
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Stock markets
|
|
|
|
I. READING
THE STOCK MARKET
FINANCIAL MARKETS.
1. Stress the first syllable:
stock, origin; principal, turnover, orderly, rapid, tangible, arbitrage, barrier, dealer, retail, segment, integrate, client, tangible.
2. Stress the second syllable:
expansion, sophisticated, increasingly, provide, emerge, development, attract, quotation, contain, facility, allow, conduct, establish, reliable, appearance, ensure.
3. Stress the third syllable:
isolation, indication, popularity.
4. Read the text:
Stock Markets are the means through which securities are bought and sold. The origin of stock markets goes back to medieval Italy1. During the 17th and 18th centuries Amsterdam was the principal centre for securities trading in the world. The appearance of formal stock markets and professional intermediation resulted from the supply of, demand for and turnover in transferable securities. The 19th century saw a great expansion in issues2 of transferable securities.
The popularity of transferable instruments as a means of finance continued to grow and at the beginning of the 20th century there was an increasing demand for the facilities provided by stock exchanges, with both new ones appearing around the world and old ones becoming larger, more organized and increasingly sophisticated.
The largest, most active and best organized markets were established in Western Europe and the United States. Despite their common European origins there was no single model which every country copied.
Members of stock exchanges drew up rules to protect their own interests and to facilitate the business to be done by creating an orderly and regulated marketplace.
Investors were interested in a far wider range of securities3 than those issued by local enterprises. Increasingly, these local exchanges were integrated into local markets.
The rapid development of communications allowed stock exchanges to attract orders more easily from all over the country and later the barriers than had preserved the independence and isolation of national exchanges were progressively removed, leading to the creation of a world market for securities. The 1980s saw the growing internationalization of the world securities markets, forcing stock exchanges to compete with each other. Cross-border trading of international equities expanded.
Although many securities were of interest to only a small and localized group, others came to attract investors throughout the world. Increasingly, arbitrage between different stock exchanges ensured that the same security commanded the same price4 on whatever market it was traded. London, Paris, New York became dominant stock exchanges.
Stock exchanges emerged as central elements in the financial systems of all advanced countries.
Potential investors, insurance companies, pension funds, governments and corporate enterprises see securities as a cheap and convenient means of finance.
An investor who purchases new securities is participating in a primary financial market. An investor who resells existing securities is participating in a secondary financial market.
There are two basic types of stock markets – (1) organized exchanges, like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the London Stock Exchange (LSE), and (2) the less formal over-the-counter markets.
The organized security exchanges are tangible physical entities, which have specially designated members5 and elected governing bodies – boards of governors.
In contrast to be organized security exchanges, the over-the-counter market is an intangible organization. It is a network of security dealers who buy and sell securities from each other, either for their own account or for their retail clients. The over-the-counter market is normally conducted by telephone and computer reporting of price quotations between brokerage firms that “make a market”: that is, agree to buy and sell a particular security. Securities that are not listed on exchanges are traded “over-the-counter”. In general these include stocks, preferred stocks, corporate bonds, and other securities.
Investors need complete and reliable information about stocks and markets. In addition to the listings, the financial pages of newspapers in all countries contain price quotations and share indexes which give a broad indication of how the stock market, or a segment of the stock market, performed during a particular day.
NOTES:
[1] The origin of stock markets goes back to medieval Italy. – Зародження фондового ринку відноситься до епохи середньовічної Італії.
2 The 19th century saw a great expansion in issues. – В 19 столітті спостерігалось різке збільшення випуску цінних паперів.
3 were interested in a far wider range of securities. – проявляли інтерес до набагато більшої кількості цінних паперів
4 the same security commanded the same price. - однакові цінні папери продаються за однаковою ціною.
5 The organized security exchanges are tangible physical entities, which have specially designated members... – Організовані фондові біржі є реально існуючими економічними суб’єктами, що мають конкретних членів.
¤ VOCABULARY LIST
stock market – фондовий ринок
origin – походження, зародження
intermediation – посередницька діяльність
transferable securities – цінні папери, які можуть бути переуступлені іншій особі
facilities – послуги
sophisticated – більш сучасний, удосконалений
facilitate – полегшити
draw up – складати
orderly – упорядкований
increasingly – все більше і більше
allow – дозволяти, робити можливим
isolation – ізоляція, відособлення
lead – приводити
force – примушувати
cross-border trading – міжнародна торгівля
expand – поширюватись, розвиватись
emerge – виникати, з’являтися
advanced countries – розвинуті країни
dealer – дилер, позабіржовий торговець
equity – звичайна акція
expand – поширюватися, розвиватися
arbitrage – арбітражні операції
ensure – забезпечувати
over-the-counter market – позабіржовий ринок
for smb’s account – за чийсь рахунок
retail client – дрібний клієнт
conduct – керувати
price quotation – котирування цін
list – вносити в курсовий бюлетень
preferred stocks – привілейовані акції
reliable – надійний
listing – допуск цінного паперу до офіційної торгівлі на фондовій біржі
share index – фондовий індекс
? ІІ. VOCABULARY EXERCISES
Ex.1. Find equivalents:


Ex.2. Find English equivalents for the following Ukrainian phrases:
цінні папери продаються і купуються; головний центр торгівлі цінними паперами; фондовий ринок з’явився в результаті...; не існувало єдиної моделі; складати правила для захисту чиїхось інтересів; полегшити ведення бізнесу; упорядкований регульований ринок; цінні папери, що виготовлені місцевими підприємствами; місцеві біржі були об’єднані в загальнонаціональні фондові ринки; міжнародна торгівля цінними паперами поширилась; позабіржовий ринок; купувати та продавати цінні папери за свій рахунок; позабіржовий ринок здійснює операції по телефону і за допомогою комп’ютерів; цінні папери, що не зареєстровані на біржі.
Ex.3. Fill in the blanks with prepositions, pronouns or conjunctions:
1.Stock Markets are the means... which securities are bought... sold.
2.The appearance... formal stock markets... professional intermediation resulted... the supply of, demand for... turnover... transferable securities.
3.Members... stock exchanges drew up rules... protect their own interests... to facilitate the business to be done by creating an orderly... regulated marketplace.
4.The rapid development... communications allowed stock exchanges... attract orders more easily... all over the country.
5.Stock exchanges emerged … central elements … the financial systems … all advanced countries.
6.An investor … purchases new securities is participating … a primary financial market.
7.An investor … resells existing securities is participating … a secondary financial market.
8.Over-the-counter market is a network … security dealers … buy … sell securities … each other, … for their own account … … their retail clients.
9.Investors need complete … reliable information … stocks … markets.
10. The financial pages … newspapers … all countries contain price quotations … share indexes … give a broad indication … how the stock market, … a segment … the stock market, performed during a particular day.
Ex.4. Fill in the blanks below with the appropriate terms from the list:
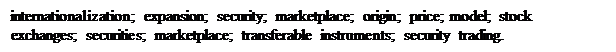
1.The _________of stock markets goes back to medieval Italy.
2.During the 17th and 18th centuries Amsterdam was the principal centre for ________ in the world.
3.The 19th century saw a great ___________ in issues of transferable securities.
4.The popularity of _____________ as a means of finance continued to grow and at the beginning of the 20th century.
5.Despite common European origins of the markets there was no single __________ which every country copied.
6.Members of stock exchange drew up rules to protect their own interests and to facilitate the business to be done by creating an orderly and regulated _____________.
7.The 1980s saw the growing ____________ of the world securities markets, forcing stock exchanges to compete with each other.
8.Arbitrage between different stock exchanges ensured that the same __________ commanded the same __________ on whatever market it was traded.
9.London, Paris, New York became dominant _________.
Ex.5. Complete the following sentences:
1. Stock Markets are ….
2. The rapid development of communications … to attract …..
3. Stock exchanges emerged as ….
4. An investor who purchases new securities is ….
5. An investor who resells existing securities is ….
6. There are two basic types of stock markets: ….
7. The organized security exchanges are …, which have ….
8. Securities that … are traded “over-the-counter”.
9. Securities which are traded “over-the-counter” include ….
10. Investors need … about stocks and markets.
11. The financial pages of newspapers contain … which ….
Ex.6. Answer the following questions:
1.What is the Stock Market?
2.What contributed to the emergence and growth of stock exchanges?
3.Where were best organized stock markets established?
4.What general trend in the stock market development has been observed over the years of its existence?
5.What stock exchanges have become most dominant?
6.What part do stock exchanges play in the financial systems of advanced countries?
7.How do investors participate in the primary and secondary financial markets?
8.What are the basic types of stock markets? How are they conducted?
9.What are the dominant stock exchanges now in the world?
Ex.7. Translate into English:
1. Фондові біржі є засобами, за допомогою яких продаються або купуються цінні папери.
2. Швидкий розвиток засобів зв’язку дозволив фондовим ринкам залучати більше клієнтів та створити світовий фондовий ринок.
3. Лондон, Париж, Нью Йорк стали домінуючими фондовими біржами.
4. Фондові біржі виникали як центральні елементи у фінансових системах усіх розвинених країн.
5. Потенційні інвестори, страхові компанії, пенсійні фонди, державні та приватні підприємства вбачають у цінних паперах дешевий та зручний засіб фінансів.
6. Інвестор, який купує нові цінні папери бере участь у первинному фінансовому ринку, а інвестор, який перепродає цінні папери – у вторинному фінансовому ринку.
7. Існує два основних типи фондових бірж: організовані біржі та менш формальні, неорганізовані.
8. Позабіржовий ринок – мережа надійних дилерів, які купують та продають цінні папери один в одного або для власної вигоди, або ж для дрібних клієнтів.
9. Цінні папери, які не внесені до курсового бюлетеню на біржах, продаються на позабіржовому ринку. Вони включають: акції, привілейовані акції, корпоративні облігації та інші цінні папери.
10. Інвестори потребують повну на надійну інформацію про акції та ринки.
Ex.8. Match each term in Column A with its definition in Column B:

Ex.9. Write several paragraphs on the following using given words and word combinations:
a) the appearance of formal stock markets:
professional intermediation; supply of; demand for; transferable securities; stock exchanges.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 623; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!