
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Drawbacks of Bisection Method
|
|
|
|
Advantages of Bisection Method
a) The bisection method is always convergent. Since the method brackets the root, the method is guaranteed to converge.
b) As iterations are conducted, the interval gets halved. So one can guarantee the error in the solution of the equation.
a) The convergence of bisection method is slow as it is simply based on halving the interval.
b) If one of the initial guesses is closer to the root, it will take larger number of iterations to reach the root.
c) If a function 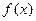 is such that it just touches the x -axis (Figure 6) such as
is such that it just touches the x -axis (Figure 6) such as
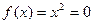
it will be unable to find the lower guess, 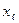 , and upper guess,
, and upper guess, 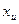 , such that
, such that
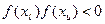
d) For functions 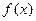 where there is a singularity[1] and it reverses sign at the singularity, bisection method may converge on the singularity (Figure 7).
where there is a singularity[1] and it reverses sign at the singularity, bisection method may converge on the singularity (Figure 7).
An example include
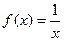
and 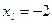 ,
, 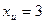 are valid initial guesses which satisfy
are valid initial guesses which satisfy
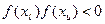 .
.
However, the function is not continuous and the theorem that a root exists is also not applicable.
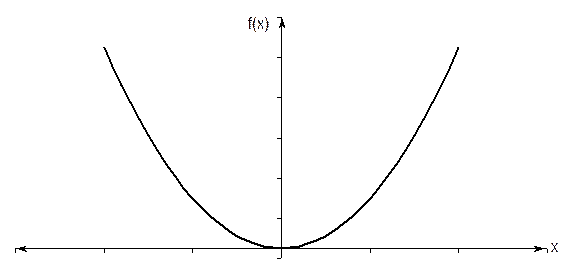
Figure 6: Function 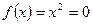 has a single root at
has a single root at 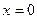 that cannot be bracketed.
that cannot be bracketed.
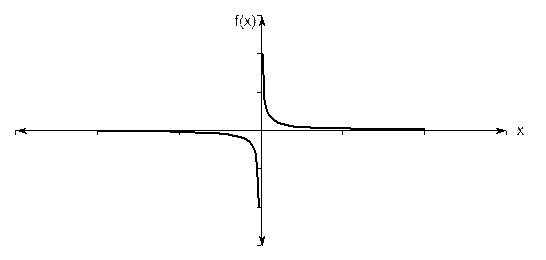
Figure 7: Function 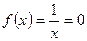 has no root but changes sign.
has no root but changes sign.
| NONLINEAR EQUATIONS | ||
| Topic | Bisection Method of Solving Nonlinear Equations | |
| Summary | These are textbook notes of bisection method of finding roots of nonlinear equation, including convergence and pitfalls. | |
| Major | General Engineering | |
| Authors | Autar Kaw | |
| Date | December 26, 2014 | |
| Web Site | http://numericalmethods.eng.usf.edu | |
[1] A singularity in a function is defined as a point where the function becomes infinite. For example, for a function such as 1/x, the point of singularity is x=0 as it becomes infinite.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 2139; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!