
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
B. RegionalNon-RP Accents of England
|
|
|
|
Non-systematic Variations in RP Phonemes
Some free phonemes have appeared under the influence of the written image of words, their spelling.
Unstressed prefixes ex- and con- have gained orthographical pronunciation: excuse [iks'kjuz] — [eks'kjrcz], exam [ig'zaem] — [eg'zaem], continue [kan'tmju:] — [kon'tinju:], consent [kan'sent] — [kon'sent].
The days of the week: Sunday ['sAndi] — ['sAnder], Monday ['mAndi] — ['mAndei].
Note also free variants in often: ['ofsn] — [ЪЛ(э)п].
Other cases: economics [.ika'nomiks] — [.eka'nDmiks].
Now by way of conclusion we would like to state that not all the changes are recognized as a norm by most affected advanced RP speakers. Some of these changes are quite stable, some tend to disappear. The language is a living body and its oral aspect is most vitally changeable. But one should realize the importance of most recent developments, which, in opinion of many prominent phoneticians, may lead to radical changes in the whole inventory of vowel and consonant phonemes.
As was stated above, we grouped regional accents of England into southern and northern ones. This division is very approximate of course, because there are western and eastern accents but their main accent variations correspond either with southern or northern accentual characteristics. Thus we would like to point out here the main differences between southern and northern accents.
In vowels
One of the main differences between these groups of accents is in the phoneme inventory — the presence or absence of particular phonemes. Typically, the vowel [л] does not occur in the accents of the north; e.g.
South North
blood [bkd] (blodj
one (wah) [won]
but [bAt] [bet]
We can also note that many northern speakers while they do not have [л] have [it] rather than [o] in words such as hook, book, look. They therefore distinguish pairs like book and buck, which in the south sound [buk] and [bAk], in the North as [bu:k] and [buk]:
South North
book [bok] [bu:k]
buck [bAk] [buk]
Another well-known feature which distinguishes northern and southern accents concerns the vowels [at] and [a].
 |
Before the voiceless fricatives [f, в, s] and certain consonant clusters containing initial [n] or [m], [ae] is pronounced in the north instead of [a].
South North
path [p<*6] [РЖ9]
dance fdctns] [daens]
Note: Speakers with more strongly regional southern substandard accents may not have the contrast or, at most, have a contrast that is variable.
In the south, however, [ae] is often pronounced as [a:]:
RP South
bad Ibaedj [bad]
A = [as] in path
В = (a] in path
С = [as] — [a] contrast absent or in doubt
One more major north — south differentiating feature involves the final [t] like in words dry, money, etc. In the north of England they have [i]. In the south of England these words are pronounced with [i:], e.g.
| South | North | |
| city money | i'siti:] 1'тлш:] | I'sitij ('тот] |
In consonants
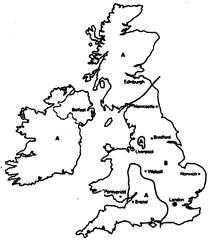
It has been mentioned above that some English accents are "rhotic" or "r-full" and other are non-rhotic or "r-less". Rhotic accents are those which actually pronounce [т], corresponding to orthographic "r" in words like bar and farm. This [r] sound is post-vocalic and is most often heard in Scotland, Ireland and in the southwest of England. The map on p. 264 shows the spread of post-vocalic [r] (A = post-vocalic [r] present, В = post-vocalic [r] absent).
In most regional accents the glottal stop is more widely used than in RP. In some areas, especially the north-east of England, East Anglia and Northern Ireland, the glottal stop may also be pronounced simultaneously with the voiceless [p, t, k], most strikingly between vowels: pity ['pit?i:].
Many non-RP speakers use [n) in the suffix "-ing" instead of [rj]; sitting ['sitm]. In an area of western central England which includes Birmingham, Manchester and Liverpool they pronounce fog]: singer ['singa], wing [wing].
Now about [jj-dropping. In most accents [j] is dropped after [t, s]: student ['stu:dant], suit [su:t]. In parts of the north the change has progressed a good deal further, it has been lost after [0]: enthusiasm [3n'6u:zi3zm].
In large areas of eastern England [j] is lost after every consonant. In London У] is lost after [n, t, d]: news [nu:z], rune [tu:n].
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-31; Просмотров: 1946; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!