
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Ответьте на вопросы к тексту. Fabric structures have been in use for a very long time as temporary forms of construction
|
|
|
|
FABRIC
Текст C
Fabric structures have been in use for a very long time as temporary forms of construction. The important characteristics of fabric structures are their flexibility in bending, although the forces that are developed in supports and foundations by fabric structures can be very large. Fabrics require different methods of design compared to the large majority of building structures which are rigid and cannot change shape when the loads change.
Fabrics may be made of mineral fibres, such as glass, organic fibres such as cotton, metal fibres such as stainless steel, or synthetic fibres. A film or coating is usually applied to a fabric so as to improve its properties. A mesh may be used as reinforcement to plastic film. In the latter case the mesh is usually sandwiched between two layers of film and is then known as a reinforced film. Important general characteristics of fabrics and fabric structures compared to other building materials and structures are as follows:
Fabric has moderate to high tensile strength but no effective compressive strength. The strength of the fabric depends mainly on the fibre which is used.
Fabric has a low or zero shear modulus, that is, the material can be made that shears with little or no effort. A fabric which does possess shear stiffness is less tolerant of errors in the design of a structure that is made from it and less easily adapts its shape to changes in load.
Fabric has low weight and a very high strength to weight ratio.
Fabric which is made from synthetic materials loses strength when it is loaded over a period of time. An increase in temperature also causes a loss of strength. A problem with some fabrics, especially fabrics that are made from synthetic fibres, is creep, that is, the constant increase in length of the fabric, under a constant load. Temperature and humidity can increase the creep of some materials.
Fabrics are generally elastic materials. At high load they show some plasticity, that is, they have a permanent extension even after the load is removed. The plasticity is influenced by the rate of loading.
Fabrics can be made reasonably durable, that is reasonably resistant to tears. Tears can exist in a fabric under stress for a long period of time.
Fabric structures may be erected in low temperature conditions. They may also be designed for very quick erection.
The dimensional stability of a coated fabric, that is, the degree to which it changes its dimensions over time and under different conditions depends mainly on the fibre. On the other hand the light transmission, fire resistance, permeability, weathering and durability will depend mainly on the coating in use.
High temperatures decrease the strength and increase the stretch of fabric. On the other hand, low temperatures decrease stretch of the fabric but make it easier for tears to develop. The qualities of most fabrics will not become worse to any significant extent in the range of temperatures from at least - 40°C (- 40°F) to + 60°C (+ 140°F).
Notes:
cotton n. хлопок
dimensional stability стабильность размеров
film n. плёнка
majority n. большинство
mineral fibre минеральное волокно
organic fibre органическое волокно
shear modulus модуль упругости при сдвиге
shear stiffness жёсткость при сдвиге
synthetic adj. синтетический
tear n. разрыв, разрез
zero adj. нулевой
1. How have fabric structures been used?
2. What are the important characteristics of fabric structures?
3. Why do fabric structures differ (отличаться) from most of the other building structures?
4. What are fabrics made of?
5. Why is coating applied to fabric?
6. How is fabric reinforced?
7. What is the strength of fabrics?
8. What are the problems of fabrics made from synthetic materials?
9. What does plasticity of fabric mean?
10. What does dimensional stability of a coated fabric mean?
11. How do high temperatures influence fabric?
12. How do low temperatures influence it?
Лексическое упражнение
В списке А даны некоторые слова и выражения, которые использованы в тексте для домашнего чтения. Найди их правильный перевод в списке В.

II семестр
Урок 2.1
Фонетическое задание
Прочитайте транскрипцию в списке A, соотнесите её с соответствующим словом из списка B и переведите слово на русский язык. Учтите, что не все слова списка В даны в списке А.
A
[pIq]; ['strRtqm]; ['SxlqV]; ['xdIkwIt]; ['mIqlI]; ['jHtIlaIz]; ['neICq]; [flqVt]; ['ekskqveIt]; [In'tWnl]; ['beqrIN]; ['trxnsfW]; ['nesIsqrI]; [faVn'deISqn]
B
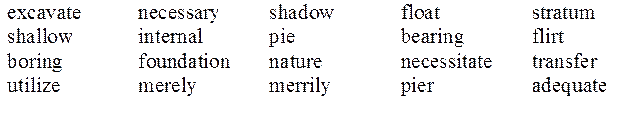
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-16; Просмотров: 1035; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!