
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
ТЕКСТ Б Mining and Geological Higher Education in Russia
|
|
|
|
А) Выберите нужную форму глагола из приведенных в скобках.
My name (is, was, am) Victor Sedov. I (is, am, was) seventeen years old. I (is, was?am) a first-year student of the mining college. Our college (is, are, was) in th е centre of the town.
I (have, has, had) a lot of friends at the college. After the course of studies we (shall, will,are going to become mining engineers.
My grandfather (were, was, will be) a mining engineer too. He (was,
had, is, have) a student of the Moscow Mining Academy many years ago.
It (had, was, were) one of the best-known educational institutions in the
Soviet Union.It (has,had,is) well-equipped laboratories and alibrary
with many volumes Russian and foreign books and journals on
geology and mining. '
б) Расскажите о себе, используя слова и выражения из а).
20. Побеседуйте с вашим другом о Московской горной академии. Спроси
те, какие там были факультеты; как развивалась научная деятельность; каково
значение академии в развитии горного дела в стране. Используйте активную
лексику урока, вопросительные слова, а также разговорные формулы иа с. 20.
|
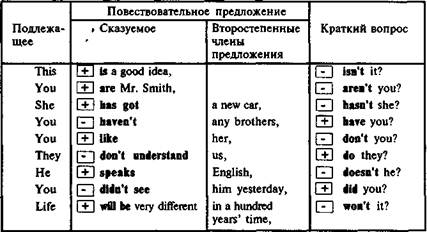
| ГРАММАТИКА Разделительный вопрос |
Разделительный вопрос, как показано в таблице, состоит из утвердительного или отрицательного предложения и краткого вопроса, имеющего то же подлежащее, что и предложение (всегда местоимение), и вспомогательный глагол.
Если предложение отрицательное, то краткий вопрос утвердительный, и наоборот — если предложение утвердительное, то краткий вопрос содержит отрицание. (См. знакиЩиОв таблице.) Краткий вопрос переводится на русский язык обычно как «не так ли», «не правда ли». Последнее предложение в таблице следует перевести: «Жизнь через 100 лет будет непохожей на нынешнюю, не правда ли?» (Переведите самостоятельно остальные примеры в таблице.)
Разделительные вопросы широко используются в устной речи. Значение вопроса меняется в зависимости от того, как вы произносите вопросительную часть. Если голос повышается, то это обычный общий вопрос, который требует ответа «да» или «нет» и содержит оттенок удивления, заинтересованности и т.п.
— You haven't seen your — Вы не видели своего
manager today, thave you? управляющего сегодня,
(=Have you seen your не правда ли?
manager?)
— No, I am afraid not. — Боюсь, что нет.
Если вопрос произносится с понижением голоса, то говорящий уверен в том, что он утверждает, и просит собеседника подтвердить это.
— You are free tonight, — Вы ведь сегодня вече-
i aren't you? ром свободны.
— Yes, I am. — Да.
ПРЕДТЕКСТОВЫЕ УПРАЖНЕНИЯ
21. а) Прочитайте вслух следующие слова:
[ае] — 'graduate, 'value, 'language, 'practical
[л] — 'number,'study,'other, thus, us,,under'graduate, in'dustrial,
'structural [ai] — de'sign, de'signer, mine, 'mining, 'science, hy'draulic,
pro'vide, kind, higher [f] — 'physical, 'physics, phone [k] — me'chanical, 'chemist, 'chemistry, me'chanics, tech'no-
logy, 'chemical [fl — ma'chine, ma'chinery, shape, 'specialist
б) Прочитайте следующие слова и запомните их произношение:
know [nou] — knowledge ['пэ1к!з] specialize ['spejalaiz] — specialization [.spejalai'zeijh] require [n 'kwaia] — requirement [n 'kwaiamant] introduce [.mtra'djurs] — introduction [,mtr3'dAkf(3)n]
22. Прочитайте следующие слова и сочетания 1-2 раза про себя, затеи
вслух и постарайтесь запомнить их.
change [tjemd3] v изменяться), ме- determine [di'ta:min] v определять,
нять(ся); syn. transform, alter; • устанавливать
n изменение, перемена; прев- engineering [.епйзГшэпп] л техника;
ращение технология; машиностроение;
composition [Дэтрэ'21/(э)п) л сгрук- syn. technics, technology; tech-
тура, состав niqne; machinery,
connect [ka'nekt] v соединять(ся); enterprise ['entapraiz] л предприятие;
syn combine, link предприимчивость
deal [di:l] (dealt) v (with) иметь де- environment [in' vaisrsnmsnt] л окру-
ло с; рассматривать жающая обстановка; среда
demand [di'ma:nd] л зд. спрос field [fi:ld] л область, сфера деятель-
design [di'zain] л проект; план, ности; поле, участок, месторож-
чертеж; конструкция; v проек- дение; бассейн; syn. basin, branch
тировать, планировать; кон- graduate ['graedjueit] v окончить
струировать (высшее учебное заведение);
амер. окончить любое учебное recreation [,rekn'eij(s)n] л отдых,
заведение; ['graedjuit] n ли- восстановление сил, развлечение
цо,окончившее высшее учеб- reveal [ri'vi:!] v показывать, обна-
ное заведение; undergraduate руживать
(student) студент последнего rock [rok] n горная порода
курса; postgraduate (student) shape [feip] л форма
аспирант; graduation paper software ['softwes] n программное
дипломная работа обеспечение; программные средст-
hardware ['haid^es] л аппаратура, ва
(аппаратное) оборудование, skill [skil] л мастерство; умение;
аппаратные средства; техниче- skilled а квалифицированный;
скос обеспечение опытный; умелый
hydraulic'[hai'doilik] а гидравли- surrey ['server] n съемка, маркшей-
ческий, гидротехнический дерская съемка; [ss'vei] v произ-
introduction [,ш1гэ'с!лкДэ)п] л вве- водить маркшейдерскую или то-
дение, вступление пографическую съемку, произво-
management ['maenidsmant] л дить изыскания; л surveying
управление, заведование; syn. съемка, маркшейдерские работы
administration; direction thus [8л$] adv таким образом
offer ['afa] v предлагать (помощь, value f'vaelju:] л ценность, стои-
работу); предоставлять; л пред- мость; величина; v ценить, оце-
ложение „ нивать; valuable а ценный
property [ 'ргэрэи] л свойство workshop [ 'wa:kjop] л мастерская,
protection [ргэ'1ек/(э)п] л защита, цех; семинар
охрана
range [reinds] л область, сфера; предел; диапазон; радиус действия; ряд; серия
to be of importance иметь значение
to give an opportunity of дать возможность
to meet the requirements удовлетворять требованиям (потребности)
23. Определите значения выделенных слов по сходству их корней с корнями соответствующих слои в русском языке:
special institutes; geologists and mining engineers; mechanical and electrical engineers; social sciences; specialized subjects; the type of specialization and qualification; theoretical courses; economic geology; structural geology; to prospect for minerals; skilled engineering specialists; mining operations; mining technology; hydraulic engineering; electrical engineering; industrial electronics; mine machinery laboratories; control systems; rock mechanics; the use of computers; mineral dressing; mining research and its practical application; prospecting parties
I 24. Прочитайте текст Б и найдите • нем предложения, в которых гово- |рвтся о том: 1) что изучает геология; 2) какие основные дисциплины Должны изучать будущие геологи и горные инженеры:
i
In Russia young people get mining education at special institutes which train geologists and mining engineers for coal and ore mining. The total number of students of an institute includes full-time students, part-time students and postgraduate students.
Russian higher educational establishments offer different specializations for the students. Thus, at the geological institutes, the students specialize in geology, the science which deals with different problems connected with the Earth, its history, the study of rocks, their physical and chemical properties. One of the mai.i tasks of geology is to prospect, discover and study the deposits of useful minerals.
Geology is both a theoretical and an applied science. Mining geology is of great importance to the mining engineer. As a rule, mining geology includes economic geology.
The outstanding Russian geologist V.A. Obruchev says that geology is the science of the Earth which reveals to us how the Earth took shape, its composition and its changes. Geology helps prospect for ores, coal, oil, salt and other useful minerals.
Higher mining schools (universities, academies, institutes and colleges) develop a wide range of courses and programmes that meet the requirements of the society.They offer courses in mining technology, machinery and transport, hydraulic engineering, electrical engineering, industrial electronics, automation, surveying, geodesy, information technology, etc.
The main trend in the development of higher mining education
is the introduction of courses in environmental protection, manage
ment (environmental human resources), economics and manage
ment of mining enterprises, marketing1 studies, computer-aided
design (CAD)2 and others. ',.
Computer science is also of great importance. The course aims at providing students with understanding how software and hardware technology helps solving problems.
Laboratory work is an important part in training specialists. Experiments in laboratories and workshops will help students to develop their practical skills. They have a short period of field work to gain working experience.
The students go through practical training at mines, plants and other industrial enterprises.. They become familiar with all stages of production and every job from worker to engineer. Here they get practical knowledge and experience necessary for their diploma.(graduation) papers.
A lot of students belong to students' scientific groups. They take part in the research projects which their departments usually conduct. Postgraduates carry out research in different fields of science and engineering.
Sport centres give the students opportunities to play different sports such as tennis, football, basketball, volleyball, swimming, ' skiing, water polo, boxing, wrestling and others. (
Students graduate from mining and geological higher schools as mining engineers, mining mechanical engineers, ecologists, mining electrical engineers, geologists, economists and managers for mining industry.
ПОЯСНЕНИЯ К ТЕКСТУ Б
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 2808; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!