
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Grammatical Categories. The Use of Cases
|
|
|
|
THE NOUN
The OE noun had two grammatical or morphological categories: number and case. In addition, nouns distinguished three genders, but this distinction was not a grammatical category; it was merely a classifying feature accounting, alongside other features, for the division of nouns into morphological classes.
The category of number consisted of two members, singular and plural. As will be seen below, they were well distinguished formally in all the declensions, there being very few homonymous forms.
The noun had four cases: Nominative, Genitive, Dative and Accusative. In most declensions two, or even three, forms were homonymous, so that the formal distinction of cases was less consistent than that of numbers.
Before considering the declension of nouns, we shall briefly touch upon the meaning and use of cases.
The functions of cases in OE require little explanation for the Russian student, since they are those which ought to be expected in a language with a wel1-developed case system.
The Nom. can be loosely defined as the case οf the active agent for it was the case of the subject mainly used with verbs denoting activity; the Nom. could also indicate the subject characterised by a certain quality or state; could serve as a predicative and as the case of address, there being no special Vocative case, e. g.:

The Gen. case was primarily the case of nouns and pronouns serving as attributes to other nouns. The meanings of the Gen. were very complex and can only roughly be grouped under the headings “Subjective” and “Objective” Gen. Subjective Gen. is associated with the possessive meaning and the meaning of origin, e. g.:

Objective Gen. is seen in such instances as 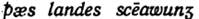 ‘surveying of the land’; and is associated with what is termed "partitive meaning" as in sum hund scipa ‘a hundred of ships’, husa selest 'best of the houses'. The use of the Gen. as an object to verbs and adjectives was not infrequent, though the verbs which regularly took a Gen. object often interchanged it with other cases, cf.:
‘surveying of the land’; and is associated with what is termed "partitive meaning" as in sum hund scipa ‘a hundred of ships’, husa selest 'best of the houses'. The use of the Gen. as an object to verbs and adjectives was not infrequent, though the verbs which regularly took a Gen. object often interchanged it with other cases, cf.:

Dat. was the chief case used with prepositions, e. g.:

The last example illustrates another frequent use of the Dat.: an indirect personal object.
The OE Dat. case could convey an instrumental meaning, indicating the means or manner of an action:
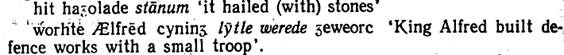
Alongside the Acc., Dat. could indicate the passive subject of a state expressed by impersonal verbs and some verbs of emotion:
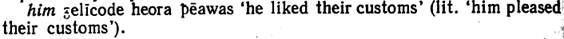
The Acc. case, above all, was the form that indicated a relationship to a verb. Being a direct object it denoted the recipient of an action, the result of the action and other meanings: 94
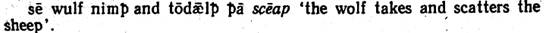
(Its use as an object of impersonal verbs, similar to the use of Dat., is illustrated by

Besides these substantival functions the oblique cases of OE nouns, especially the Acc. case, could be used in some adverbial meanings, e.g. to indicate time or distance:

It is important to note that there was considerable fluctuation in the use of cases in OE. One and the same verb could be construed with different cases without any noticeable change of meaning. The semantic functions of the Gen., Dat. and Acc. as objects commonly overlapped and required further specification by means of prepositions. The vague meaning of cases was of great consequence for the subsequent changes case system.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 781; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!