
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Budget Constraint
|
|
|
|
When goods are “free,” an individual should consume until the MU of a good is 0. This will insure that total utility is maximized. When goods are priced above zero and there is a finite budget, the utility derived from each expenditure must be maximized.
An individual will purchase a good when the utility derived from a unit of the good X (MUX) is greater than the utility derived from the money used to purchase the good (MU$). Let the price of a good (PX) represent the MU of money and the MUX represent the marginal benefit (MBX) of a purchase. When the PX > MBX, the individual should buy the good. If the PX < MBX, they should not buy the good. Where PX = MBX, they are in equilibrium, they should not change their purchases.
Given a finite budget (B) or income (I) and a set of prices of the goods (PX, PY, PN) that are to be purchased, a finite quantity of goods (QX, QY, QN) can be purchased. The budget constraint can be expressed,
B=PxQx + PyQy +…+ PnQn
Where B – budget, Pn – price of Nth good, Qn–quantity of Nth good
For one good the maximum amount that can be purchased is determined by the budget and the price of the good
Qx that can be perchased = Budget/Price=B/Px
The combinations of two goods that can be purchased can be shown graphically. The maximum of good X that can be purchased is B/ Px, the amount of the Y good is B/ Py. All possible combinations of good X and Y that can be purchased lie along (and inside) a line connecting the X and Y intercepts. This is shown in Figure.
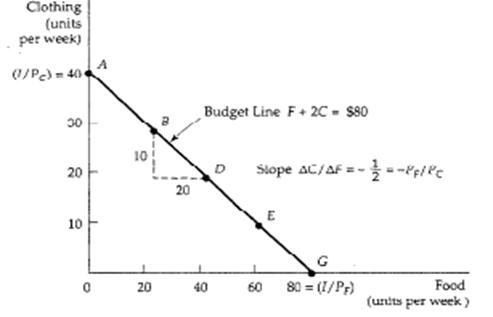
The slope of the budget line equals the ratio of the price of good X on the horizontal axis divided by the price of good Y on the vertical axis.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 464; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!