
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
AM mechanical static characteristic in S and M coordinates
|
|
|
|
AM moment quadratic dependence of supply voltage is the cause of significant AM sensitivity to supply voltage vibrations (voltage decreasing, for example, is the cause of 2 times moment decreasing, that in turn grow the motor in 4 times).
Such quadratic dependence is typical for all motors and other mechanical systems of inductive type. Because of using in real conditions of only one type of induction motor that is asynchronous, it is the only motor that is sensitive to supply voltage vibrations.
Because of these reasons the value of alternating current supply voltage is strictly regulated. So, the operation of asynchronous motors is prohibited by standards, if the mains voltage drop is higher than 10 %.
Such characteristic is well-known from the course of electrical machines. Let`s remind its some peculiarities.
The curve has 4 characteristic points:
synchronous mode (point 0), 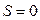 ,
, 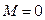 ;
;
- nominal mode (point N), at this  ,
,  ;
;
- critical mode (point К), at this the moment made by motor in motor mode is maximal  , and sliding that corresponds to that mode is critical
, and sliding that corresponds to that mode is critical  ;
;
- initial start mode (point Р), at this sliding  , and moment is starting
, and moment is starting  .
.

Figure 3.33 – AM mechanical characteristic in  coordinates.
coordinates.
Along the numerical axis (the numbers change from 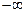 to
to  ) it should to mark the limits of sliding change:
) it should to mark the limits of sliding change:
а) at  – the motor mode;
– the motor mode;
b) at  – mode of counter switching braking;
– mode of counter switching braking;
с) at  – generator mode of recuperative braking.
– generator mode of recuperative braking.
From equation (3.36) it is seen, that maximal moment for motor mode (by magnitude) is less, than maximal moment of generator mode

(the signs „ ” in denominator of equation(3.36)) effect on it, because the resistance
” in denominator of equation(3.36)) effect on it, because the resistance
 .
.
The value of critical sliding for motor and generator modes (by magnitude) is the same
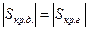
Equation of mechanical characteristic (3.37) corresponds to more or less accurate ratios of characteristic parameters, as it taken into account the voltage drop on stator active resistance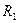 . In real conditions the value of stator active resistance (particularly for AM of average and great powers) is insignificant and it can be neglected (with sufficient accuracy for practical calculations)
. In real conditions the value of stator active resistance (particularly for AM of average and great powers) is insignificant and it can be neglected (with sufficient accuracy for practical calculations)
 . (3.38)
. (3.38)
With accounting of (3.38) the equation of mechanical characteristic (3.37) takes such a view
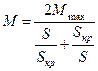 . (3.39)
. (3.39)
The equation (3.39) is called the simplified AM mechanical characteristic in S and M coordinates. However for the motors of high powers (where R1 is small) this equation is rather accurate corresponds to AM physical processes.
Equation (3.37) is also called as Kloss equation, and the equation (3.39) is the simplified Kloss formula.
If into equation (3.39) to substitute the nominal values  ;
;  , instead of current values of S and M, and the maximal moment multiplicity
, instead of current values of S and M, and the maximal moment multiplicity  (overload capacity) to designate as
(overload capacity) to designate as  :
:  , then after transformations the equation (3.39) will have such a view:
, then after transformations the equation (3.39) will have such a view:
 . (3.40)
. (3.40)
In equation (3.40) it should to use only “+” sign before a radical, because the “ - ” sign is correspond to a case of finding the points  and
and  on mechanical characteristic in a region, where
on mechanical characteristic in a region, where 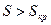 . This case doesn`t have the practical meaning, because the characteristic area where
. This case doesn`t have the practical meaning, because the characteristic area where 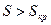 is not the operation area or AM characteristic.
is not the operation area or AM characteristic.
The value of AM overload capacity λ has a significant practical meaning during ED operation and its value is regulated by State standard. For three-phase AM of general application in a wide power range AM λ has such a limits:  , at that the higher value of
, at that the higher value of  corresponds to AM synchronous speed
corresponds to AM synchronous speed  , and the lower is for
, and the lower is for .
.
For special AM series the overload capacity is higher. So, for crane and metallurgy AM it is  .
.
3.12 Analysis of AM mechanical characteristic M=f(S), presented as simplified Closs`s formula
This characteristic can be divided into 2 sections:
The 1st section. At high sliding values 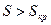 the second member of denominator in equation (3.39) can be neglected
the second member of denominator in equation (3.39) can be neglected , then the formula (3.39) will has such a view
, then the formula (3.39) will has such a view
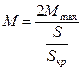 ;
; 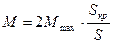 ;
;  , (3.41)
, (3.41)
where 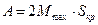 is constant value.
is constant value.
Equation (3.41) in a view  from the point of mathematics view is interpreted as hyperbola equation (
from the point of mathematics view is interpreted as hyperbola equation (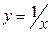 ).
).
Thereby the characteristic section , where the sliding values are high
, where the sliding values are high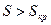 , presents the hyperbolic moment dependence of sliding. As it has seen this section is spread on motor mode of non-operation part and on whole mode of counter switching braking.
, presents the hyperbolic moment dependence of sliding. As it has seen this section is spread on motor mode of non-operation part and on whole mode of counter switching braking.

Figure3.34 – For analysis of AM mechanical characteristic in  coordinates.
coordinates.
The 2nd section. At small sliding values 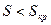 the first member of denominator in equation (3.39) can be neglected
the first member of denominator in equation (3.39) can be neglected 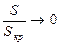 , then the formula (3.39) will have such a view:
, then the formula (3.39) will have such a view:
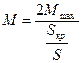 ;
;  ;
;  , (3.42)
, (3.42)
where  is constant value.
is constant value.
The equation (3.42) in a view  from the point of mathematics view is interpreted as equation of straight line passing through the origin (
from the point of mathematics view is interpreted as equation of straight line passing through the origin ( ).
).
Thereby the characteristic section DC where the small sliding values 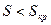 presents a straight linear AM moment M dependence of sliding S. As it has seen this section is spread on generator mode of recuperative braking and on the generative mode of its operational part; here is the point if rated operational mode N of a motor and the point of synchronous mode 0; AM operates in steady-state mode at this section.
presents a straight linear AM moment M dependence of sliding S. As it has seen this section is spread on generator mode of recuperative braking and on the generative mode of its operational part; here is the point if rated operational mode N of a motor and the point of synchronous mode 0; AM operates in steady-state mode at this section.
3.13 AM mechanical characteristic in ω and M coordinates (dependence ω= f (M))
If mechanical characteristic will be given in 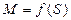 coordinates (the fragment a)) then two different AM modes can be given at the same quadrant, for example at 1st quadrant there is both motor and braking modes. It is very convenient during analysis of ED operational modes together with actuating mechanism.
coordinates (the fragment a)) then two different AM modes can be given at the same quadrant, for example at 1st quadrant there is both motor and braking modes. It is very convenient during analysis of ED operational modes together with actuating mechanism.
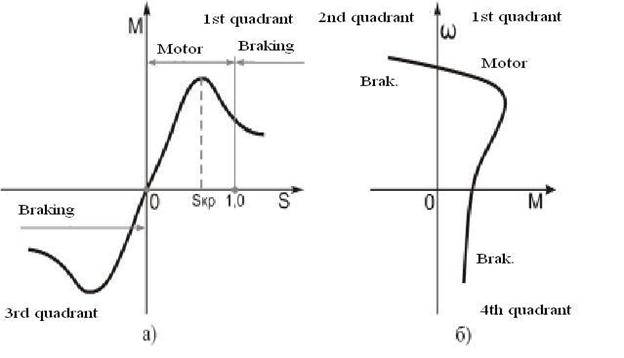
Figure 3.35 – The ways of AM mechanical characteristic representing
That`s why for creating of convenient analysis of ED mechanical characteristic, in theory of ED the mechanical characteristic in coordinates 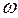 and
and 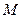 , that is
, that is  (fragment б of figure 3.35) is used instead of
(fragment б of figure 3.35) is used instead of 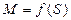 characteristic.
characteristic.
To transit from one characteristic to another is very simple, because the sliding S is relative speed: 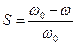 , solving this equation relatively to current angular velocity
, solving this equation relatively to current angular velocity 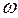 will obtain:
will obtain:
 . (3.43)
. (3.43)
With taking into account equation (3.43) the characteristic 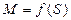 will be easily transformed into characteristic
will be easily transformed into characteristic  .
.
Mechanical static characteristic  has those advantages, which in it graphical representation every quadrant of rectangular coordinate system has one and only one mode (motor and generator mode). The 1st and the 3rd quadrants are corresponds to the motor mode, and the 2nd and 4th quadrants are corresponds to the braking modes (as in DC motor).
has those advantages, which in it graphical representation every quadrant of rectangular coordinate system has one and only one mode (motor and generator mode). The 1st and the 3rd quadrants are corresponds to the motor mode, and the 2nd and 4th quadrants are corresponds to the braking modes (as in DC motor).

Figure 3.36 – For analysis of AM mechanical characteristic in  coordinates.
coordinates.
Characteristic has the same sections (hyperbolic and straight linear) as characteristic
has the same sections (hyperbolic and straight linear) as characteristic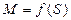 , section
, section  is hyperbolic; section
is hyperbolic; section  is straight linear, and the same characteristic points, as in
is straight linear, and the same characteristic points, as in 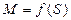 :
:
- synchronous mode (point 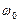 ) with coordinates
) with coordinates 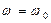 ;
; 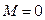 ;
;
- rated mode (point 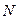 ) with coordinates
) with coordinates  ;
;  ;
;
- critical mode (point  )with coordinates
)with coordinates  ;
; 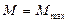 ;
;
- initial starting mode (point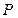 ) with coordinates
) with coordinates 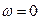 ;
;  .
.
From the graphs 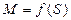 and
and  it is seen, that the point
it is seen, that the point  , that corresponds to critical mode, it is a point of division of hyperbolic and straight linear characteristic parts, and the section of a curve
, that corresponds to critical mode, it is a point of division of hyperbolic and straight linear characteristic parts, and the section of a curve  on the both graphics is undefined part of mechanical characteristic and it can not be described by equation (3.39) – because here in the limits
on the both graphics is undefined part of mechanical characteristic and it can not be described by equation (3.39) – because here in the limits  the equation (3.39) losses its physical and mathematical essence and transforms into equality
the equation (3.39) losses its physical and mathematical essence and transforms into equality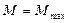 :
:
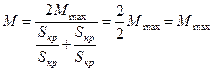 .
.
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 728; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!