
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких компонентах центрального процессора и их значениях вы узнали. Переведите текст
|
|
|
|
Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
Идентификация оружия по дроби, картечи, пыжам, специальным и самодельным пулям.
Изъятые дробь, картечь исследуются с целью установления способа их изготовления (заводская или самодельная, катанка или литая). Это решается на основе изучения внеш.признаков изучаемых объектов: формы, размера, веса, особ-тей строения поверх-ти и т.д., а также данных спектрографического анализа их хим. состава.
По данным признакам м. проводить и сравнит. исслед-ние 2х групп объектов (# изъятых с места происшествия и обнаруженных у подозр-мого), чтобы установить их однородность или неоднородность.
При обнаружении сов-ти признаков сравниваемых образцов, свид-щих об изготовлении дроби или картечи из одного куска свинца, или обработке поверх-ти с пом. одного и того же приспособления, или хранении в одном и том же месте, м.б. сделан вывод о едином источнике происхождения сравниваемых объектов, что повышает доказ-венное значение проведённого исслед-ния.
Путём исслед-ния пыжей удаётся установить приблизит. калибр патронов, в которых они м.б. использованы. Для исслед-ния самодельно изгот-ных пыжей используют трасологич. методы.
to manage ['mænιdჳ] – управлять; организовывать; справляться
to obtain [әb'teιn] – получать; достигать; добиваться
to cause – заставлять; вынуждать; вызывать; быть причиной; причина, основание
flow ['flou] – поток; ход (выполнения программы); последовательность
counter ['kauntә] – счетчик
register ['redჳιstә] – регистр; устройство регистрации; счетчик; датчик
instruction register – регистр команд
storage register – регистр памяти; запоминающий регистр
address register – адресный регистр
temporarily ['tempәrәrιlι] – временно
decoder [dι'koudә] – дешифратор
operand address [ეpә'rα:nd ә'dres] – адрес (хранения) операнда
mark ['mα:k] – отметка; маркер; знак; помечать; обозначать; выделять
timing mark – отметка времени
accumulator – сумматор; накапливающийся регистр; устройство суммирования
compare [kәm'pεә] – сравнивать; соотноситься
comparer [kәm'pεәrә] – компаратор; устройство сравнения
content ['kეntәnt] – содержимое; смысл; объем; количество
involve [ιn'vეlv] – включать; содержать; заключать (в себе)
core ['kე:] – суть; основная часть; ядро; оперативная память
add ['æd] – складывать; суммировать; прибавлять; присоединять
added – добавочный; дополнительный
adder – сумматор; блок суммирования
at least – по крайней мере
Text 2. THE CPU MAIN COMPONENTS
 As it is known the two functional units of the CPU are the control unit (CU) and the arithmetic-logical unit (ALU). The control unit manages and coordinates the entire computer system. It obtains instructions from the program stored in main memory, interprets the instructions, and issues signals that cause other units of the system to execute them.
As it is known the two functional units of the CPU are the control unit (CU) and the arithmetic-logical unit (ALU). The control unit manages and coordinates the entire computer system. It obtains instructions from the program stored in main memory, interprets the instructions, and issues signals that cause other units of the system to execute them.
The control unit operates by reading one instruction at a time from memory and taking the action called for by each instruction. In this way it controls the flow between the main storage and the arithmetic-logical unit.
The control unit has the following components: a counter that selects the instructions, one at a time, from memory; a register that temporarily holds the instructions read from memory while it is being executed; a decoder that takes the coded instruction and breaks it down into individual commands necessary to carry it out; a clock, which produces marks at regular intervals. These timing marks are electronic and very rapid.
The sequence of control unit operations is as follows. The next instruction to be executed is read out from primary storage into the storage register. The instruction is passed from the storage register to the instruction register. Then the operation part of the instruction is decoded so that the proper arithmetic or logical operation can be performed. The address of the operand is sent from the instruction register to the address register. At last the instruction counter register provides the address register with the address of the next instruction to be executed.
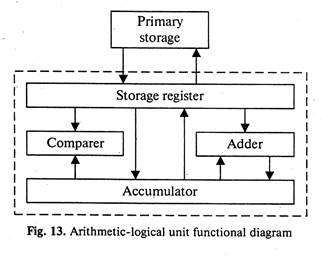
The arithmetic-logical unit (ALU) executes the processing operations called for by the instructions brought from main memory by the control unit. Binary arithmetic, the logical operations and some special functions are performed by the arithmetical- logical unit.
Data enter the ALU and return to main storage through the storage register. The accumulator serving as a register holds the results of processing operations. The results of arithmetic operations are returned to the accumulator for transfer to main storage through the storage register. The comparer performs logical comparisons of the contents of the storage register and the accumulator. Typically, the comparer tests for conditions such as “less than”, “equal to”, or “greater than”.
So as you see the primary components of the arithmetic-logical unit are banks of bistable devices, which are called registers. Their purpose is to hold the numbers involved in the calculation and hold the results temporarily until they can be transferred to memory. At the core of the ALU is a very high-speed binary adder, which is used to carry out at least the four basic arithmetic functions (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division). The logical unit consists of electronic circuitry which compares information and makes decisions based upon the results of the comparison.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-06-04; Просмотров: 539; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!