
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Test yourself
|
|
|
|
Public Speaking
TYPES OF DIODES
Making presentations
5. Make a presentation on the topic: “Types of diodes”. You may present all types of diodes, or two of them to compare, or just the only one. Use the information in the table to help you.
| How do I start? | · You could grab your audience's attention by starting with a question or a challenging statement. Use pictures or objects. So, how much do you know about...? Have you ever asked yourself why...? What I'm going to tell you about today will change the way you think about... Pass around the picture/object. What do you think it is? |
| How do I organize the presentation? | · Make it short. Write down the points you want to make, edit them, then decide which order you are going to make them in. Introduce each point with an expression from the list below. The first/key thing to say about _________ is... The main point to make about _________ is… What you really need to know about__________ is... Now let's look at... Let's turn to/move on to... Another interesting thing to say about__________ is... Finally, I'd like to say a few words about... |
| What do I say? | · After introducing the point, add information briefly in two, three, or, at the most, four sentences. Use markers like the ones below to construct long, well-balanced sentences. Anyway...; Naturally...; Of course... Similarly...; Surprisingly …; Remarkably... Despite...; However...; Although...; Whereas... Consequently...; In addition...; Moreover...; Furthermore... Incidentally...; By the way...; It's worth noting that... |
| How do I finish? | · Conclude the presentation by briefly summarizing what you have said, or the points you have made. You could end by asking for comments or questions. In conclusion...; To sum up... So, remember that……..is all about ……., and... So, there are three things to remember about… Does anybody have any questions? |
1. Deliver your presentations on different types of diodes.
2. Match the definitions 1 – 9 with the types of diodes in the Fig. 2.6.
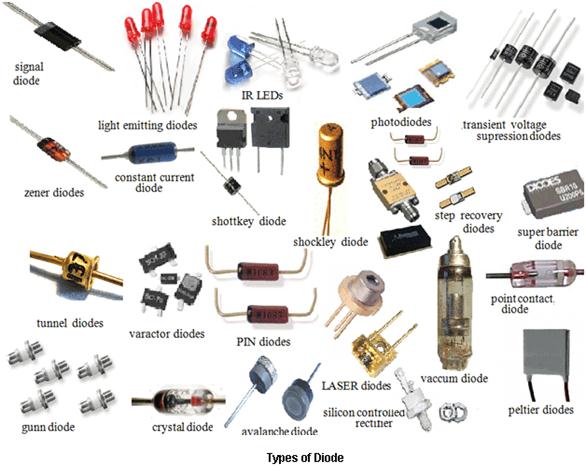
Fig. 2.6.Types of diodes.
1) ……………. is also called snap-off diode or charge-storage diode or memory varactor that has the ability to generate extremely short pulses and is used in microwave electronics as pulse generator or parametric amplifier.
2) ……………. is also known as a transferred electron device (TED) and used in high-frequency electronics. Its internal construction is unlike other diodes, it consists only of n-doped semiconductor material.
3) ……………. is a diode which allows current to flow in the forward direction in the same manner as an ideal diode, but will also permit it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as the breakdown voltage.
4) …………… uses the barrier formed between a specially prepared semiconductor surface and a metal point to produce the rectifying action.
5) …………… allow a current through them to rise to a certain value, and then level off at a specific value. Unlike Zener diodes, these diodes keep the current constant instead of the voltage constant. These devices keep the current flowing through them unchanged when the voltage changes.
6) …………… is used to protect sensitive electronics from voltage spikes induced on connected wires. It is a clamping device, suppressing all overvoltages above its breakdown voltage.
7) …………… incorporate the low forward voltage drop of the Schottky diode with the surge-handling capability and low reverse leakage current of a normal p–n junction diode.
8) ……………. is capable of very fast operation, well into the microwave frequency region, by using the quantum mechanical effect called tunneling.
9) ……………. emits invisible light when an electric current passes through it.
3. Do this multiple choice test on types of diodes.
1) Light-emitting diodes are:
a) used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for other lighting;
b) capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation.
2) Laser diode:
a) acts as a heat pump which can cool or warm when current is passed through it;
b) produces coherent radiation in the visible or infrared (IR) spectrum when current passes through it.
3) Varactor diode is
a) a type of diode whose capacitance varies as a function of the voltage applied across its terminals;
b) a specialized diode that has a layer of intrinsic semiconductor material between the P and N materials.
4) Schottky diode is:
a) designed to pass very small currents, and have several applications in signal processing;
b) also known as hot carrier diode with a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action.
5) A Shockley diode is:
a) identical to a thyristor with its gate left disconnected;
b) is a two-electrode vacuum tube.
6) A Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR) is:
a) designed to go through avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage;
b) a four-layer solid state current controlling device.
4. Match the types of diodes with their electronic symbols. The symbol used for a semiconductor diode in a circuit diagram specifies the type of diode.
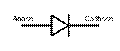
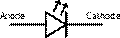
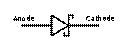
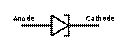


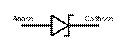

| Tunnel diode Varicap Schottky diode Transient voltage suppression (TVS) diode Light - emitting diode (LED) Diode Zener diode Photodiode |
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 517; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!