
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Part III. Short-bored piled foundations are used 1)_____ small houses and lightweight framed buildings constructed 2) _____ soils that expand and contract 3) _____
|
|
|
|
TYPES OF FOUNDATION
Short-bored piled foundations are used 1)_____ small houses and lightweight framed buildings constructed 2) _____ soils that expand and contract 3) _____ changes in the moisture content. These soil types include clay and black cotton.
The type of foundation shown in Figure 8.8 can be constructed quite quickly and avoid the need to dig deep trenches. Short-bored piles are more effective and cheaper than conventional foundations if the soil responds easily to the changes 4) _____ the atmosphere.
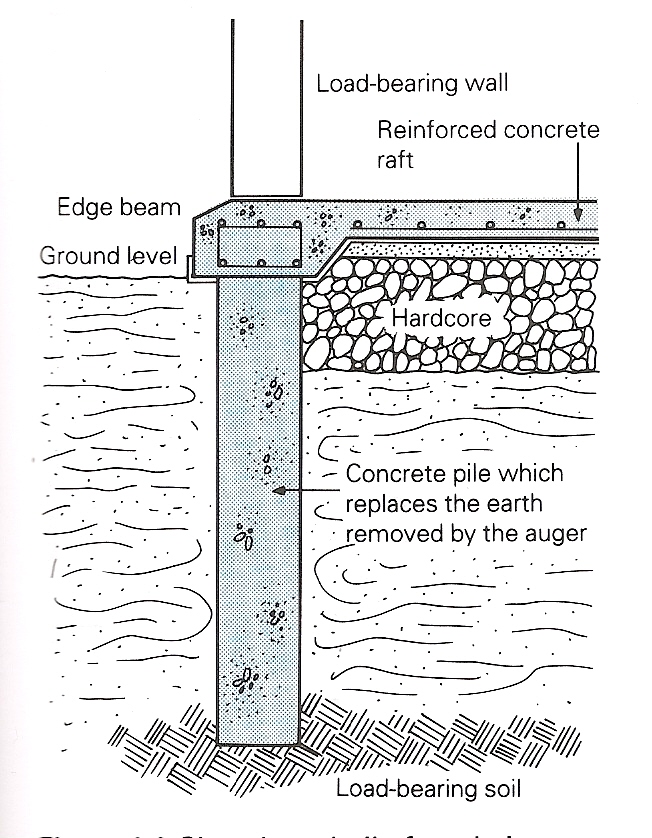
Figure 8.8 Short-bored Pile Foundation
These foundations are not suitable 5) _____ use on rock, flint or sites with many tree roots because the holes must be straight and consistent in diameter.
The holes are dug 6) _____ hands with an auger and then concrete is poured 7) _____ them to form a column in the ground when it hardens. The concrete columns in the holes in the ground are the piles.
The measurements in Table 8.1 are typical dimensions for short-bored piles.
Table 8.1 Measurements for Short-bored Piles
| Components | Measurements (mm) |
| Depth of the hole for the piles | 2500-3000 |
| Pile diameter | 250-360 |
| Pile spacing | |
| Beam width for 225 mm wall | |
| Beam depth for 225 mm wall | 150-200 |
| Reinforcement diameter | 15 mm with 6 mm stirrups |
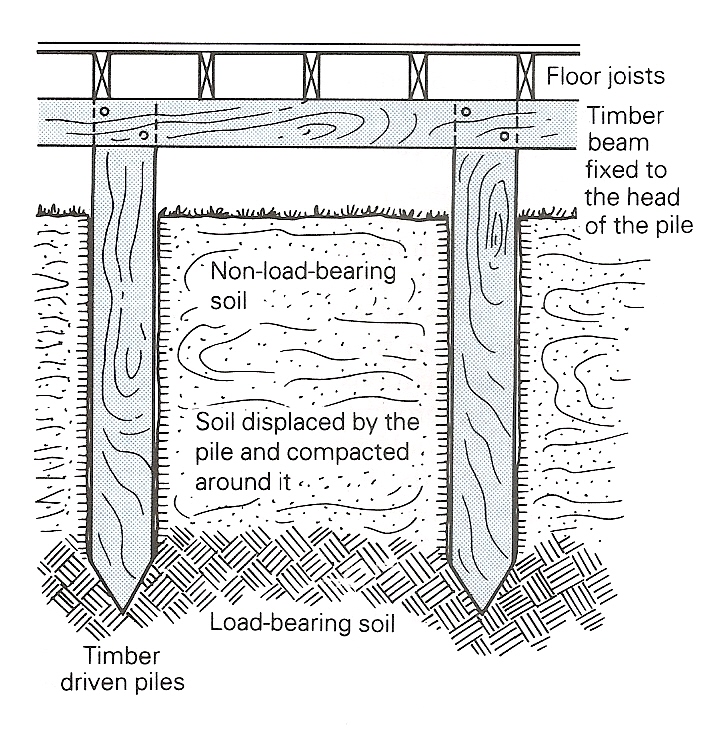
Figure 8.9 Timber Displacement Piles
Figure 8.9 represents timber displacement piles for lightweight buildings. For this foundation straight tree trunks should be used and treated with preservative and sharpened 8) _____ the ends to drive them 9) _____ the ground. It is better to use an auger to remove some 10) _____ the pile-driving process is started.
| at before by for(x2) in(x2) into on with |
12 Match the English terms (B) and their definitions (A).
There are two extra terms in column B:
| A | B |
| a) lowest load-bearing part of a building, typically below ground level | 1. load 2. concrete 3. water table 4. ground 5. foundation 6. pile 7. trench 8.pressure 9.measurement 10. clay |
| b)the size, length, or amount of something | |
| c) a weight or source of pressure borne by someone or something | |
| d) the level below the surface of the ground where water can be found | |
| e) a long narrow channel that is cut into the ground, for example in order to lay pipes or get rid of water | |
| f) a stiff, sticky fine-grained earth that can be moulded when wet, and is dried and baked to make bricks, pottery, and ceramics | |
| g)building material made from a mixture of broken stone or gravel, sand, cement, and water, which can be spread or poured into moulds and forms a stone-like mass on hardening | |
| h)a heavy stake or post driven vertically into the bed of a river, soft ground, etc., to support the foundations of a superstructure |
13 a)Fill in the table with the information from the text given and your additional info:
| Foundation | Material | Measurements | Application | Additional Info |
b) Say whether these statements are true (T) or false (F):
1. The natural foundation is the ground underneath the artificial foundation.
2. Artificial foundations ensure the stability of the building.
3. Load-bearing walls require strip or deep strip foundation.
4. Columns and piers require pad foundations.
5. Light loads or poor soil conditions require raft foundations.
6. Very poor conditions such as clay and sand require piled foundations.
7. The size of a foundation is determined by the pressure of the load and the strength of the soil.
8. Stepped foundations are used on sloping sites to reduce costs.
9. Piles can be: replacement piles at that are concrete-filled holes; displacement piles that are timbers driven into the ground.
| LISTENING |
14 Audio “How to Lay Foundations”.
Listen to the information twice and be ready to answer the questions below (1-7):
1. Is it a hard job to dig a foundation?
2. Why is it necessary to dig a foundation properly?
3. What main instruments and materials are needed for foundation digging?
4. What are the parameters of footings for small walls?
5. How are trenches marked?
6. For what period should concrete be dried?
7. What are the main steps of foundation laying?
| VIDEO |
15 Watch the video and present the main idea of each episode in 4-5 sentences using the expressions from Appendix 2.
| WRITING |
16 Render the text in English using the expressions from Appendix 2:
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 3424; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!