
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
B) Explain the words in bold from the text and make up sentences of your own. Use English-English dictionaries to help you
|
|
|
|
ROOFS
Unit 9
| ROOFS |
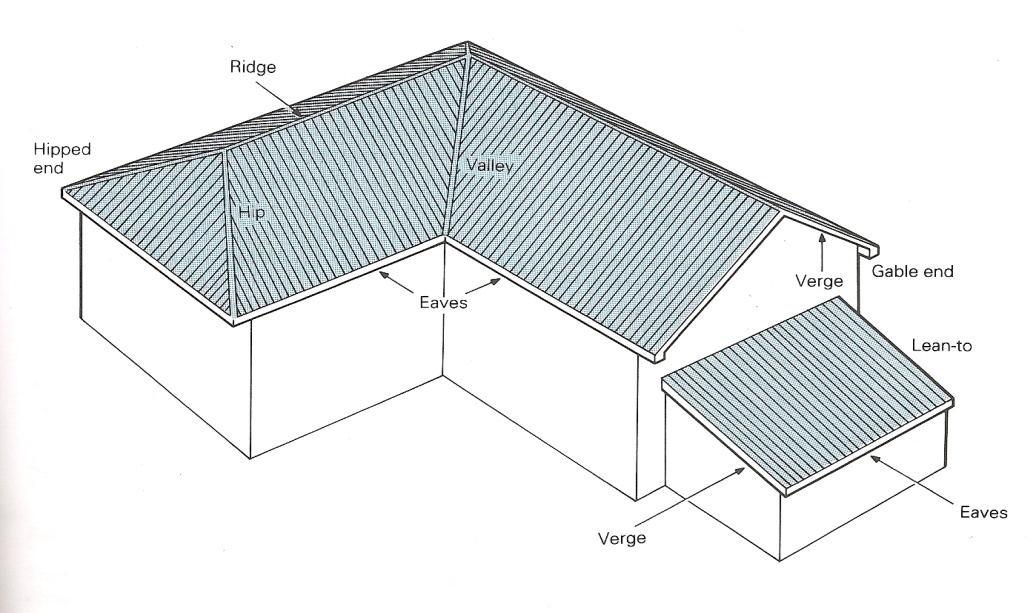
Figure 9.1 Pitched Roof Structure
1 Match the columns to remember some technical words for parts of a roof.
Figure 9.1 may help you:
| 1. covering | a) a thin timber board that is fixed to the end of rafters or roof joints to support the gutters |
| 2. eaves | b) a short rafter that spans the hip and eaves or valley and ridge |
| 3. fall | c) the horizontal board that can be fixed to finish the roof structure at the eaves |
| 4. fascia | d) it can be: a) a horizontal timber member that provides support to the rafters; b) a timber member spanning between roof trusses that supports roof sheets |
| 5. hip | e) the horizontal distance between the supports of structural members such as the rafters |
| 6. jack rafter | f) the timber member fixed to the top of a wall to secure a flat roof joist or rafter |
| 7. pitch | g) the timber member that spans from the eaves to the ridge in a pitched roof |
| 8. purlin | h) a timber at the apex of the roof that takes the tops of the rafters |
| 9. rafter | i) the bottom end of the roof where it meets the wall |
| 10. ridge | j) the point where two inclined roof surfaces meet over an internal angle |
| 11. ridge tile | k) the external material that is laid over the roof structure to protect the inside of the building |
| 12. soffit | l) the edge of a roof that meets a gable wall |
| 13. span | m) a tile that caps the top of the roof |
| 14. valley | n) the angle formed by the slope of the roof |
| 15. verge | o) the slope required on flat roofs for water run-off |
| 16. wall plate | p) the point where two inclined roof surfaces meet over an external angle |
2 a) What types of roofs do you know? Use English-English dictionaries.
b) Look at the pictures. What roof would you prefer for your house? Explain your choice in 3-5 sentences:

| 
|
a) Cross Gabled Roof b) Arched Roof

| 
|
c) Mansard Roof d) Pyramid Roof
3 Discuss the following:
| Rain does not fall on the roof alone. (Proverb) |
| “Compromise makes a good umbrella but a poor roof.” (James Russell Lowell) |
• Write a paraphrase. • Say whether you agree or not, and why.
| READING |
4 a) Transcribe the following words:
retain, ensure, weighted, storage, triangular, require, joists, corrugated, securely.
b)In what context do you think the following words and phrases will appear in the text?
• topmost part • interior cool • resisting fire • supporting structure • storage space • gable end • meet right angles • water-proof covering •corrugated sheets • galvanized steel ties• rafter
3 Read the text and check your answers:
A roof is the topmost part of a building. It is a covering constructed over the enclosed space to:
- keep out rain and wind;
- provide shade from the sun;
- keep the interior cool;
- retain heat in cool weather;
- ensure that the structure is properly weighted down.
Roofs should meet the following basic standards of performance: 1) allowing rainwater to flow freely away; 2) expanding and contracting without failure; 3) resisting fire adequately; 4) providing light and ventilation; 5) durability.
In this unit two types of roofs are considered: pitched roofs and flat roofs.
A pitched roof is often a popular choice. The main supporting structure is timber, which is easy to work and transport. A pitched roof is stablein most weather and its slope disposes of rainwater quickly. Additionally, the space enclosedby the roof can add some extra living or storage space.
In simple roof construction these types of roof are usually found:
| Gable roof In this type of roof the ends of the roof enclose the end walls. The triangular wall between the roof verges is called the gable end. | 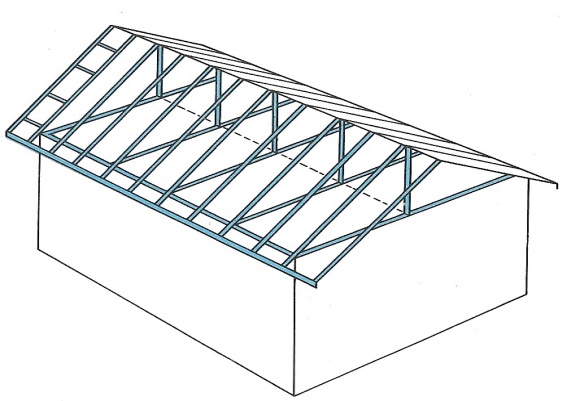
|
| Hipped roof A hipped roof is formed when two roof slopes meet right angles. | 
|
| Lean-to roof This roof has a single pitch that rests against a higher wall. | 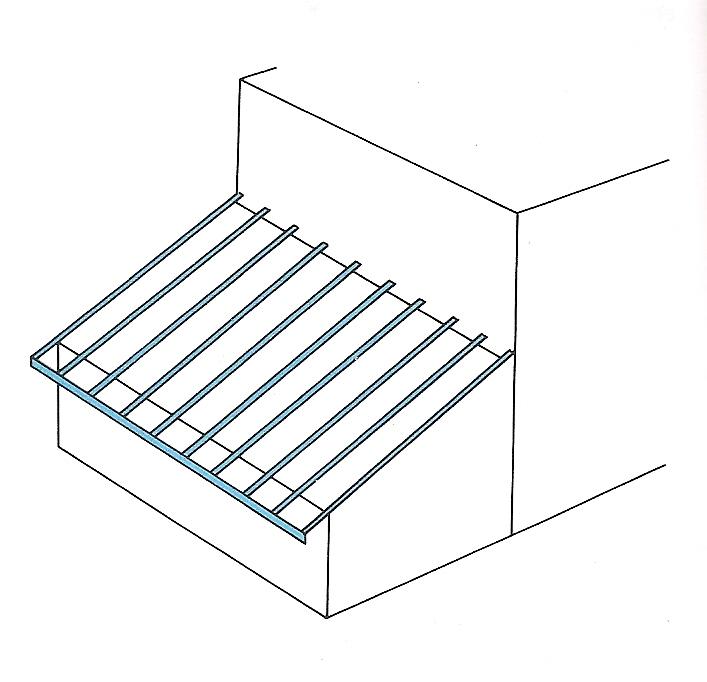
|
| Mono-pitch roof This roof has a pitch in one direction. The ridge does not rest against anything. | 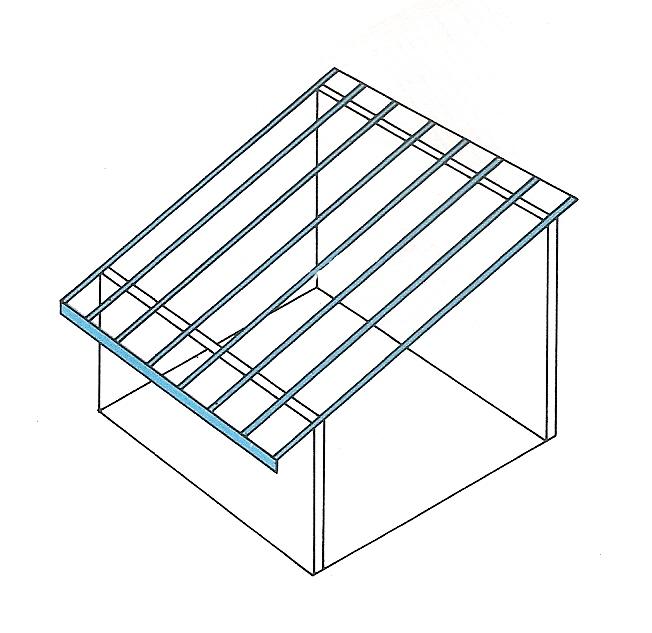
|
Three parts of a pitched roof affect the structural design: span; pitch; roof covering.
The span is the distance between the masonry structures that support the roof. The structure of the roof becomes more complex as the span increases.
The pitch is the angle of the slope of the roof measured from the horizontal. A steeper pitch needs more roof covering material, which increases the weight to be supported. The surface area affected by wind is also greater. The roof needs to be strong enough to allow for these factors.
The roof covering material varies from lightweight sheets that weigh 12 kg/m2 to plain clay tiles that weigh 65 kg/m2.
Flat roofs, which can be timber or reinforced concrete, are popular forms of roofing for houses. Their advantages are:
- they are very easy to put up;
- they can create extra usable space if they are accessible;
- they are easily maintained.
Their main disadvantages are that:
- they lose heat;
- they are not as weatherproof as pitched roofs;
- the finishes do not last as long as roof tiles.
The structure of a flat timber roof is shown in Figure. 9.2. and it requires: a deck or a slab; a method for disposing of rainwater; a watertight covering; some insulation.

Figure 9.2 Flat Timber Roof Structure
The joists span between the supporting walls and boarding is fixed over the joists to form a deck for the water-proof covering. Here the deck must have enough slope to get rid of rainwater. Slopes can be made by fixing strips of wood called firrings to the top of the joists.
Wind pressure can strip off tiles, lift overhanging eaves and verges and blow off corrugated sheets. If the roof covering is fixed very securely to the roof framework, then a strong wind could lift off the timbers of the roof structure.
This can be prevented by using galvanized steel ties every 1800 mm. They should be taken across the wallplate and down the wall for 600 mm and embedded in mortar joint. The ties can also be taken around the rafters to secure the roof structure against the lifting action of wind.
5 Read the text again and answer the questions that follow (1-8):
1. What are the purposes of roof construction?
2. There are five basic standards of performance, aren’t there? What are they?
3. How many types of roofs are considered in this unit? Name them.
4. How can you characterize types of roofs in simple roof construction?
5. What affects the structural design of a pitched roof? Describe these parts.
6. What are the advantages/ disadvantages of flat roofs?
7. What forms a deck for the water-proof covering?
8. Can you offer the ways how to cope with wind pressure?
Follow-up
6 a) Find the synonyms in the text and rephrase the sentences using them:
construction, coating, satisfy criteria, to take into consideration, firm (strong), inclosed, besides, general forms, available, demand, to rid oneself of, impacted.
7 Give the English equivalents to the following and use 5 of them in small situations:
покрытие (обшивка); удерживать тепло; утеплять; удовлетворять основным стандартам; без повреждений; обеспечивать доступ света и вентиляции; несущая/ опорная конструкция; дополнительное пространство; края крыши; два уклона образуют прямой (90°) угол; опираться на стену; влиять на строительное проектирование; плоская керамическая черепица; виды кровли; легко построить; легко содержать и обслуживать; стойкий против атмосферных влияний; водонепроницаемое покрытие; изоляция; несущая стена; обшивка досками; оцинкованный; стенная балка; заделанный в раствор; вокруг стропила.
8 Read and translate the text and make 5 questions to it:
What most home owners desire is a roof that is not too expensive, requires no maintenance, and lasts forever. But most roofs are replaced - or at least repaired - every ten years. By carefully choosing your home's roofing material, you can reduce the cost of replacement.
You can realize other environmental benefits from your roofing choices. If you select a light-colored surface or a material that does not absorb heat from the sun, you significantly reduce your home's cooling needs. When your attic stays cooler, your cooling bills go down.
There is a wide choice of materials used to roof a house, ranging from thatch – dried grass, to slate – pieces of stone. Modern products like plastic, fiberglass and concrete are available, and some innovative, energy-efficient homes are being roofed with sod. New products are being developed to overcome the shortcomings of older roofing materials, meet the demands of modern building techniques, and conform to increasingly stringent building codes.
Cost alone does not determine quality. But by carefully selecting the right material, making sure it's installed properly and performing modest maintenance occasionally, you can have a roof that functions properly for 20 to 50 years – or even longer.
| LANGUAGE FOCUS |
9 Use the words below to complete the sentence:
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 3067; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!