
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Foundations
Unit 8
PART III. ARCHITECTURE OF CIVIL BUILDINGS
B) Talk about clear finish varnish coat.
21 Read the text. Make up a dialogue based on the text using the expressions from Appendix 1:
WHAT MAKES a WOOD STAIN “GREEN?”
“Waterborne wood stains are safer than oil-based versions,” according to William and Shari Steber, owners of Timber Pro Coatings, Portland, OR. “Our stains are waterborne or made primarily from bio-preferred, plant-based oils and blended with a small percentage of acrylic to boost durability.”
Ever watched rain drops bead up on a flower petal? That’s the design Timber Pro Coatings tries to mimic. They use natural ingredients because they believe Mother Nature knows the best way to repel water absorption.
Manufacturing environmentally safe wood stains and finishes for 17 years, Timber Pro Coatings was one of the country’s first manufacturers of low toxicity wood stains. The Stebers are fully aware of industry greenwashing, and they make it a point to warn consumers about so-called green terms that are more about marketing than safety.
Shari Steber says, “The term non-toxic does not truly apply to wood stains, because non-toxic would mean you could practically drink or bathe in the product! We consider it dangerous to label a wood stain as non-toxic.”
How can you know you’re getting an eco-friendly stain? The best way is to ask to see the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) on the product. Stores are required to keep a sheet on file for every coating product they sell.
The MSDS will also list the percentage of hazardous ingredients, which should be below 10%. Any wood stain or sealer marked flammable is most likely not eco-friendly. Ideally, clean up should involve only soap and water. The mineral spirits needed to clean your tools and equipment after using flammable oil based stains or sealers are certainly toxic.
22 Topics for projects and presentations:
1. Types of paints and their properties.
2. Qualities of a good paint.
3. Siding stain.
4. Classification of varnishes.
5. Colour perception.
“High buildings have a low foundation.”
Thomas Fuller (writer)
| FOUNDATIONS |

| 
| 
|
| a) raft foundation | b) strip foundation | c) pad foundation |
| LEAD-IN |
1 Match the columns:
| 1. raft foundation | a) is basically a strip, or ribbon, of insitu concrete running under all the loadbearing walls |
| 2. strip foundation | b) is used to support individual point load such as that due to a structural column |
| 3. pad foundation | c) is used to spread the load from a structure over a large area, normally the entire area of structure |
2 a) What is the purpose of foundations? Express your opinion in 3-5 sentences.
Read the following passages and compare your ideas:
1. The main purpose of the foundation is to distribute the structural load over a large bearing area without causing bearing capacity failure and excessive settlement to obtain a level and hard strata or bed for building operations to increase the stability of the structure as a whole.
2. A good strong foundation ensures good strong stable ground for a good strong and lasting structure. If you build a house on sand and the sand around one of the corners of the house washes away due to rain water falling off your building the building will begin to sink in that corner and the result will eventually begin cascading further along the buildings edges and sides until the entire building is consumed by leaning caused by unstable ground.
3. При наших совсем не «плюсовых» зимах слой грунта сверху промерзает. Вода, содержащаяся в нем, замерзает и расширяется. И грунт вспучивается, в зависимости от количества воды в его замерзшем слое. Коэффициент расширения у сильнопучинистых грунтов иногда достигает 12%, а обычно – около 10. Это означает, что при глубине промерзания 1,7 м грунт может приподняться на 10-15 см. Чтобы эти зимние вспучивания не разрушили или не перекосили дом, и нужен фундамент.
L t1UKDXHTtVBSKC5JzEtJzMnPS7VVqkwtVrK34+UCAAAA//8DAFBLAwQUAAYACAAAACEA67N1ZMMA AADcAAAADwAAAGRycy9kb3ducmV2LnhtbESP0YrCMBRE3xf2H8Jd8G2brqJINYorLhQfBKsfcGmu TWlzU5qs1r83guDjMDNnmOV6sK24Uu9rxwp+khQEcel0zZWC8+nvew7CB2SNrWNScCcP69XnxxIz 7W58pGsRKhEh7DNUYELoMil9aciiT1xHHL2L6y2GKPtK6h5vEW5bOU7TmbRYc1ww2NHWUNkU/1ZB vtvnjZzti+Zy/jWbwtXhsNsqNfoaNgsQgYbwDr/auVYwnkzheSYeAbl6AAAA//8DAFBLAQItABQA BgAIAAAAIQDw94q7/QAAAOIBAAATAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABbQ29udGVudF9UeXBlc10ueG1s UEsBAi0AFAAGAAgAAAAhADHdX2HSAAAAjwEAAAsAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALgEAAF9yZWxzLy5yZWxz UEsBAi0AFAAGAAgAAAAhADMvBZ5BAAAAOQAAABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAKQIAAGRycy9zaGFwZXht bC54bWxQSwECLQAUAAYACAAAACEA67N1ZMMAAADcAAAADwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACYAgAAZHJzL2Rv d25yZXYueG1sUEsFBgAAAAAEAAQA9QAAAIgDAAAAAA== ">
| “A successful man is one who can lay a firm foundation with the bricks others have thrown at him. “ (David Brinkley) |
| “The loftier the building, the deeper must the foundation be laid.” (Thomas Kempis) |
• Write a paraphrase. • Say whether you agree or not, and why.
| READING |
4 a) Transcribe the following words:
drought, load-bearing, strength, weight, artificial, endanger, plumbing, superimposed, depth, specific.
b) In what context do you think the following words and phrases will appear in the text?
•ground level •stability •protection •natural foundation •artificial foundation •loads and pressure •concrete •specific conditions of the building •types
c) Read the text quickly and check your answers:
The foundation is the part of the construction where the base of the building meets the ground.
Foundations are usually placed below ground level because the surrounding ground provides:stability, protection against impact, protection from the extremes of weather such as excessive rain or drought.
Although the depth will vary according to the conditions on site, the best load-bearing ground is normally 900 mm below the surface.
The choice of foundation depends on:
a) the strength of the natural foundation;
b) the weight of the building and its loads.
Foundations are divided into two types:
1. The natural foundation. This is the ground underneath the base of the building after the excavations are completed;
2. The artificial foundation. This is the structure that lies between the building and the natural foundation.
An artificial foundation transfers the loads from the building to the ground. This prevents settlement or building movement, which might cause instability and endanger the occupants.
The following building loads place the most pressure at the bottom of the building, where the artificial foundation is located (Figure 8.2):
i. Dead loads. These are the weights of all the fixed parts of the building such as the walls, floors, roofs, ceilings and services such as sanitary fittings and plumbing;
ii. Superimposed or live loads. These are the weights of the people, furniture and machines that will occupy the building after the completion;
iii. Wind loads. These are the pressures on the walls and roof from the wind. The pressure from wind loads on foundations is more important in tall buildings.
The artificial foundation lies between the natural foundation and the building. Its purpose is to: transfer the building loads to the soil and spread the load evenly across soil that can support the load.
When choosing the correct type of artificial foundation the following conditions should be considered:
1. the load-bearing capability of the ground;
2. the depth where the suitable load-bearing soil can be founded;
3. the distance from trees which can affect the stability of the soil;
4. the level of the water table;
5. the normal variation in the water table;
6. the total weight of the building. If the building is heavier than the soil that was removed, then there will be some settlement as the soil adjusts to the new load.
Although concrete is the preferred material for the construction of the artificial foundations, the form will depend on the specific conditions of the building and environment.
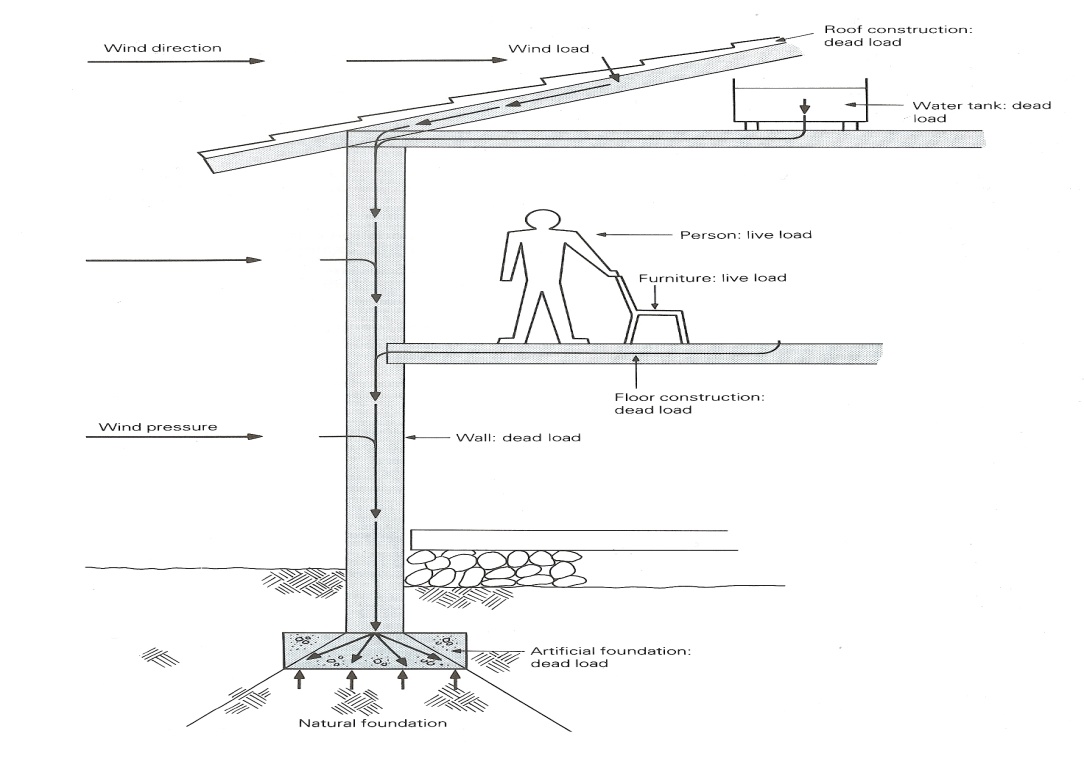
Figure 8.2 Loads on natural and artificial foundations
Types of Foundation
Many small buildings are constructed with load-bearing walls on strip foundations. But you may find out that the soil requires alternative types of foundation which are:
- concrete strip foundation;
- deep strip foundation;
- raft foundation;
- piled foundation;
- pad foundation;
- stepped strip foundation.
5 Read the text again and answer the questions that follow (1-5):
1. Give the definition of the term “foundation”.
2. What building loads does artificial foundation carry?
3. What is the purpose of artificial foundation?
4. What are the principle conditions when choosing the correct type of a foundation?
5. What types of foundations have you read about?
Follow-up
6 a) Find the synonyms for the following words:
foundation, to be placed, protection, excessive, to be completed, natural, artificial, settlement, to occupy, to cause, purpose, to support, to transfer, to be considered, environment, to be constructed, to require.
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 1305; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!