
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Solution of system of equations using an inverse matrix
|
|
|
|
Let the system (2.1) consist of 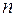 linear equations with
linear equations with 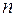 unknowns and its determinant
unknowns and its determinant 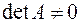 . Write this system in a matrix form as
. Write this system in a matrix form as
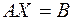 . (2.2)
. (2.2)
Let us multiply both parts (2.2) by the inverse matrix  on the left. Then we obtain
on the left. Then we obtain
 .
.
Since  and
and 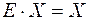 we can get a solution by the formula
we can get a solution by the formula 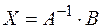 .
.
Let’s illustrate this method by example.
Example 2. Let’s find a solution of the system from example 1 by the matrix method.
Solution. Here  ,
, 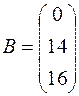 ,
, 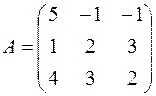 .
.
Let’s calculate the determinant of the given system:

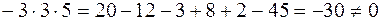 .
.
Its determinant is non-zero. Let’s find the inverse matrix by cofactors:
 ,
, 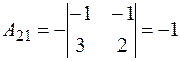 ,
,  ,
,
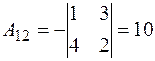 ,
, 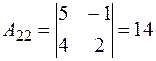 ,
, 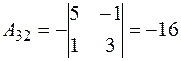 ,
,
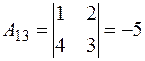 ,
, 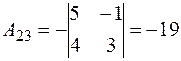 ,
, 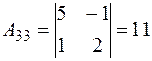 ,
,
 .
.
Let’s check the condition 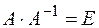 :
:
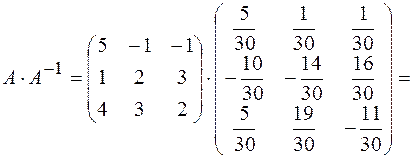

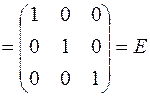 .
.
The solution of given system is 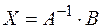 . Then
. Then

 .
.
Thus  ,
, 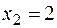 ,
, 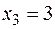 .
.
2.4. Solution of system of equations using Jordan–Gauss method
Definition. Matrices obtained one from another by elementary row operations are called equivalent. The equivalence of matrices is marked by the sign 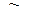 .
.
Jordan–Gauss method is used to solve the system (2.1), which consists of m linear equations with n unknowns. This method includes sequential elimination of unknowns to following scheme.
1. Create an augmented matrix of the given system 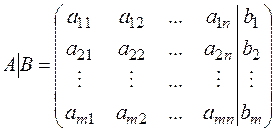 . The augmented matrix is called an array with the matrix
. The augmented matrix is called an array with the matrix 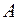 on the left and the matrix-column
on the left and the matrix-column  of free terms on the right and denoted by
of free terms on the right and denoted by 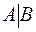 . The vertical line separates the matrix-column
. The vertical line separates the matrix-column  .
.
The leading row and the leading element in 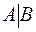 that corresponds to the choice of the leading equation and the leading unknown in the system (2.1) are chosen. The system should be transformed in order to let the leading equation be the first one.
that corresponds to the choice of the leading equation and the leading unknown in the system (2.1) are chosen. The system should be transformed in order to let the leading equation be the first one.
2. The leading unknown by means of the leading equation is eliminated from the other equations. For this the certain elementary row operations of the matrix 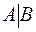 are performed it is possible:
are performed it is possible:
1) to change the order of rows (that corresponds to change of the order of the equations' sequence);
2) to multiply rows by any non-zero numbers (that corresponds to multiplying the corresponding equations by these numbers);
3) to add to any row of the matrix 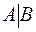 its any other row multiplied by any number (that corresponds to addition to one equation of the system another equation multiplied by this number).
its any other row multiplied by any number (that corresponds to addition to one equation of the system another equation multiplied by this number).
Due to such transformations we obtain an augmented matrix, equivalent to the initial one (i. e. having the same solutions).
On the second step a new leading unknown and a corresponding leading equation are chosen and then this variable is eliminated from all the other equations. The leading row in the matrix 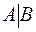 remains without change. After such actions the initial matrix A will be reduced to the triangular (1.1) or truncated-triangular form (1.2) with the elements of the main diagonal equal to 1.
remains without change. After such actions the initial matrix A will be reduced to the triangular (1.1) or truncated-triangular form (1.2) with the elements of the main diagonal equal to 1.
Let’s illustrate this method by example.
According to the method by Jordan–Gauss the leading unknown by means of the leading equation on the current step is eliminated not only from equations of the corresponding subsystem but also from the leading equations on previous steps and on any step the leading unknown has the coefficient equal to 1.
Example 3. Let’s find a solution of the system from example 1 by Jordan-Gauss method.
Solution. By elementary row operations of the augmented matrix, we obtain

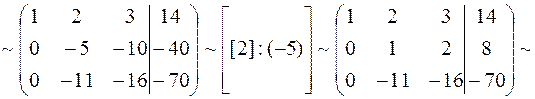

 .
.
A unit matrix on the left of the vertical line is obtained. The column on the right of the vertical line is values of unknown quantities.
Then write down the received augmented matrix as the system of questions:
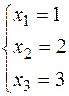 .
.
Thus,  ,
, 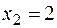 ,
, 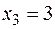 .
.
Let’s solve the initial system using elementary transformations with equations:
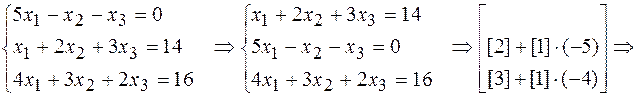

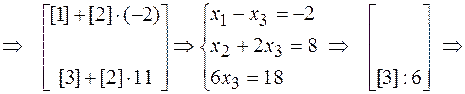
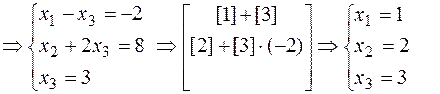
Thus, we obtain the same answer:  ,
, 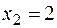 ,
, 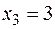 .
.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 574; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!