
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Introduction. Conditional Sentences
|
|
|
|
Plan.
CONDITIONAL SENTENCES
Lecture № 3.
I wish.
As long as.
If only.
In case.
We use in case to talk about doing something now to avoid a future problem. It gives a reason.
I will call my parents in case they are worried about me.
If only can be used to express hope or regret:
1)If only + present/will = hope
If only he comes in time.
2) If only + past simple/past perfect = regret
If only he didn’t drive so fast!
We use as long as to express a condition, to say that something will happen only on condition that something else happens. It expresses that one thing depends on another.
As long as you listen to my problems I won’t feel so depressed.
You can go to the party as long as you come back before midnight.
We use the past simple for a present situation after wish. Wish is used to say that we regret something, that something is not as we would like it to be.
I wish I knew Sue’s telephone number.
! We can use were instead of was after wish.
We use past perfect after I wish when you say that you regret something that happened or didn’t happen in the past.
I wish I had known that Ann was ill. I would have gone to see her.
1. The meaning of conditional sentences
2. Conditional type 0
3. Conditional type 1
4. Conditional type 2
5. Conditional type 3
6. The ways to replace “if”
(The meaning of conditional sentences)
A conditional sentence (or “conditional” for short) is commonly composed of two parts: conditional clause + main clause. Despite the many possible sequences of verb forms are conditionals, the following four types represent perhaps the commonest and the most useful ones:
- If you heat ice, it melts.
- If we catch the 10 o’clock train, we will get there by lunchtime.
- If we caught the 10 o’clock train, we would get there by lunchtime.
- If had caught the 10 o’clock train, we would have got there by lunchtime.
IMPORTANT:
- We can reverse the order: If it rains, I will stay at home / I will stay at home if it rains.
- We write a comma (,) after the if-clause, when we begin with the if-clause.
There are four types of Conditional Sentences. Each type contains a different pair of tenses. With each type certain variations are possible.
2. TYPE O: GENERAL CONDITION.
The 0 (zero) conditional is the easiest to understand! It is also called the real or factual conditional because it is used to talk about facts, or something that is always true.
| If / unless | Subject | Present tense | Subject | Present tense |
If I eat too much, I get sick.
The result [ I get sick ] is always true of the condition [ if I eat too much ]. It is a fact! There is a fixed connection between the two events.
This conditional is easy because we don’t have to remember which clause goes where or which verb tense is used, we just have to remember:
§ facts, habits, daily routines, rules, general truths = present simple
Every day I take the train to work. If I miss the train, I drive to work.
If-clause à Present Simple
Main-clause à Present Simple
e.g.: If you eat too much, you feel bad.
If I don´t get enough sleep, I feel tired.
If you mix yellow and blue, you get green.
We use this structure to talk about habits and general truths.
Here if = whenever
We can also use modals in the result clause:
I can’t drive if I don’t have my glasses.
If you want to go to university, you must study hard.
If you want to lose weight, you should eat less and exercise more.
You can’t drive a car if you don’t have a license.
WE can also use the imperative in the result clause
If you drink, don’t drive.
Please don’t disturb me if I am asleep!
If you’re hungry, eat something!
Notice that 'unless' means the same as 'if not'.
- Unless he asks you politely, refuse to do any more work on the project.
- Unless prices are rising, it's not a good investment.
3. TYPE 1: REAL CONDITION
This type of condition shows that it is still possible for the event or the action to happen. It is called “ Conditional Clause- Type 1”.
| If/when/unless | Subject | Present tense | Subject | Will Can May | Infinitive verb without “to” |
- If the weather is bad, we will cancel the meeting.
- We will cancel the meeting if the weather is bad.
- If my friend invites me, I’ll visit him.
- I will visit my friend if he invites me.
Unless = [ If + not ]
If you don’t study hard, you’ll fail.
Unless you study hard, you’ll fail.
You’ll fail unless you study hard.
There is a difference between If and When?
Study the following 2 conditional clauses:
A) If he comes, I will tell him the truth.
B) When he comes, I will tell him the truth.
When we use if, we are not sure about the event to happen or not.
But when we use when we are sure about the event to happen. So, in (B) we are sure that he will come. But in (A) we are not sure about his coming.
Variations to Type 1:
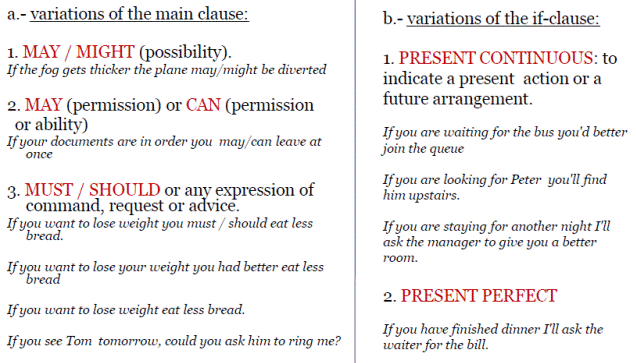
4. TYPE 2: UNREAL CONDITION
This type of condition shows that it is impossible for the event or the action to happen. It is called “ Conditional Clause- Type 2 ”.
| If / unless | Subject | Past tense | Subject | Would Could Might | Infinitive verb without “to” |
- If I were you, I wouldn’t waste my time. [ Used to give advice ]
- If the weather was/ were bad, we would cancel the meeting.
- We would cancel the meeting if the weather was/ were bad.
-If they have enough time, they will finish the work. [ Type 1 ]
-Unless they have enough time, they will not finish the work.
-If they had enough time, they would finish the work. [ Type 2 ]
-Unless they had enough time, they would not finish the work.
-If he didn’t go, he could be punished.
-Unless he went, he could be punished.
Variations to Type 2:

5. TYPE 3: IMPOSSIBLE OR CONTRARY TO FACT CONDITION
This type of condition shows that it is contrary to fact. It is called “ Conditional Clause- Type 3 ”.
| If/unless | Subject | Past perfect Had + 3rd form | Subject | Would have Could have Might have | 3rd form |
- If the weather had been bad, we would have canceled the meeting.
- We would have canceled the meeting if the weather had been bad.
Here the meaning implies that we didn’t cancel the meeting and the weather was fine and not bad.
- If they have enough time, they will finish the work. [ Type 1 ]
- If they had enough time, they would finish the work. [ Type 2 ]
- If they had had enough time, they would have finished the work. [ Type 3 ]
Variations to Type 3:

6. IF CAN BE REPLACED BY:
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 848; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!