides the greatest protection and is the easiest to use under survival conditions. Therefore, it is the most desirable method.
If shielding is not possible, use the other two methods to the maximum extent practical.
Shielding actually works by absorbing or weakening the penetrating radiation, thereby reducing the amount of radiation reaching your body. The denser the material, the better the shielding effect. Lead, iron, concrete, and water are good examples of shielding materials.
The presence of fallout material in your area requires slight changes in first aid procedures. You must cover all wounds to prevent contamination and the entry of radioactive particles. You must first wash burns of beta radiation, then treat them as ordinary burns. Take extra measures to prevent infection. Your body will be extremely sensitive to infections due to changes in your blood chemistry. Pay close attention to the prevention of colds or respiratory infections. Rigorously practice personal hygiene to prevent infections. Cover your eyes with improvised goggles to prevent the entry of particles.
As stated earlier, the shielding material's effectiveness depends on its thickness and density. An ample thickness of shielding material will reduce the level of radiation to negligible amounts.
The primary reason for finding and building a shelter is to get protection against the high-intensity radiation levels of early gamma fallout as fast as possible. Five minutes to locate the shelter is a good guide. Speed in finding shelter is absolutely essential. Without shelter, the dosage received in the first few hours will exceed that received during the rest of a week in a contaminated area. The dosage received in this first week will exceed the dosage accumulated during the rest of a lifetime spent in the same contaminated area.
The thickness required to weaken gamma radiation from fallout is far less than that needed to shield against initial gamma radiation. Fallout radiation has less energy than a nuclear detonation's initial radiation. For fallout radiation, a relatively small amount of shielding material can provide adequate protection. Figure 23-1 gives an idea of the thickness of various materials needed to reduce residual gamma radiation transmission by 50 percent.
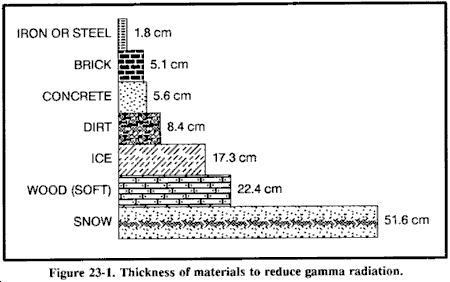
The principle of half-value layer thickness is useful in understanding the absorption of gamma radiation by various materials. According to this principle, if 5 centimeters of brick reduce the gamma radiation level by one-half, adding another 5 centimeters of brick (another half-value layer) will reduce the intensity by another half, namely, to one-fourth the original amount. Fifteen centimeters will reduce gamma radiation fallout levels to one-eighth its original amount, 20 centimeters to one-sixteenth, and so on. Thus, a shelter protected by 1 meter of dirt would reduce a radiation intensity of 1,000 cgys per hour on the outside to about 0.5 cgy per hour inside the shelter.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 393; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!