
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Electric motor power calculation at enduring operation mode (S1) and at different cyclic load
|
|
|
|
At long-term variable load calculation of chosen motor should be done about the heating by specification maximal real temperature and then given insulation class of EM should be compared to the allowable over temperature.
And the condition should be succeeded:

Where  - real steady maximal temperature of heated motor of the cycle:
- real steady maximal temperature of heated motor of the cycle:
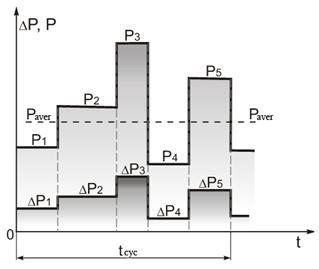

Power verification of motor takes a lot of time to plot the heating and cooling curves.
In practice they use another way.
Choosing of motor to the max or min power isn`t perfect way, because the max power is overstated, the min one is understated.
The average power way is also not perfect, because motor is heated by losses, that are specified by load. These losses are proportional to the square load current. The more the load is the more the difference between them is. So the average power is underrated.
In practice power motor calculation is specified less precisely, than the method of plot the heating curves, but it is pretty simply in the long-term mode and alternative cycle load. There two basic methods:
-method of average load;
-equivalent current method.
Method of average load
The essence of method is the fact, that the over temperature at the constant heat transfer is specified by average losses in a cycle.
 , (6.1)
, (6.1)
де 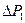 - the
- the  -th interval power of losses;
-th interval power of losses;
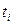 - duration of
- duration of  -th – interval;
-th – interval;
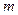 - amount of intervals;
- amount of intervals;
 - cycle time.
- cycle time.
Cycle losses are equal for the figure:
 . (6.2)
. (6.2)
Found average cycle losses  correspond to the rated one
correspond to the rated one  .
.
If  , then over temperature
, then over temperature isn`t greater than allowable value
isn`t greater than allowable value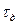 , thus
, thus .
.
equivalent current method.
When the current consumption per cycle is known, the motor power can be found by equivalent current method.

This method is specified by substitution the real motor current by equivalent current of precise value that involves the same losses that the real current does.
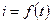 .
.
Average losses power (e.g. DC motor) are equal under the equivalent current:
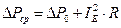 , (6.3)
, (6.3)
where  - power of losses that are independent of load. They are constant;
- power of losses that are independent of load. They are constant;
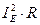 - varying losses power that depend on copper losses
- varying losses power that depend on copper losses
Average cycle loses power is equal:
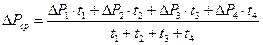 . (6.4)
. (6.4)
Substituting constant ant variable components by power losses:
 (6.5)
(6.5)
Here it is:
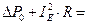
 . (6.6)
. (6.6)
The following transformation takes place:

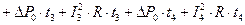 ;
;
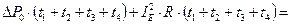
 ;
;
 . (6.7)
. (6.7)
In the general form the formula looks:
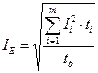 , (6.8)
, (6.8)
Where  are the same as in the (6.1).
are the same as in the (6.1).
Thus if curve of current changing is known, then the motor power can be chosen by average losses methodand the the value of  by the formula (6.8) and to compare it with the з
by the formula (6.8) and to compare it with the з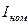 of chosen motor.
of chosen motor.
If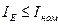 , then the motor is good for the mechanism with given graph of load.
, then the motor is good for the mechanism with given graph of load.
There are situations whe the power or moment are known but not the current changing. In this case method of equivalent moment or power should be used:
 ,
,
 .
.
Equivalent value methods are used for any motor but they should have been checked and analyzed before.
So the equivalent current method cannot be applied to wide-grooving asynchronous motors with squirrel-cage or double-cage rotor as they have R=var.
The equivalent moment method can be applied to the motors that the equivalent current method is ok to. As M=1, this equality DC motors of independent excitation have as AM do. As it was said, this method fails for DC motors of series excitation, because their equality is M≠1.
Equivalent power method can be applied to the motors where P=1, and ∆P=const, R=Const, Φ=Const and ω=Const=ωratconditions are hold. So it can be applied to the synchronous motors, asynchronous motors, DC motors of independent excitation, if they operate at the rated current with variable or constant velocity.
Equivalent power method can`t be applied to the motors with variable velocity as ∆P=Var, ω=Var.
All foresaid cases where equivalent methods fails the average losses method should be applied.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 466; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!