
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Electric motors
|
|
|
|
For rotational electric motors relationship of angular speed to its rotating moment is called mechanical characteristic of electric motor:
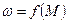 ,
,
where 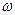 - is angular speed of motor,
- is angular speed of motor, 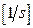 ;
;
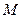 - electromagnetic rotating moment developed by electric motor,
- electromagnetic rotating moment developed by electric motor, 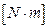 .
.
Almost all electrical motors have speed, which is decreasing function of electrical motor moment. All DC electrical motors, asynchronous motors, AC collector motors and others have such characteristic.
Degree of speed decreasing for different electric motors is different and is characterized with the rigidity of mechanical characteristic.
Rigidity of mechanical characteristic of motor is the ratio:
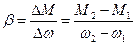 , (3.5)
, (3.5)
i.e. the ratio of difference of motor electromagnetic moments in any points 1 and 2 of the characteristic to corresponding difference of motor speed in that points.
In the most cases on the working parts the mechanical characteristic has negative rigidity
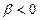 .
.
If the mechanical characteristic is straight line one, its degree of rigidity is constant
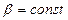 ,
,
And if it is non-linear, its degree of rigidity is not constant
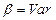
and is defined in this case accordingly (3.5) in each point of characteristic as derivative of moment to angular speed
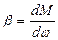 .
.
The whole variety of electrical motors can be divided into four groups (classes) with the approximately same character of mechanical characteristic rigidity changing in the each class, see the figure 3.2.
І class. Electric motors of first class have absolutely rigid mechanical characteristic. With this the speed of motor remains stable at changing of its moment, i.e.:
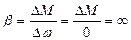 ,
,
the degree of rigidity is infinity, and characteristic is represented by straight line parallel to abscissa axis.
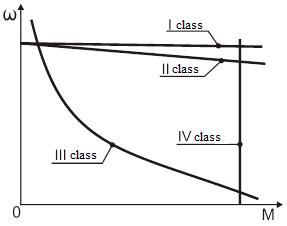
Figure 3.2 – Mechanical characteristics of electric motors.
At any load of electrical motor, its speed remains constant. Only one type of motors has such characteristic – synchronous ones.
ІІ class. Motors of second class have rigid characteristic. With this speed of electrical motor almost doesn’t change (decreases insignificantly) at changing of it moment, i.e. rigidity 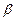 has significant negative value as per module. Characteristic is represented by inclined line almost parallel to abscissa axis. DC electrical motors of independent (parallel) excitation, asynchronous motors in limits of operating real loads and some others have such mechanical characteristic.
has significant negative value as per module. Characteristic is represented by inclined line almost parallel to abscissa axis. DC electrical motors of independent (parallel) excitation, asynchronous motors in limits of operating real loads and some others have such mechanical characteristic.
ІІІ class. Motors of third class have soft mechanical characteristic. With this the speed of electrical motors changes significantly at its moment changing. DC motors of series excitation, especially in limits of small loading moments, have such mechanical characteristic. With this rigidity of mechanical characteristic can have small as per module negative value.
IV class. Electric motors of fourth class have absolutely soft mechanical characteristic. With this moment of electric motors remains constant at any speed, i.e.:
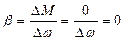 ,
,
the degree of rigidity is equal to zero, and characteristic is represented by straight line parallel to ordinate axis. DC electrical motors of independent excitation have such characteristic at feeding of its armature circuit from current source or at its operating in closed SAC in regime of armature current stabilization.
It worth mentioning that in real conditions such features that have the characteristics typical for other classes but with different degree of rigidity of mechanical characteristics can be applied to real electrical motors.
So that asynchronous motor has variable degree of rigidity (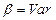 ), for example, in the whole range of speeds in motor regime (with changing of sliding from 0 to 1):
), for example, in the whole range of speeds in motor regime (with changing of sliding from 0 to 1):
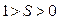 .
.
In the limits of operating loads (a part of characteristic AB) characteristic is straight line and has the rigidity:
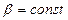 ,
,
and on the part of characteristic CD has hyperbolic character, and rigidity is:
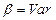 .
.
On the part of characteristic BFC rigidity is changing by enough complicated laws (see figure3.3).
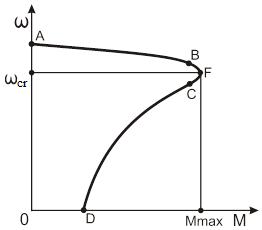
Figure 3.3 – Mechanical characteristic of AM (motor regime).
Property of the most electrical motors to have negative rigidity of mechanical characteristics causes some essential advantages of electrical motors as sources of mechanical energy comparatively to other non-electrical motors. As had been mentioned in the unit of electrical drive mechanics, when motor and executive mechanism operate in attained duty, tChe equation of mechanical motion equilibrium is:
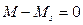 , або
, або 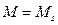 ,
,
i.e. the equilibrium of motive moment of motor and resistance moment of mechanism.
Changing of mechanism resistance moment on the shaft of the motor results in that the speed of electrical motor and moment, which it creates, can be automatically changed, and drive will continue his work stably in new attained duty (with new 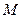 and
and  ). To establish a new equilibrium between
). To establish a new equilibrium between 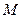 and
and 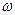 in different non-electric motors it is necessary to apply special regulators, that acts on the energy source changing with this a corresponding providing with fuel or another operating body (vapor, water and so on).
in different non-electric motors it is necessary to apply special regulators, that acts on the energy source changing with this a corresponding providing with fuel or another operating body (vapor, water and so on).
In electric motors the role of automatic regulator is played by e.m.f. of motor.
The feature of electric motors to maintain automatically the equilibrium of system if resistance moment is changing is rather essential property of electric motors comparatively to electric motors of other types.
Let’s consider this property on example of electric drive with DC electric motor of independent excitation with such characteristic, figure 3.4.
Figure 3.4 – To explanation of electric motors property automatically maintain an attained duty at load changing.
Line 3 is mechanical characteristic of electrical moment, lines 1 and 2 are mechanical characteristics of actuating mechanism of first class for two values of resistance moment 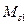 and
and 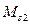 correspondently. Let us assume that characteristic 1 corresponds to idling rate of mechanism, and characteristic 2 corresponds to it operation under the load. (Mechanical characteristics 1 and 2 of executive mechanism for convenience are represented in the first quadrant, actually they should be represented in the second one, because resistance moment
correspondently. Let us assume that characteristic 1 corresponds to idling rate of mechanism, and characteristic 2 corresponds to it operation under the load. (Mechanical characteristics 1 and 2 of executive mechanism for convenience are represented in the first quadrant, actually they should be represented in the second one, because resistance moment 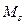 and moving moment of electric motor
and moving moment of electric motor 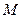 have opposite signs).
have opposite signs).
At first at idling rate of mechanism when
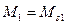
motor operates with the speed 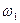 . Then, with the load increasing, motion of motor is slowed down, its speed is decreasing, thereby its e.m.f. is decreasing, with this voltage drop on the armature is increasing (in accordance with the equation of motor voltage equilibrium
. Then, with the load increasing, motion of motor is slowed down, its speed is decreasing, thereby its e.m.f. is decreasing, with this voltage drop on the armature is increasing (in accordance with the equation of motor voltage equilibrium 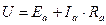 ) thus armature current is increasing and moment, which develops the motor, rises. Rising of moment is continuing till the equilibrium of moments is established
) thus armature current is increasing and moment, which develops the motor, rises. Rising of moment is continuing till the equilibrium of moments is established
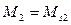 ,
,
in point B (the point of intersection of characteristic 3 of mechanism and characteristic 2 of motor under the load). A new equilibrium is established at point B, analogically to point A, but already with the lower speed 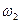 with greater moment
with greater moment 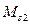 , which corresponds to load at point В. And vice versa, if under the load (point B in which electric motor operated in attained duty) to diminish the load, motor begun to run, armature e.m.f. will increase, voltage drop will decrease, current will decrease, moment will decrease and so on till the attained rest.
, which corresponds to load at point В. And vice versa, if under the load (point B in which electric motor operated in attained duty) to diminish the load, motor begun to run, armature e.m.f. will increase, voltage drop will decrease, current will decrease, moment will decrease and so on till the attained rest.
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 435; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!